Role of intraoperative computed tomography scanner in modern neurosurgery – An early experience
Date of publication: 15-Aug-2020
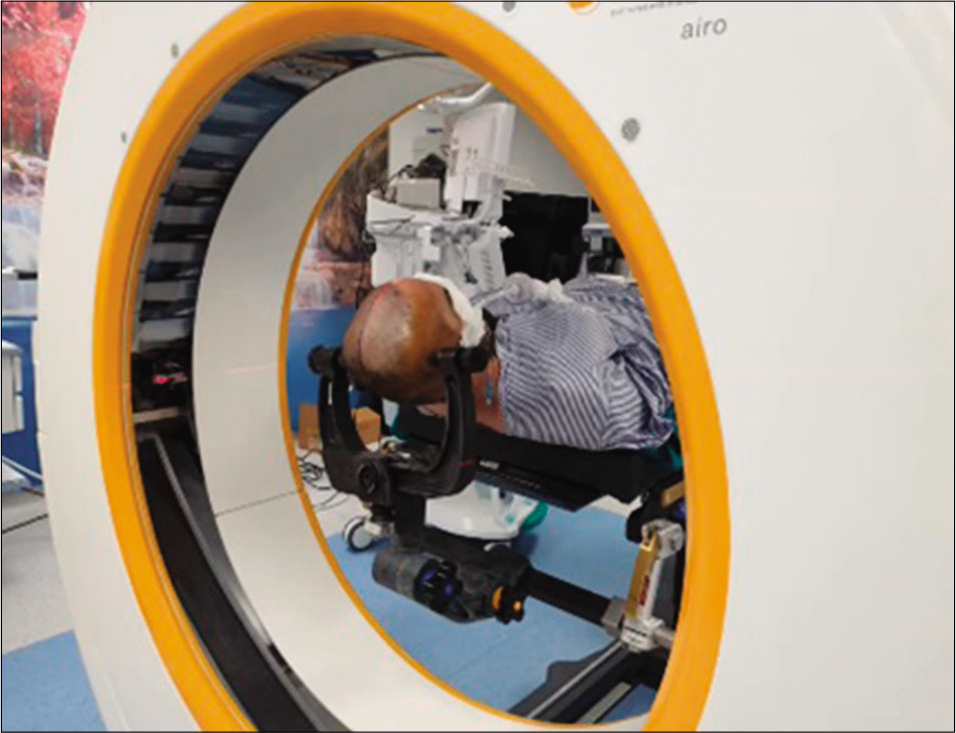
Background: Intraoperative imaging addresses the limitations of frameless neuronavigation systems by providing real-time image updates. With the advent of new multidetector intraoperative computed tomography (CT), soft tissue can be visualized far better than before. We report the early departmental experience of our intraoperative CT scanner’s use in a wide range of technically challenging neurosurgical cases.
Rathke’s cleft cyst with xanthogranulomatous change: A case report and review of the literature
Date of publication: 15-Aug-2020
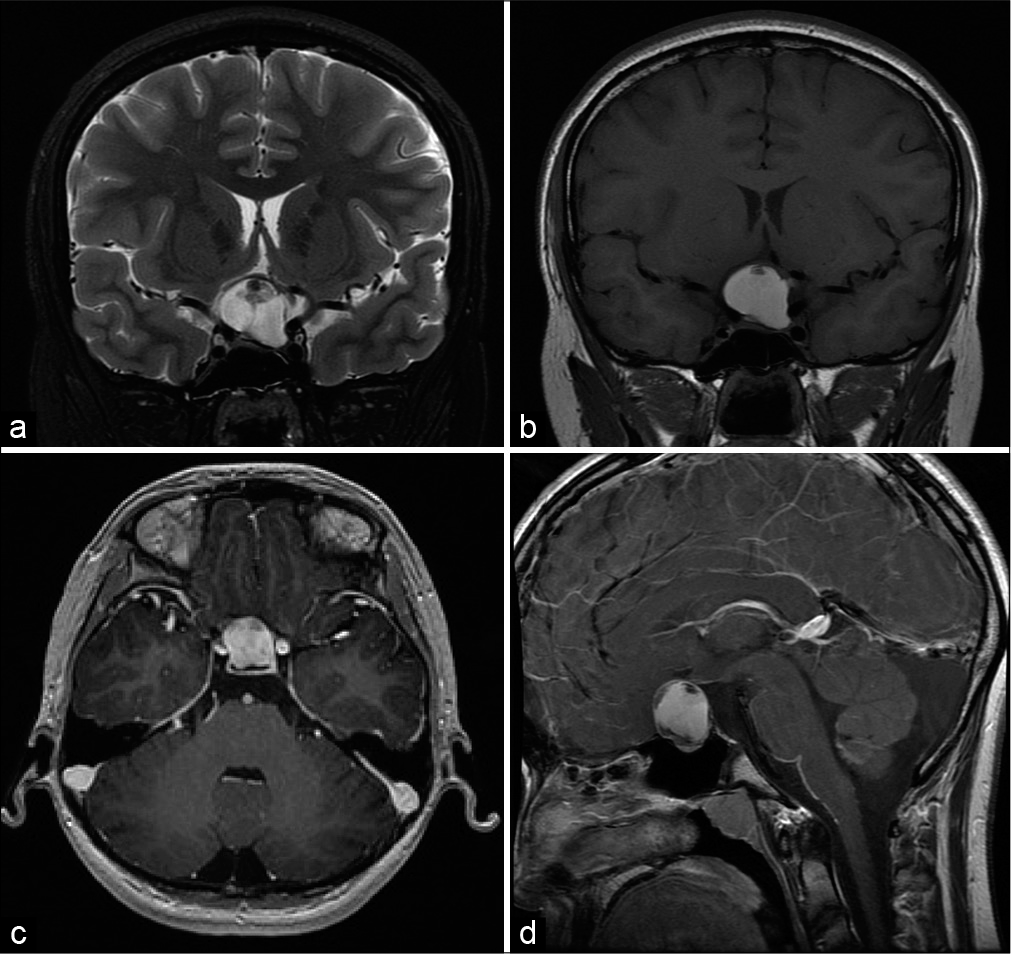
