Synovial sarcoma of the spine: A case report and review of the literature
Date of publication: 21-Aug-2020
Background: Synovial sarcoma (SS) of the spine is a rare malignant soft-tissue tumor, and there are few reported cases. The aim of this paper is to report a rare case of spinal SS involving the paraspinal muscles, and to review all such cases reported in the literature.
Burr hole microsurgery in treatment of patients with intracranial lesions: Experience of 44 clinical cases
Date of publication: 21-Aug-2020
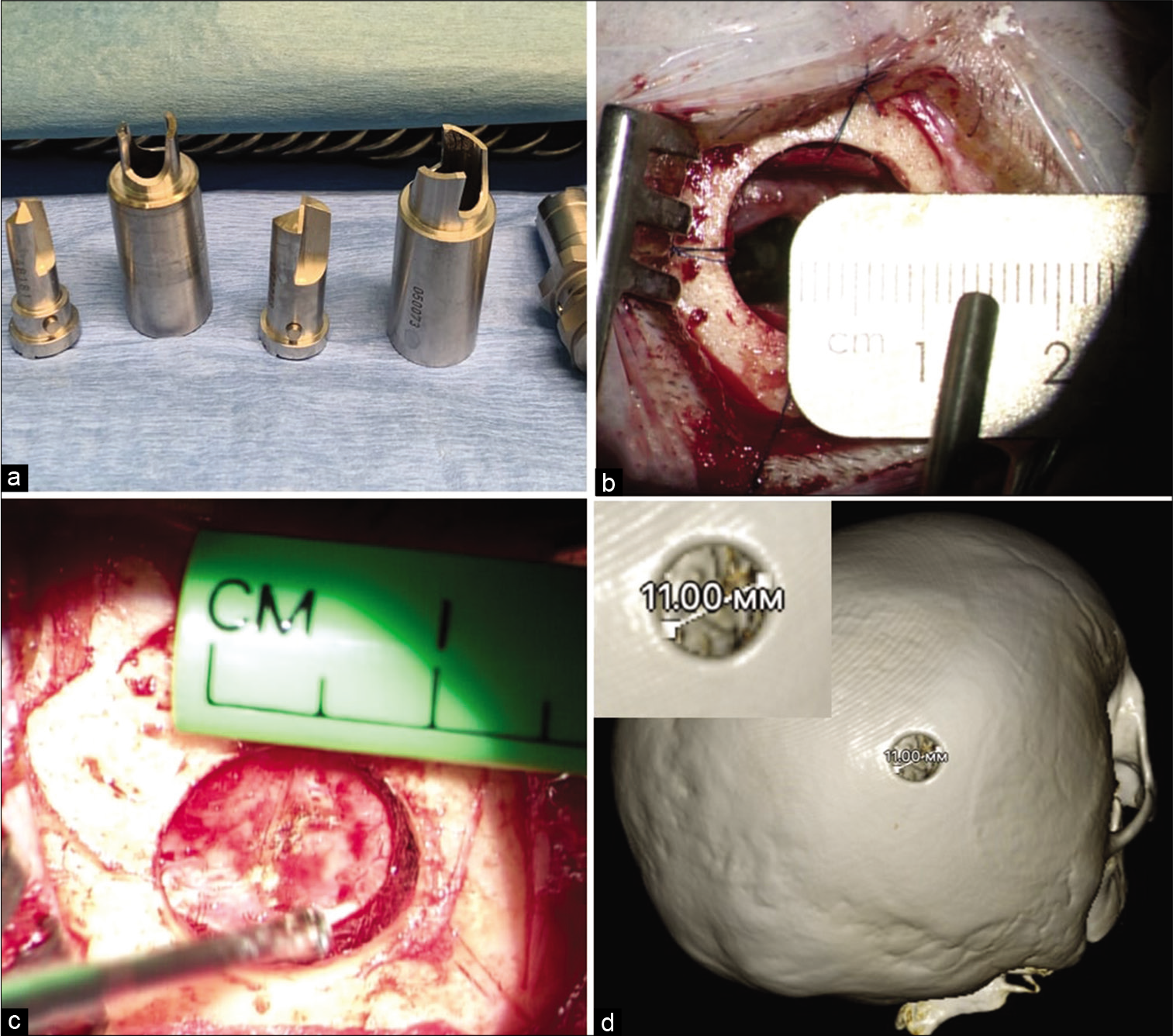
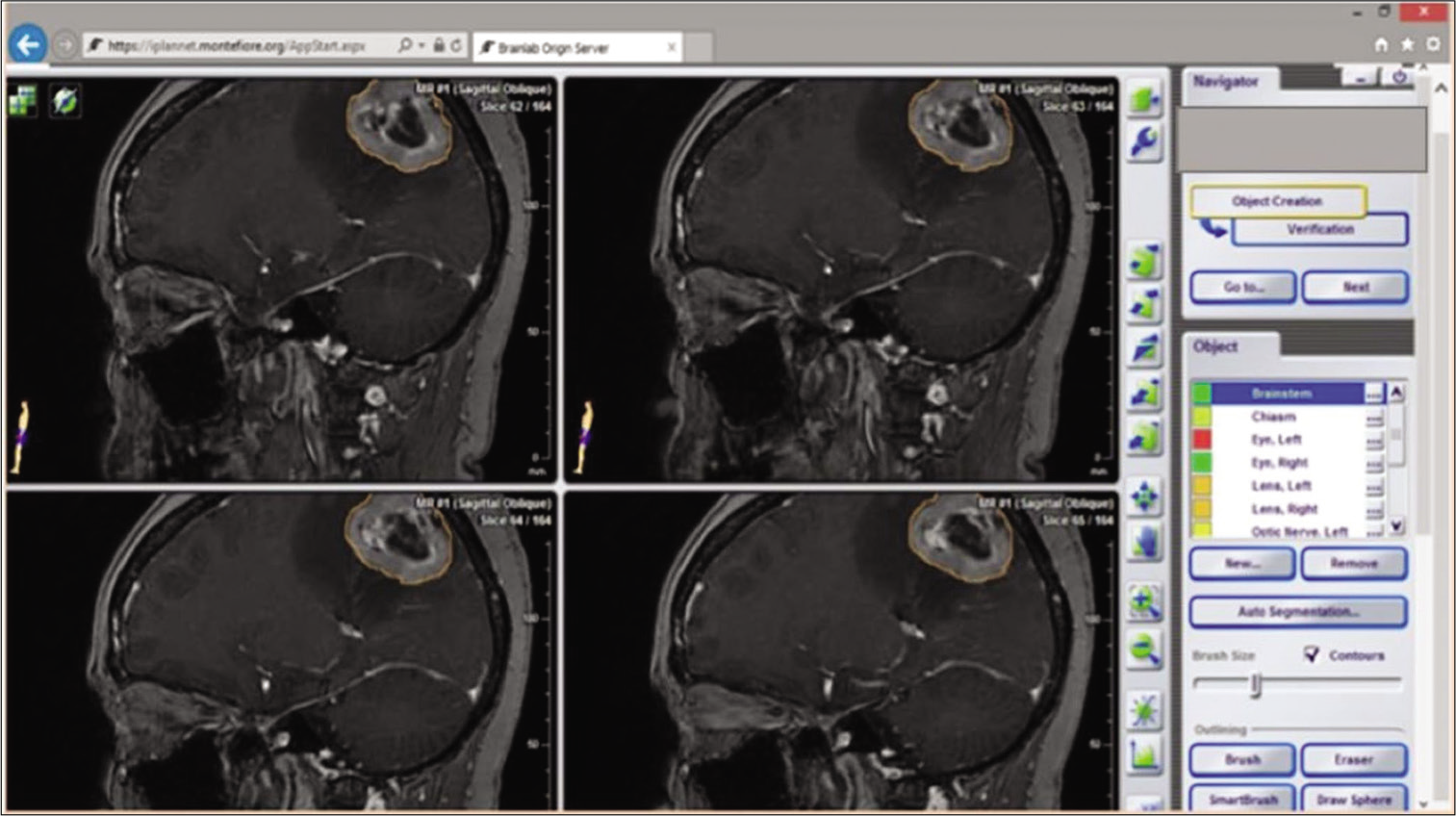
Background: Modern technical capabilities have made minimally invasive surgery increasingly popular. Small incisions can reduce surgical duration and the degree of tissue trauma, which reduces the risk of complications. Burr hole microsurgery is a relatively new minimally invasive technique used in neurosurgery. The objective of this study was to assess the feasibility and outcomes of using burr hole microsurgery for the management of intracranial lesions.
