Case Report (Precis): Two Telemedicine Consultants Miss Foot Drop: When To See Patients in Person
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Telemedicine has been rapidly adopted due to COVID-19. In the earliest days, most screenings were performed by primary care/internal medicine consultants; referrals to subspecialists were minimized. Now, as the pandemic has evolved over 6 months, secondary telemedicine consultations should be limited, and earlier involvement of appropriate subspecialists should be reconsidered to optimize patient management.
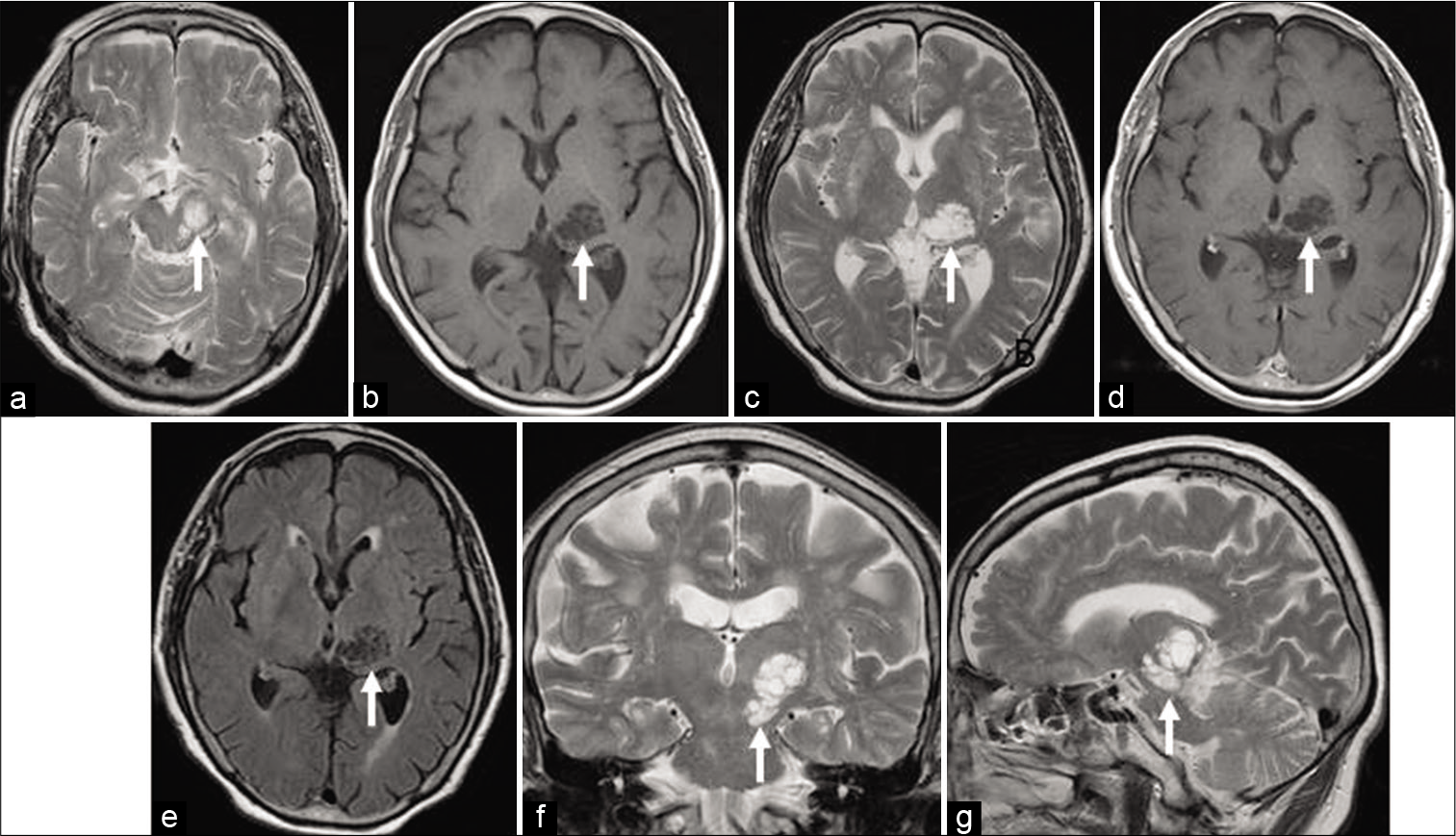
The first 3-D volumetric analysis of mesencephalothalamic giant perivascular spaces showing steady and slow growth over 17 years
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Giant perivascular spaces (PVSs) are very rare condition in the brain and can be associated with neurological symptoms. It often enlarges and causes obstructive hydrocephalus which requires surgical intervention. However, the growth velocity has never been investigated.