Background: Rathke’s cleft cysts (RCCs) are benign, typically asymptomatic sellar lesions found incidentally in adults, with a dramatically lower incidence in pediatric patients (<18 years). We present a case of RCC with xanthogranulomatous change (XGC) – an even less common subtype of RCC – treated by endoscopic endonasal surgical resection. This is the second reported instance of an RCC with XGC occurring in a pediatric patient.
Spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid otorrhea and pneumocephalus on the contralateral side of the previous cranial surgery
Date of publication: 15-Aug-2020
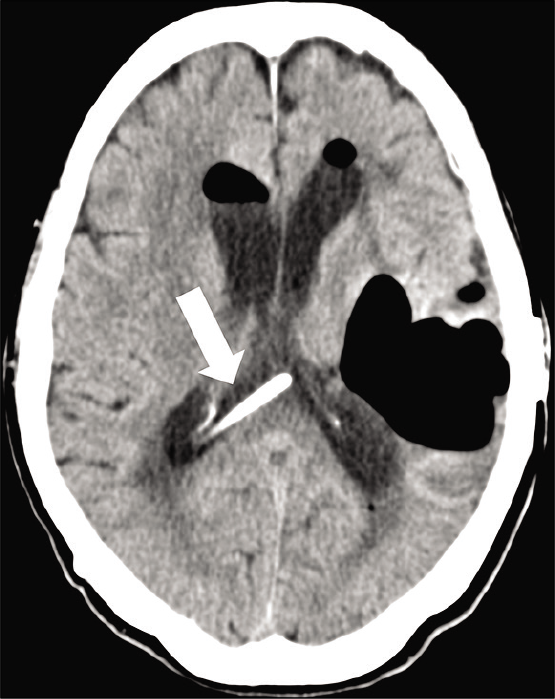
Background: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks and pneumocephalus commonly occur due to head trauma or surgical procedures. Spontaneous CSF (sCSF) leaks, however, occur without any clear etiology and are relatively uncommon.