Evaluating the natural growth rate of metastatic cancer to the brain
Date of publication: 21-Aug-2020
Background: Brain metastases are becoming increasingly more prevalent as cancer patients survive longer with both improved local and systemic therapy. Little is known, however, of the natural growth rates of brain metastases. This investigation aims to ascertain this growth rate of these lesions before the initiation of any CNS- directed therapy.
Dural sinus mechanical thrombectomy and continuous local rt-PA infusion in a child with refractory intracranial hypertension and progressive visual loss: A case report
Date of publication: 21-Aug-2020
Background: Children with intracranial hypertension are at risk for visual loss and their visual function must be closely monitored. Surgery with the insertion of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt is imperative when vision is threatened.
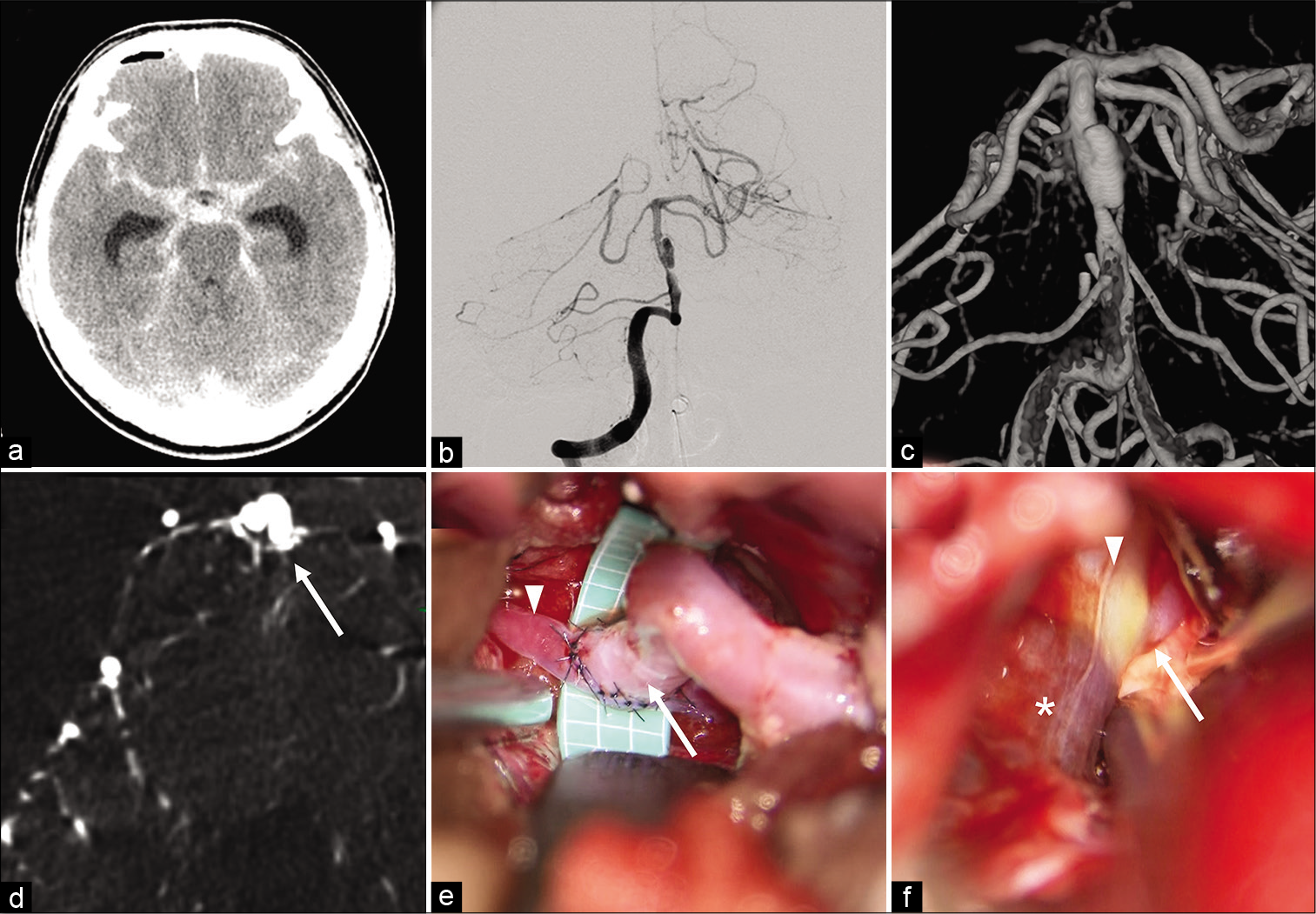
Superficial temporal artery-superior cerebellar artery bypass and proximal occlusion through anterior petrosal approach for subarachnoid hemorrhage due to basilar artery dissection
Date of publication: 21-Aug-2020
Background: Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) due to rupture of basilar artery dissection (BAD) is extremely rare and often has a poor prognosis. Since ruptured BAD has high rate of rebleeding and mortality, treatment to prevent rerupture is mandatory in the acute phase. However, to date, no optimal treatment has been established which satisfies secure prevention of rerupture and ischemia simultaneously. Herein, we report a case of SAH due to BAD treated with proximal occlusion of basilar artery with superficial temporal artery (STA)-superior cerebellar artery (SCA) bypass, preventing rebleeding securely and ensuring adequate blood flow in the upper basilar region.