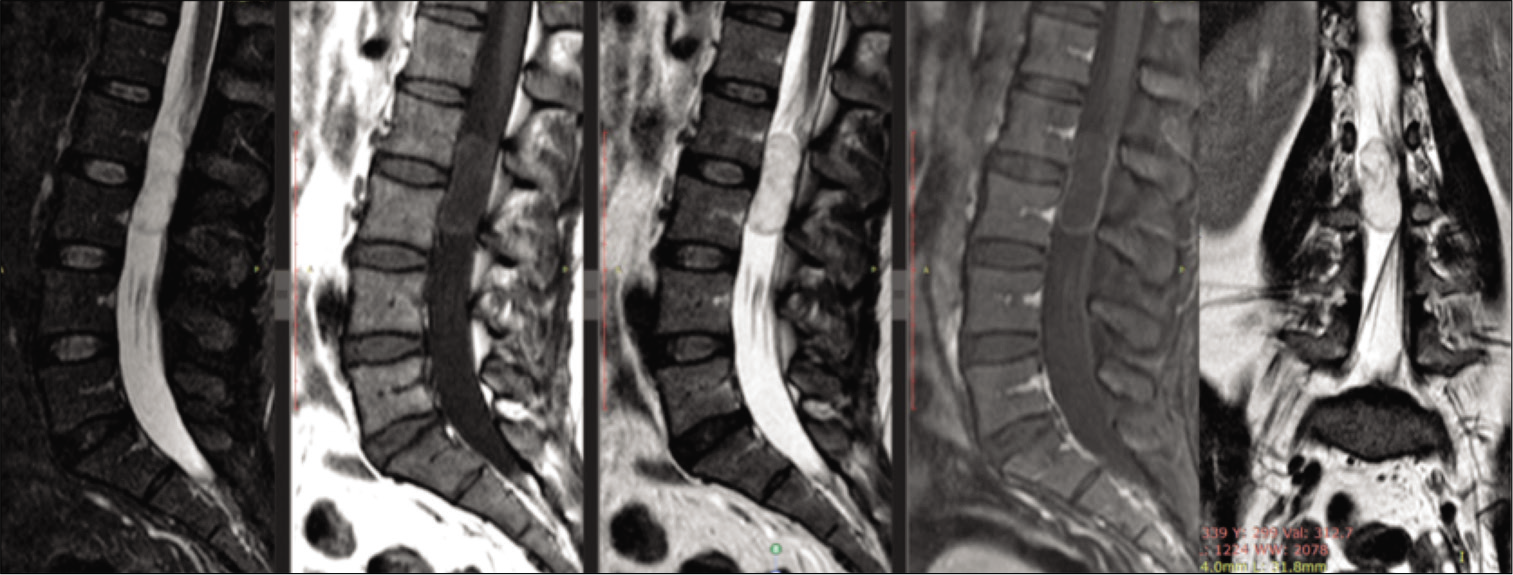
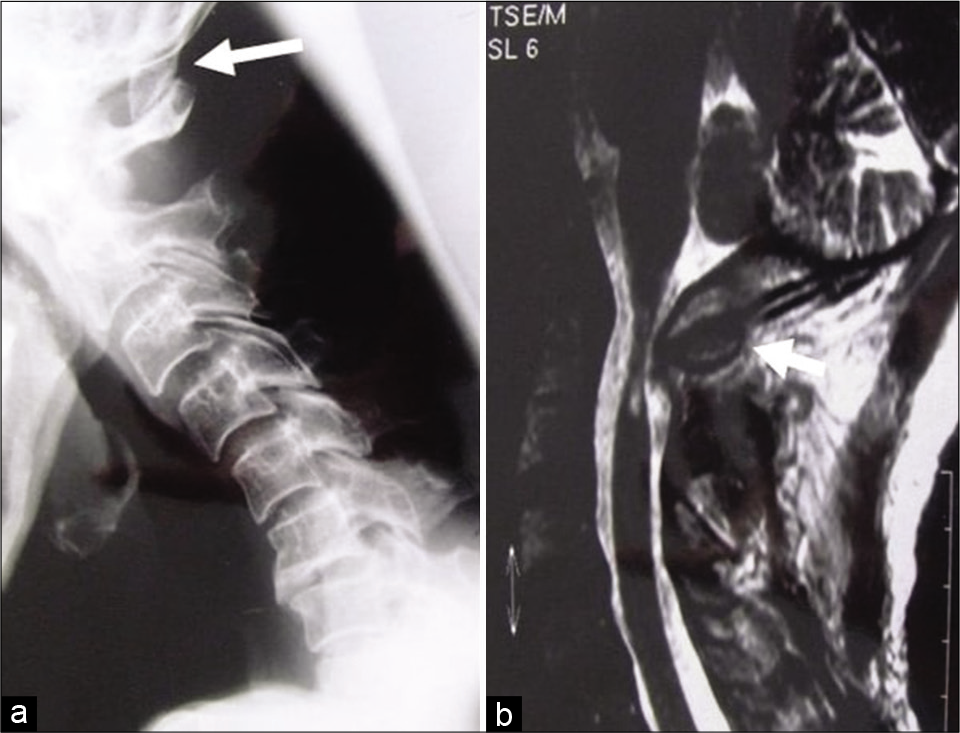
Intradural iatrogenic epidermoid cyst at cauda equina: A case report
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Spinal epidermoid accounts for <1% of all primary spinal cord tumors. They occur due to the invagination of epidermal elements into the neural tube during the embryonic period. Even more infrequent are spinal epidermoid cysts that occur without attendant spinal dysraphism (e.g., as occurs with the iatrogenic inoculation of epithelial cells in the subarachnoid space following a lumbar puncture).