Ergonomics of surgical microscopes for the sitting position as determined by ocular-corpus length
Date of publication: 15-Aug-2020
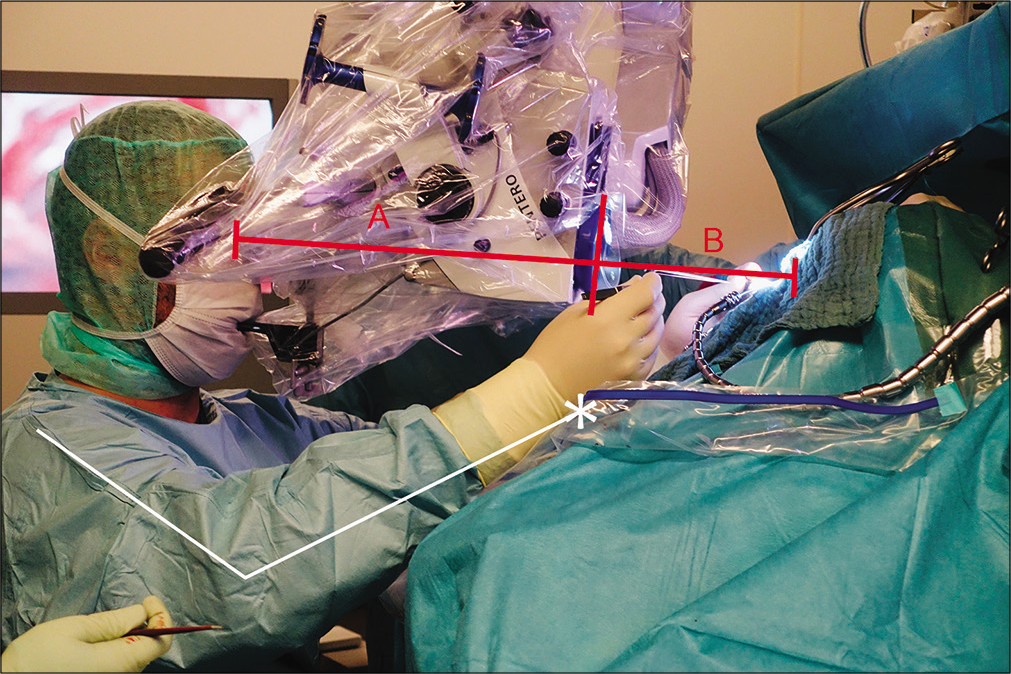
Background: The sitting position is favorable for microsurgical procedures applied to posterior midline pathologies in both the supra- and infratentorial regions. The dimensions of the microscope corpus affect the device’s comfort and handling in the hands of the microneurosurgeon for such procedures. A shorter microscope corpus provides more favorable intraoperative ergonomics for surgical practice.
Subgaleal hematoma evacuation in a pediatric patient: A case report and review of the literature
Date of publication: 15-Aug-2020
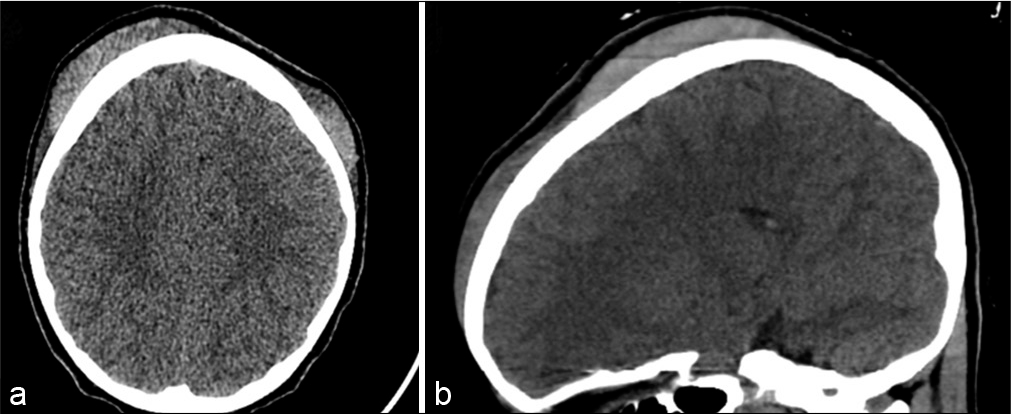
Background: Subgaleal hematoma (SGH) is generally documented within the neonatal period and is rarely reported as a result of trauma or hair braiding in children. While rare, complications of SGH can result in ophthalmoplegia, proptosis, visual deficit, and corneal ulceration secondary to hematoma extension into the orbit. Although conservative treatment is preferential, expanding SGH should be aspirated to reduce complications associated with further expansion.