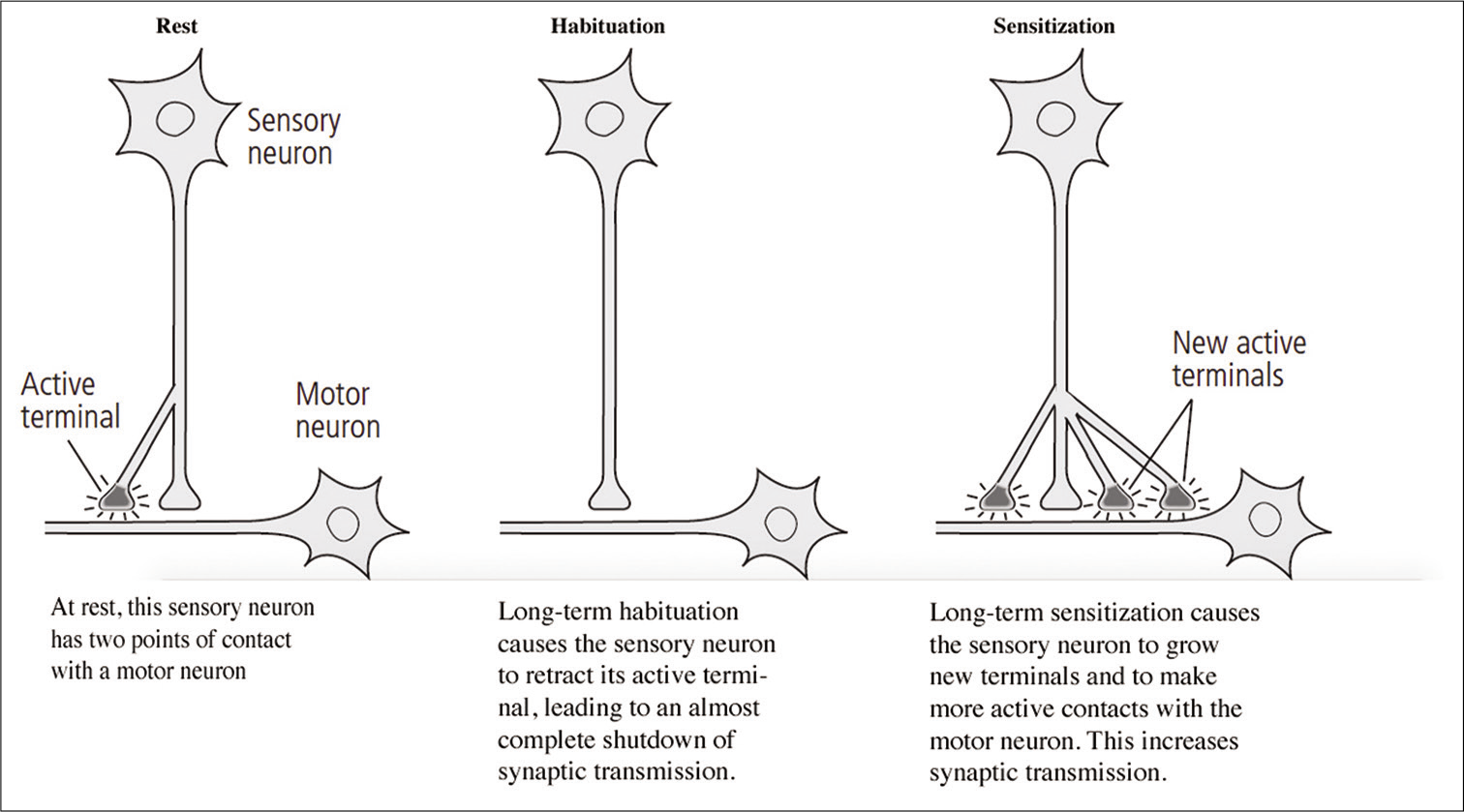
The neurobiology of learning and memory – as related in the memoirs of Eric R. Kandel
Date of publication: 15-Aug-2020
Comment regarding the article “Posttraumatic thoracic epidural capillary hemangioma”
Date of publication: 15-Aug-2020
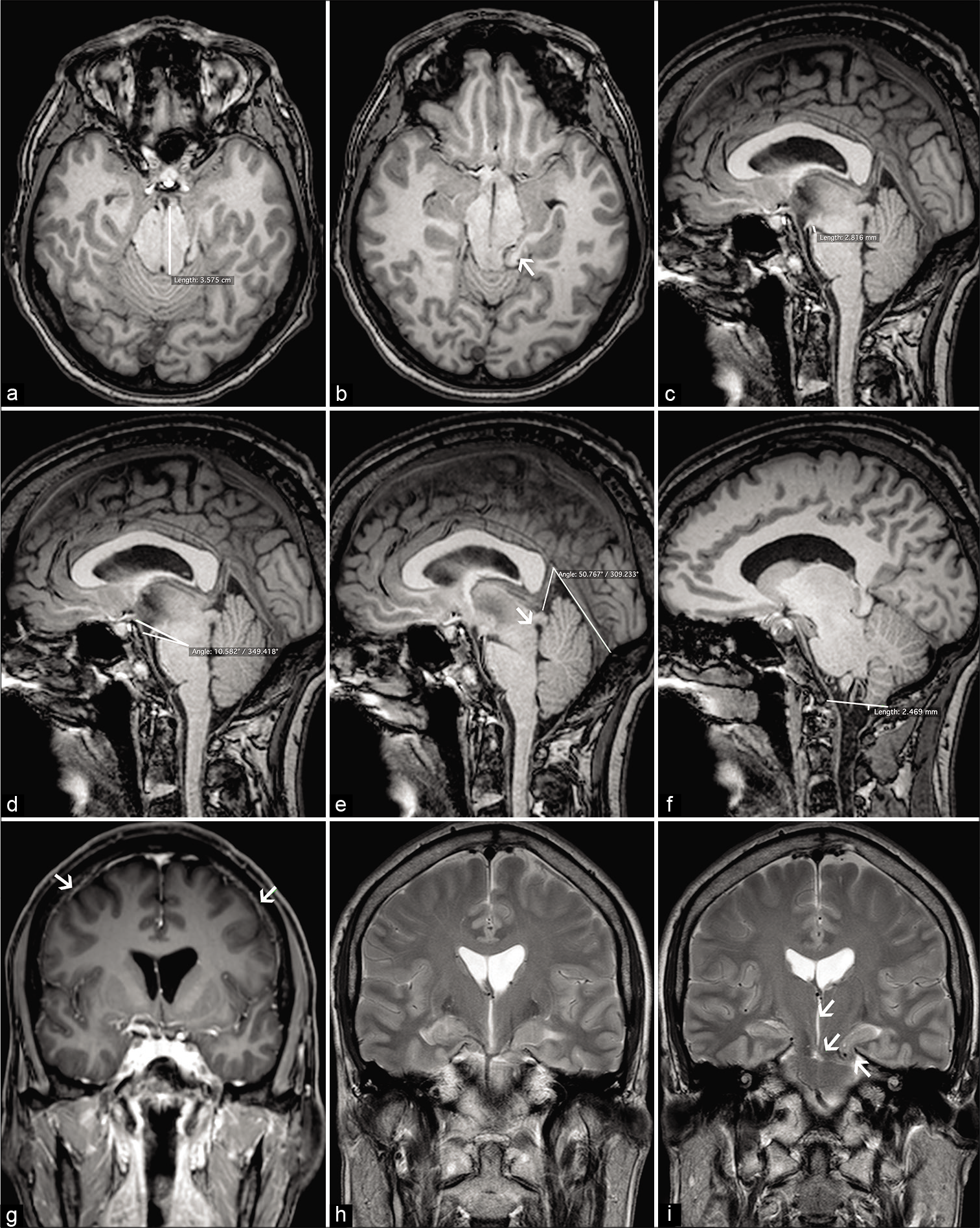
Frontotemporal brain sagging syndrome: Craniospinal hypovolemia secondary to a T6-T7 cerebrospinal fluid-venous fistula
Date of publication: 15-Aug-2020
Background: The frontotemporal brain sagging syndrome (FTBSS) is defined as an insidious/progressive decline in behavior and executive functions, hypersomnolence, and orthostatic headaches attributed to cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) hypovolemia. Here, a T6 CSF-venous fistula (e.g., between the subarachnoid CSF and a paraspinal vein) resulted in a CSF leak responsible for craniospinal hypovolemia.