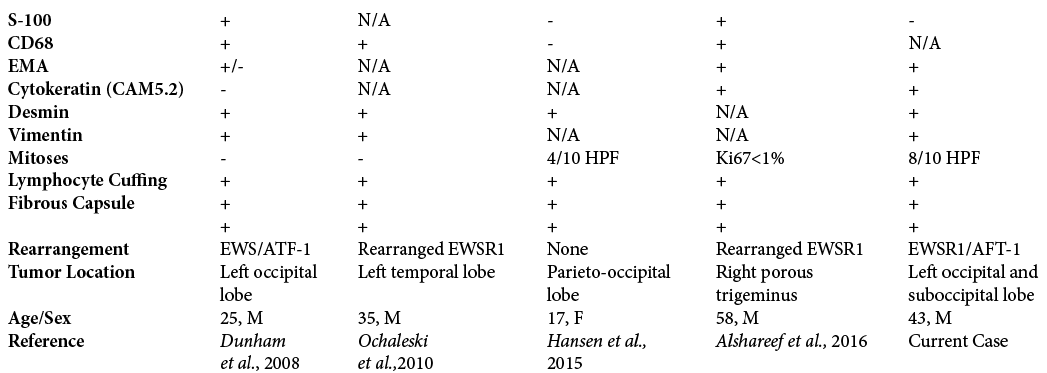
Rosai-Dorfman disease of cranial and spinal origin - A case series
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Rosai-Dorfman disease (RDD) is an idiopathic nonneoplastic lymphadenopathy disorder which is characterized by lymph node enlargement, but it may also presents primarily involving a variety of extranodal sites, including central nerves system and craniospinal axis. This study reports five cases of craniospinal RDD, with review of epidemiology, clinical presentation, imaging, and histopathological features with current management strategies.