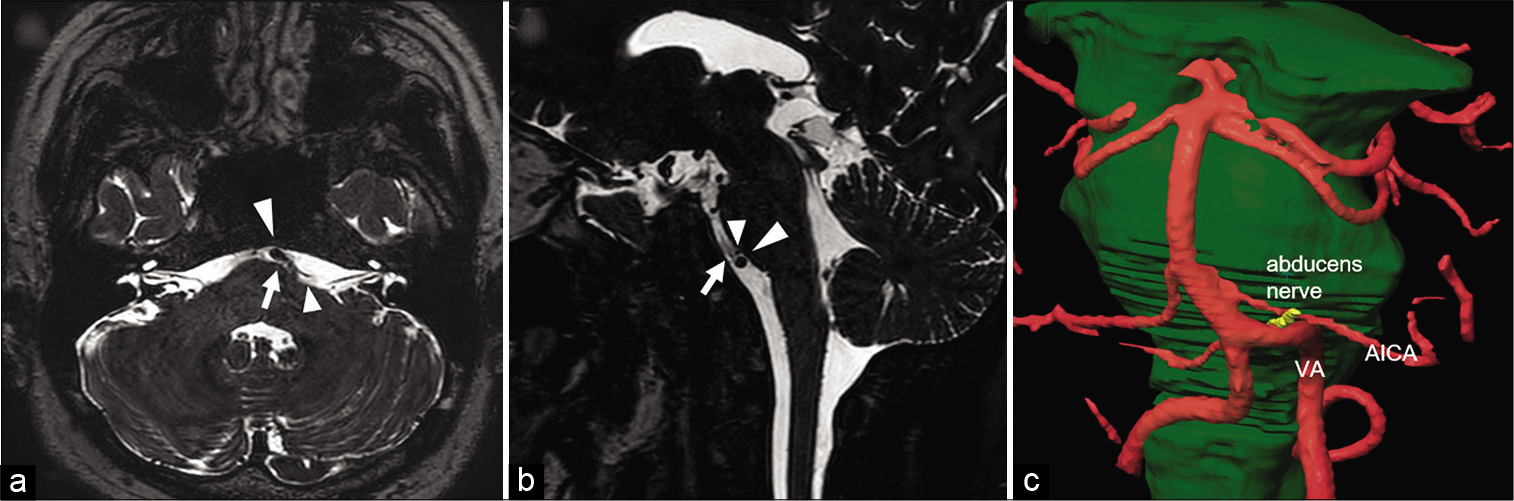
Microvascular decompression for abducens nerve palsy due to neurovascular compression from both the vertebral artery and anterior inferior cerebellar artery: A case report
Date of publication: 15-Aug-2020
Background: Neurovascular compression is an extremely rare etiology of isolated abducens nerve palsy. We describe a successfully treated case of isolated abducens nerve palsy due to sandwich-type compression by the vertebral artery (VA) and anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA).
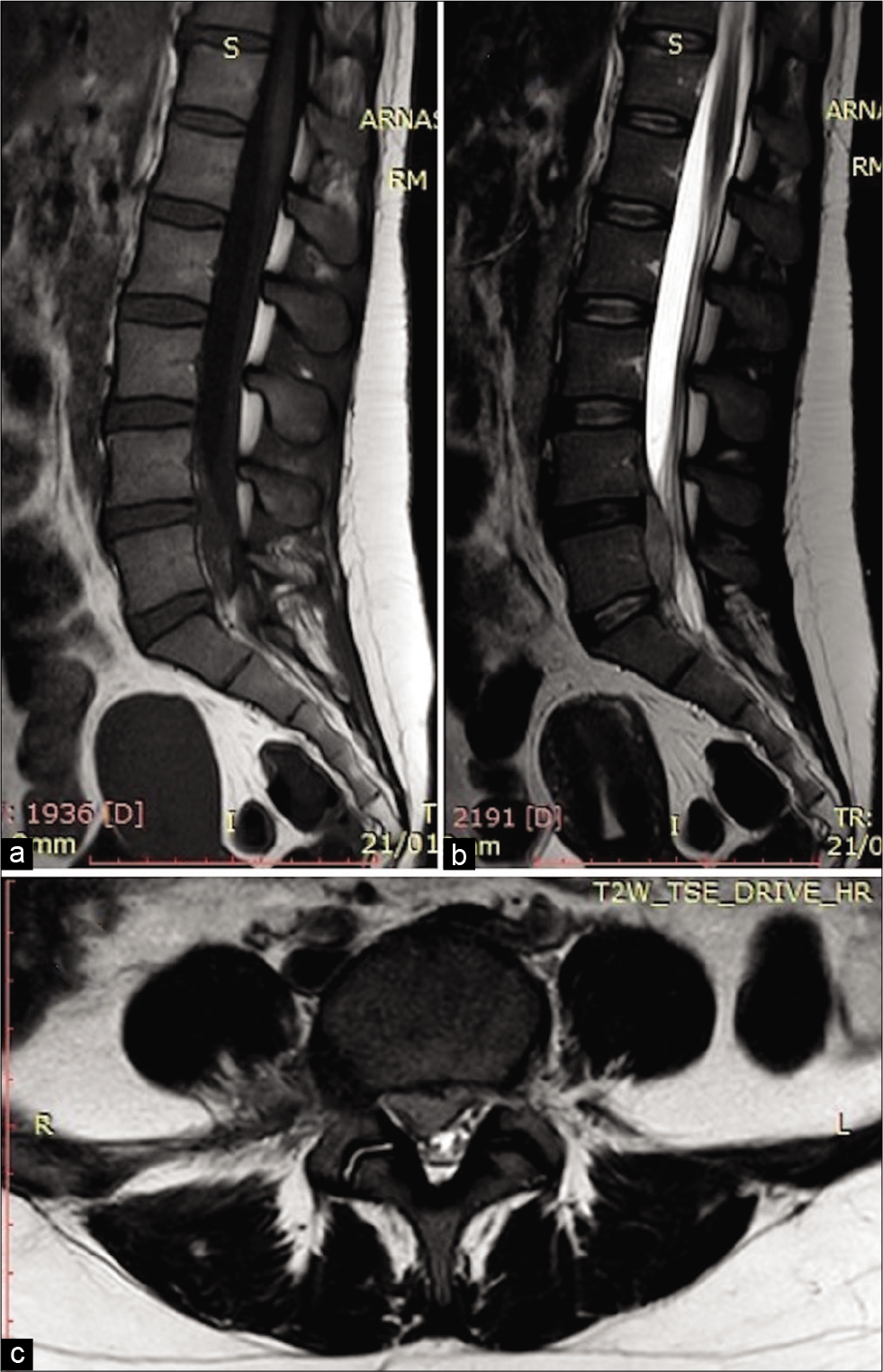
All that glitters is not gold: A spinal epidural empyema following epidural steroid injection
Date of publication: 08-Aug-2020