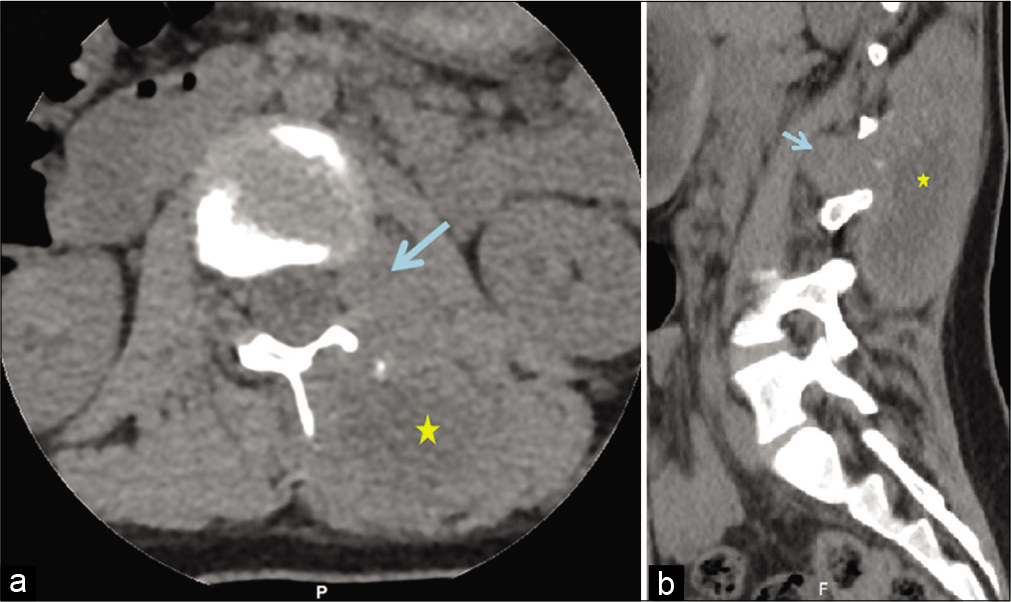
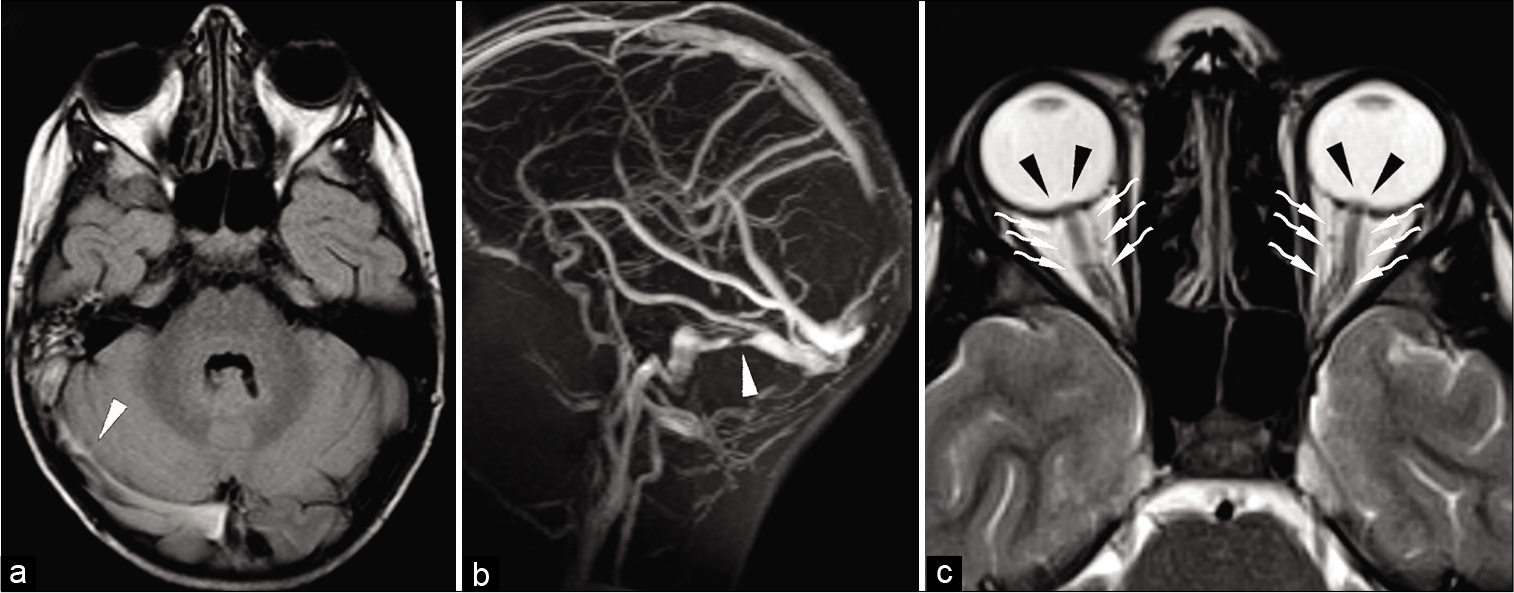
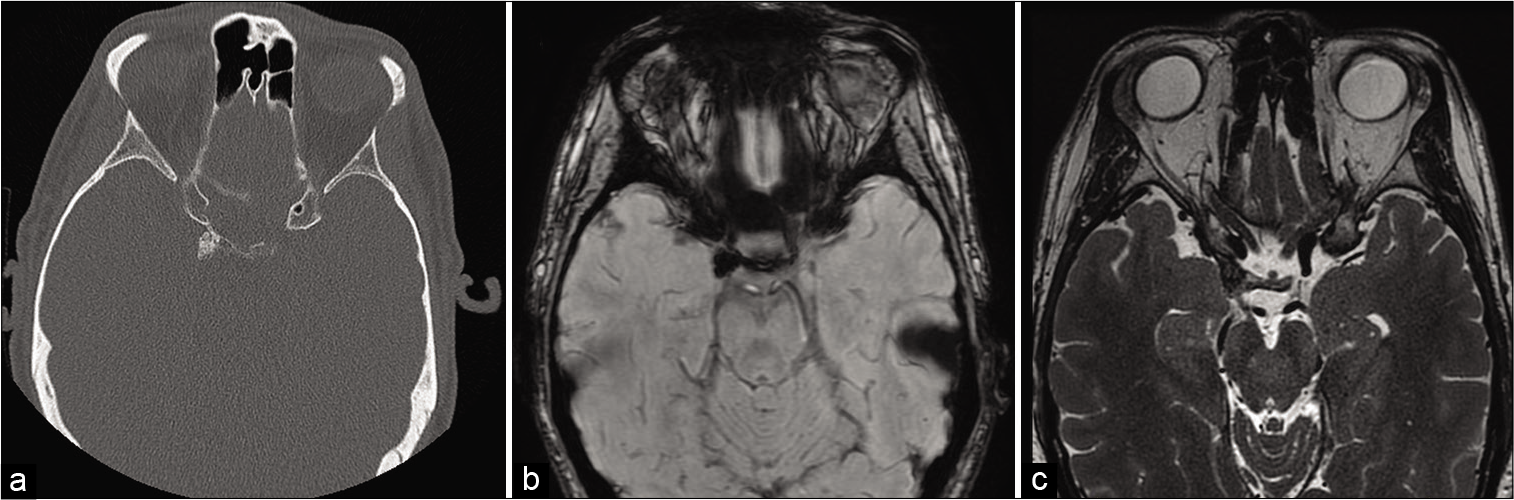
Calcifying pseudoneoplasm of the neuraxis: A rare case involving the oculomotor nerve
Date of publication: 15-Aug-2020
Background: Calcifying pseudoneoplasm of the neuraxis (CAPNON) is a rare entity which can occur at intracranial and spinal locations. Clinical presentation is due to local mass effect rather than tissue infiltration. Lesions causing significant symptoms or are showing radiological progression require surgical resection. Maximal surgical resection is considered curative for this non-neoplastic entity with only two cases of recurrence reported in the literature. Cranial nerve involvement is extremely rare and the presenting neurological deficit is unlikely to improve even with surgical intervention.