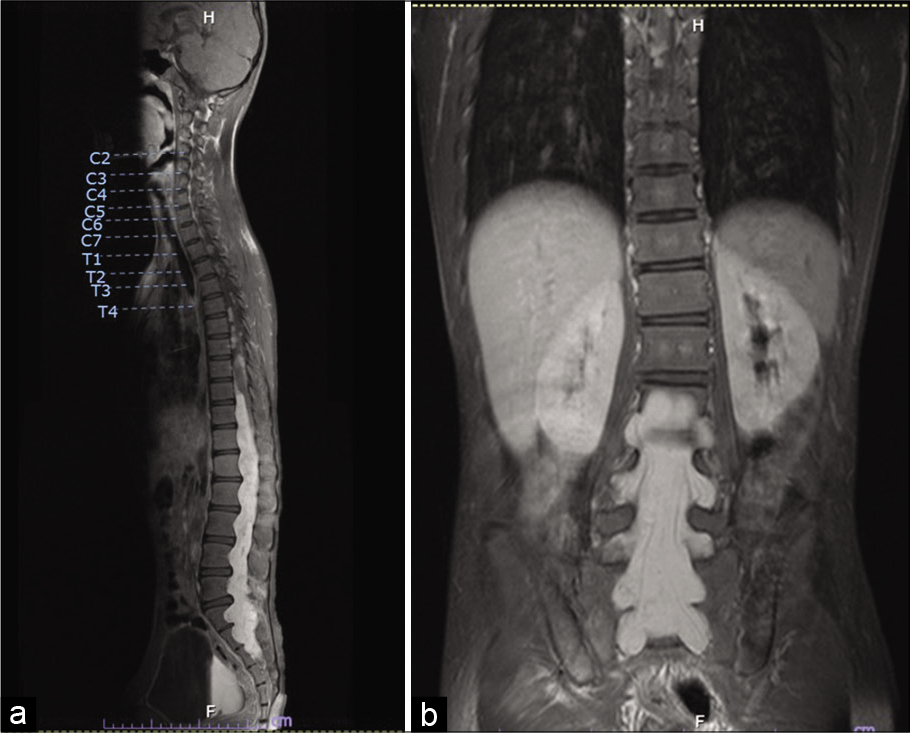
Image report: Extensive disseminated thoracolumbosacral myxopapillary ependymoma
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Myxopapillary ependymoma occurs more frequently in adults, but is found in the first two decades of life in around 8–20% of patients. Tumors are usually benign with low likelihood for dissemination.
Foramen magnum osteochondroma causing myelopathy in a patient with hereditary multiple exostoses
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Osteochondromas are commonly occurring benign bone tumors which may be either a solitary lesion or occur due to association with hereditary multiple exostoses (HMEs). There have been several reported cases of spinal osteochondromas, but intracranial lesions are rare.
Cranial angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma: A case report and review of literature
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma (AFH) is a rare low-grade soft-tissue tumor that typically arises from the deep dermal and subcutaneous tissue of the extremities in children and young adults. Intracranial AFH is exceedingly rare, and only four cases of primary AFH tumors have been reported to date.