Background: Therapeutic epidural spinal injections (ESIs) of steroids are one of the most common nonsurgical management modalities employed for alleviating pain due to chronic persistent lumbar spinal disease. However, it is well documented that they have significant risks and complications without any long-term efficacy. ESI may result in epidural empyema which may be difficult to diagnose with delays resulting in significant permanent neurological sequelae.
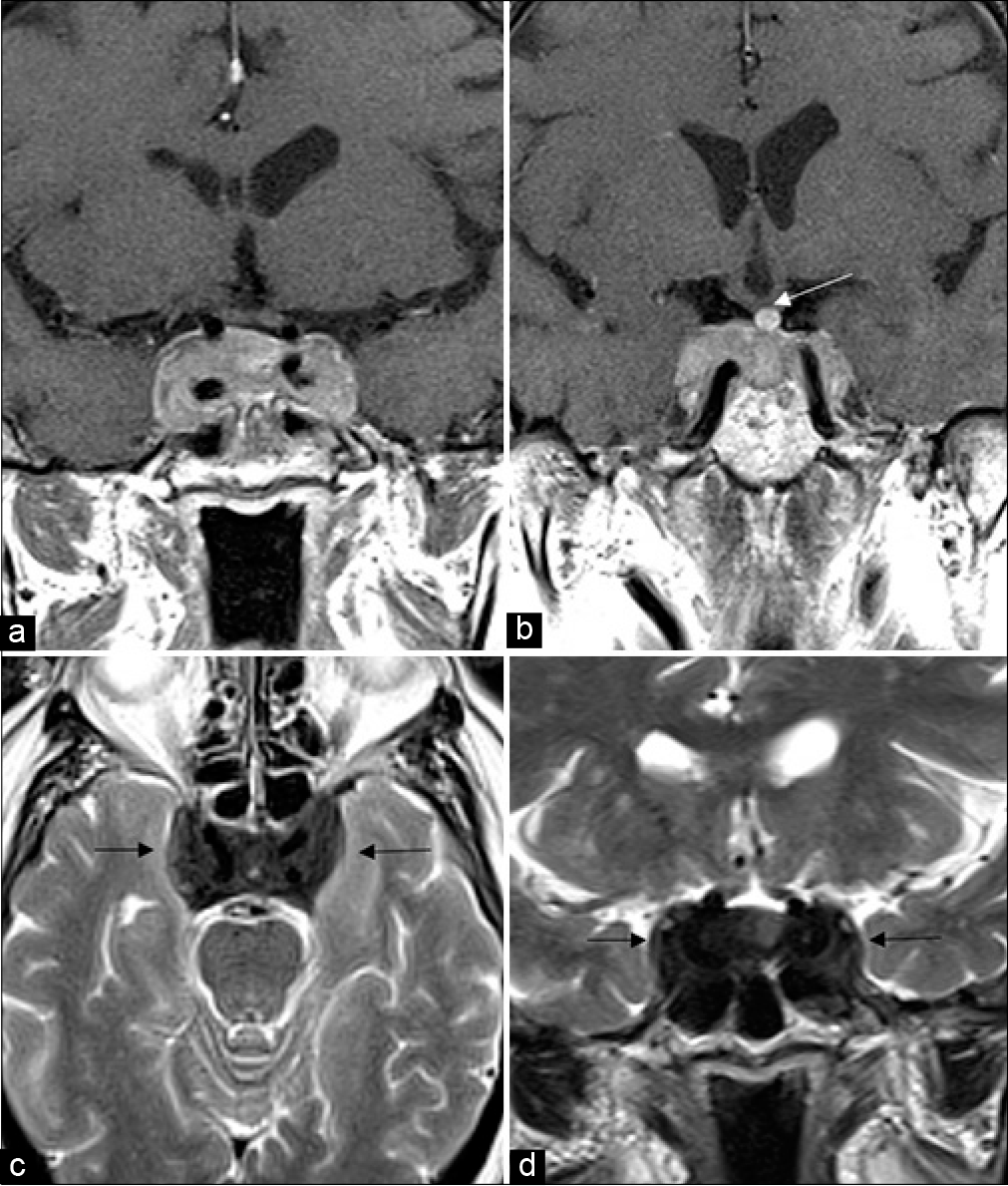
Parasellar T2 dark sign on magnetic resonance imaging to differentiate lymphocytic hypophysitis from pituitary adenoma
Date of publication: 08-Aug-2020
Background: Pituitary adenomas are the most common sellar masses in adults with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) being the imaging modality of choice. Inflammatory pituitary lesions such as lymphocytic hypophysitis (LH) can mimic pituitary macroadenoma on imaging and are often misdiagnosed as such. Although the imaging appearance on most of the sequences on MRI has similar findings, LH has a characteristic dark signal on T2 images (called dark T2 sign) which can be very helpful to reliably differentiate the two conditions.
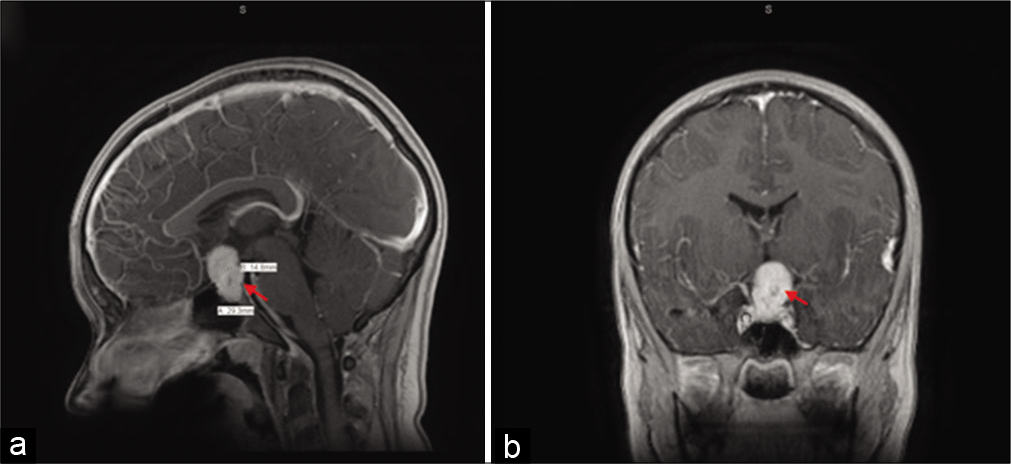
Pediatric sellar solitary fibrous tumor/ hemangiopericytoma: A rare case report and review of the literature
Date of publication: 08-Aug-2020
Background: Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT)/hemangiopericytoma (HPC) is a rare tumor which originates from the walls of capillaries and has historically been thought to be able to occur anywhere in the body that blood vessels are found. It is rarely found in the sellar region.