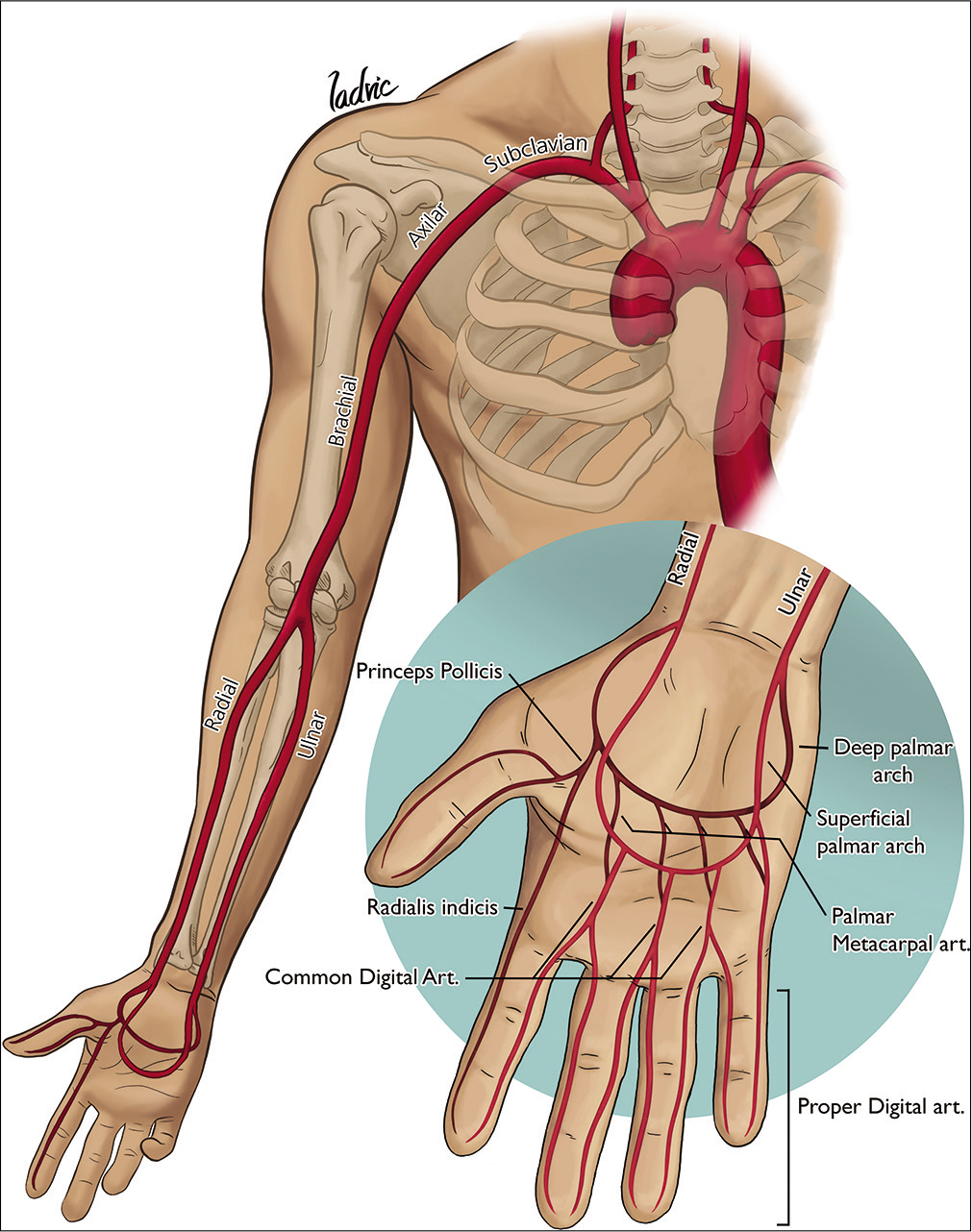
Transradial approach and its variations for neurointerventional procedures: Literature review
Date of publication: 15-Aug-2020
Background: The transfemoral approach (TFA) has been the standard in neuroradiology over the years. However, the transradial approach (TRA) and its variants offer several benefits over the TFA.