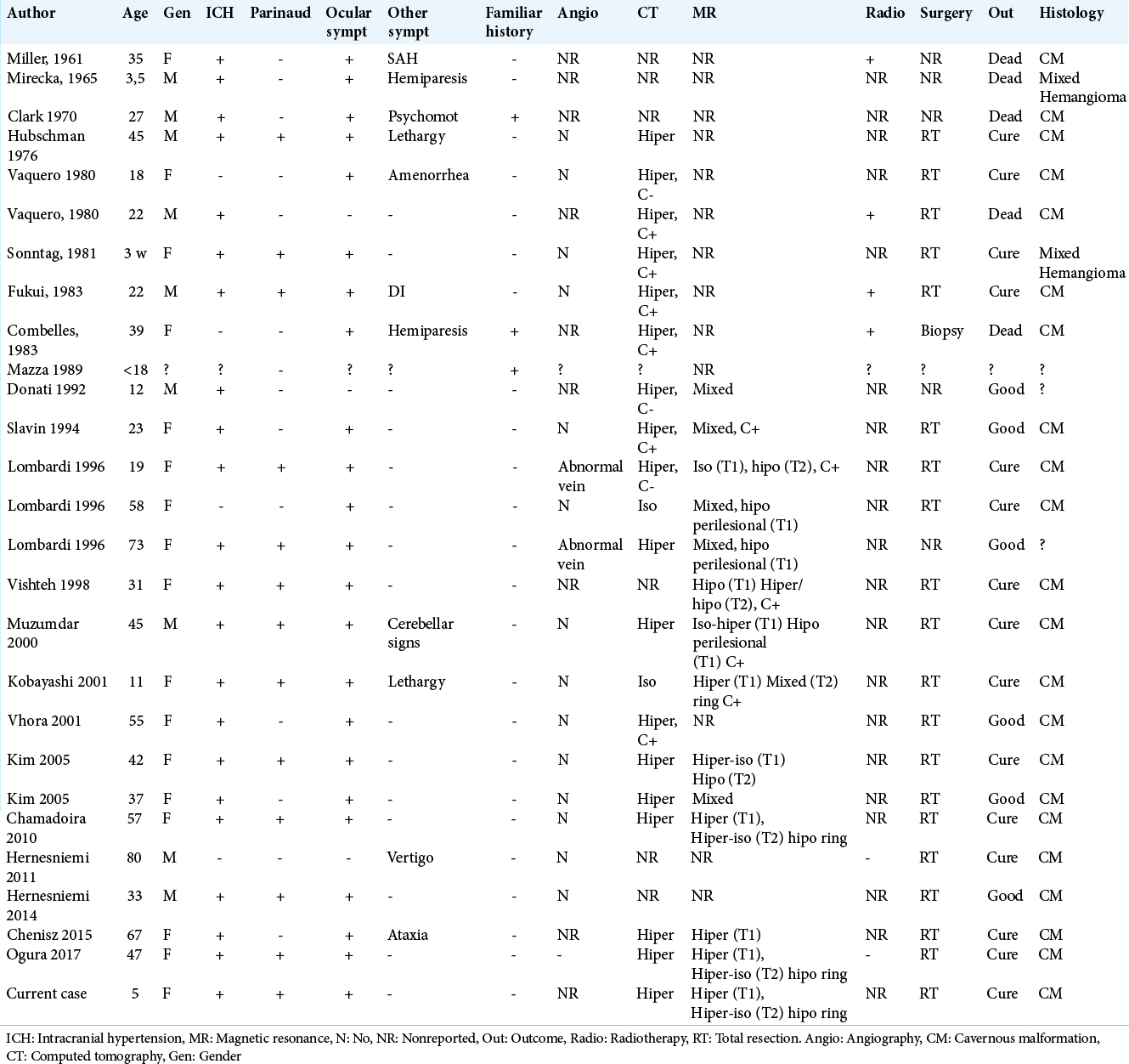
Hydrocephalus in children – A rare case of pineal cavernoma and literature review
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Cavernous malformations prevalence ranges from 0.4 to 0.6% and accounts for 5–15% of all central nervous system vascular malformations. Pineal cavernomas constitute <1% of all locations published in the literature, with a total of 26 cases reported, only 5 regarding the pediatric population until 2020. Overall annual hemorrhage rate is 2.4%. Symptoms are often due to hydrocephalus and intracranial hypertension.
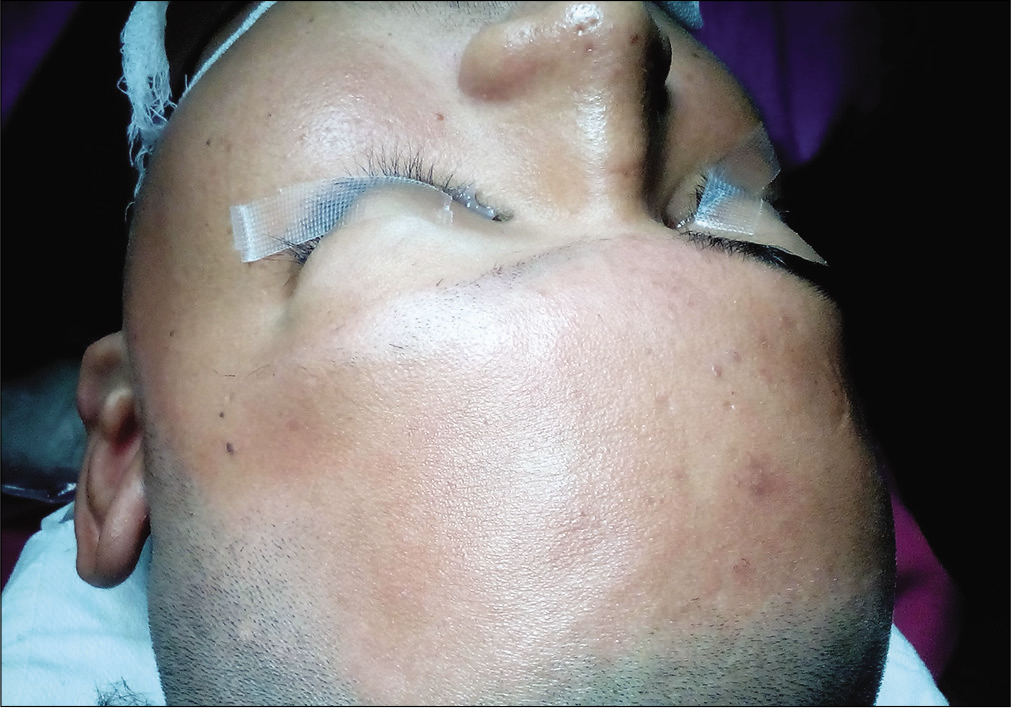
Transcranial resection of a juvenile psammomatoid ossifying fibroma of the orbit: A case report with 2-year follow-up
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Juvenile psammomatoid ossifying fibromas (JPOFs) are benign, locally invasive lesion of the craniofacial skeleton that may undergo rapid growth resulting in damage to cranial and facial structures. They usually occur before the age of 15 years and should be carefully treated as their diagnosis may be confused with other lesions such as psammomatous meningioma.
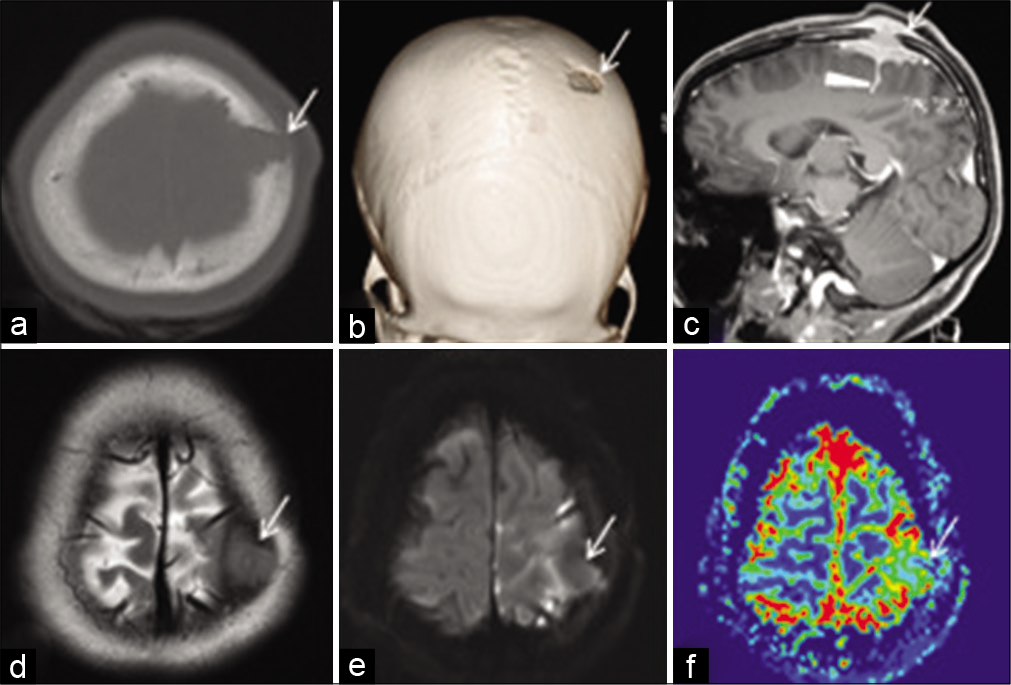
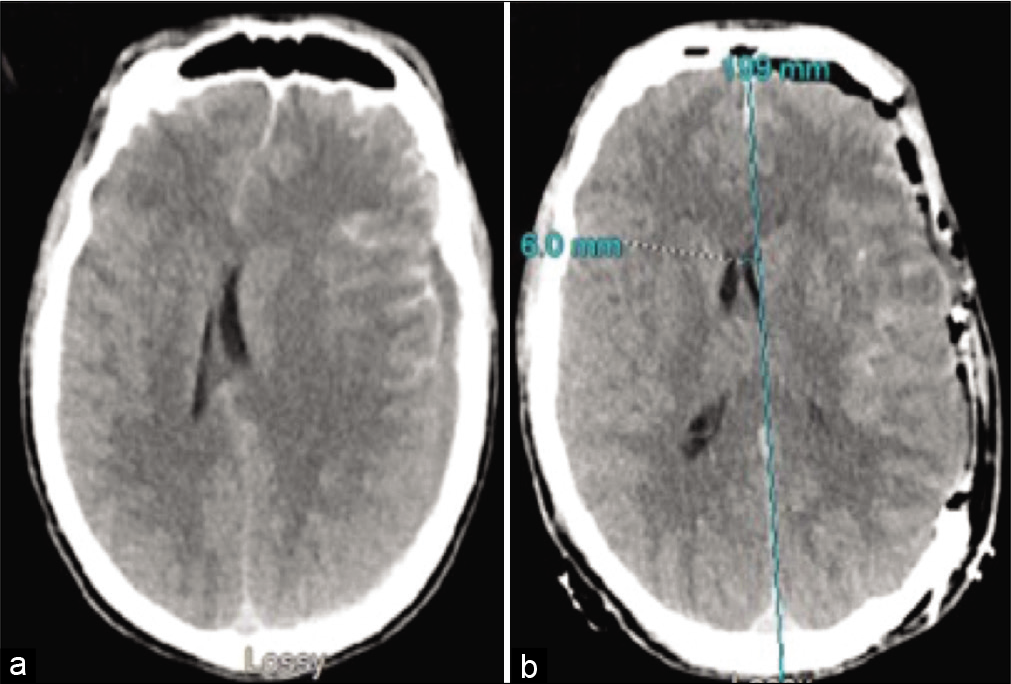
Delayed recurrence of acute subdural hematoma in a patient with plasminogen activator inhibitor mutation
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Plasminogen activator inhibitor type I (PAI-1) is important for balancing the fibrinolytic effect of plasmin, and deficiency can result in increased risk of bleeding. We report a case of a patient with PAI-1 deficiency who presented with delayed spontaneous recurrence of an acute subdural hematoma (aSDH) after evacuation.