Cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics in arachnoid cyst patients with persistent idiopathic intracranial hypertension: A case series and review
Date of publication: 08-Aug-2020
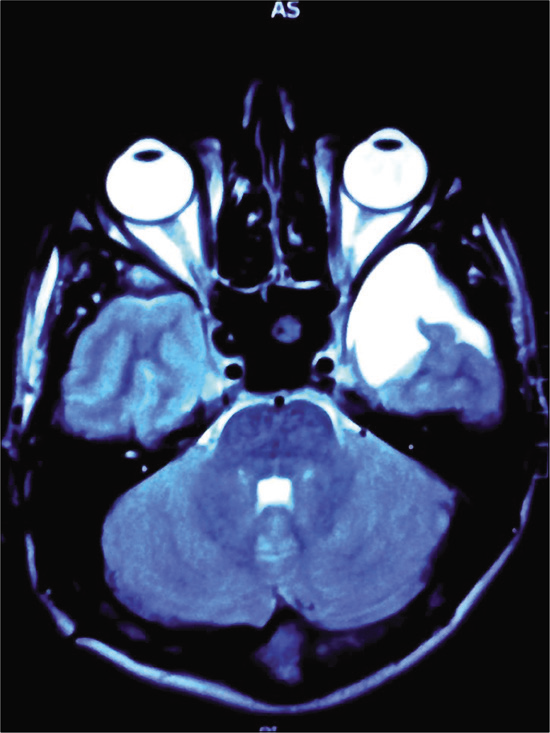
Background: A clear connection has been established between arachnoid cysts (ACs) and the evolution of idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), a connection, which is presently not well understood. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is an integral element of this condition. Little is known about either the influence of AC on CSF hydrodynamics or the specific nature of CSF, which contributes to the complex pathology of IIH.
Clinical, operative, and outcome analysis of giant extradural hematoma: A retrospective study in tertiary care center
Date of publication: 08-Aug-2020
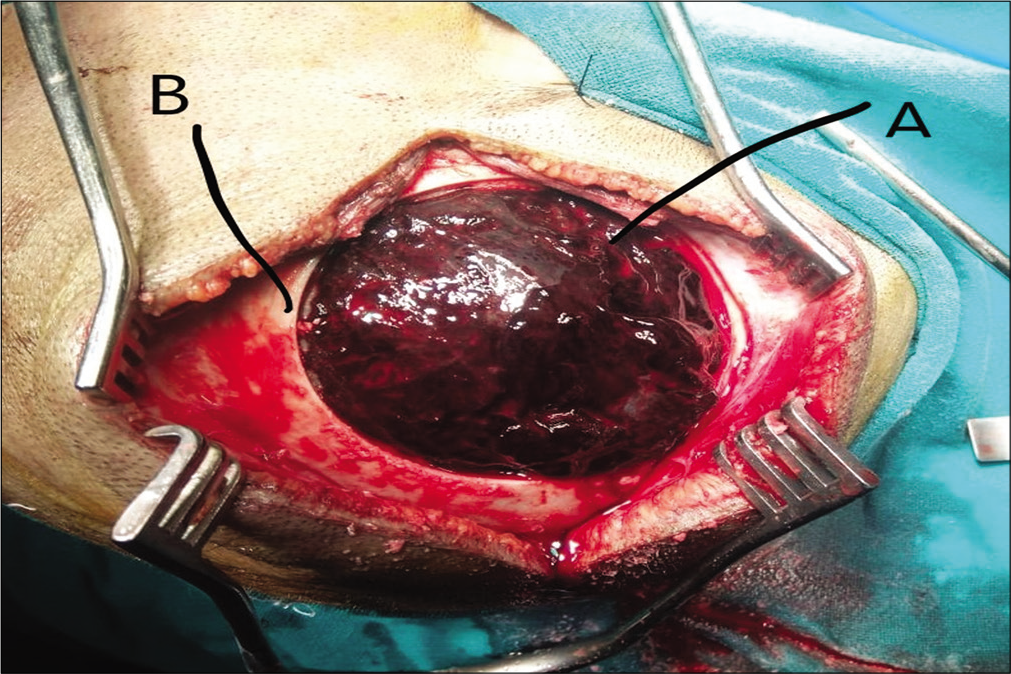
Background: This study is aimed to find a critical volume of operated giant or massive extradural hematoma (EDH) that affects outcome significantly and analyze them with respect to their clinical, surgical, and outcome perspective.
Low-dose adenosine-induced transient asystole during intracranial aneurysm surgery
Date of publication: 08-Aug-2020
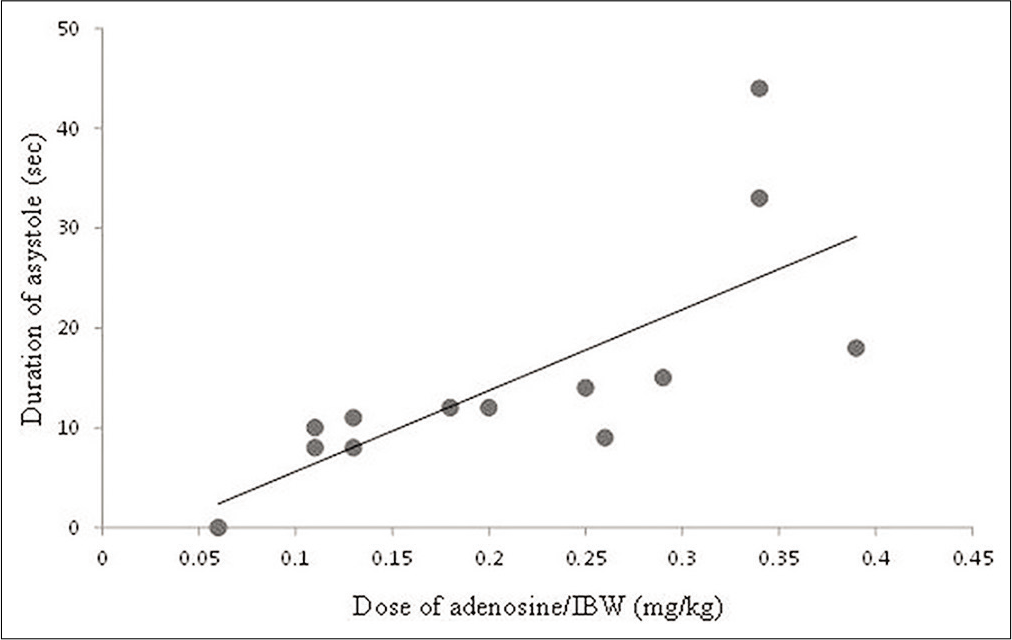
Background: Few studies have evaluated the adenosine dose that induces cardiac arrest during intracranial aneurysm surgery. We present our experiences with adenosine-induced transient asystole (AiTA) during intracranial aneurysm surgery and dosage recommendations.
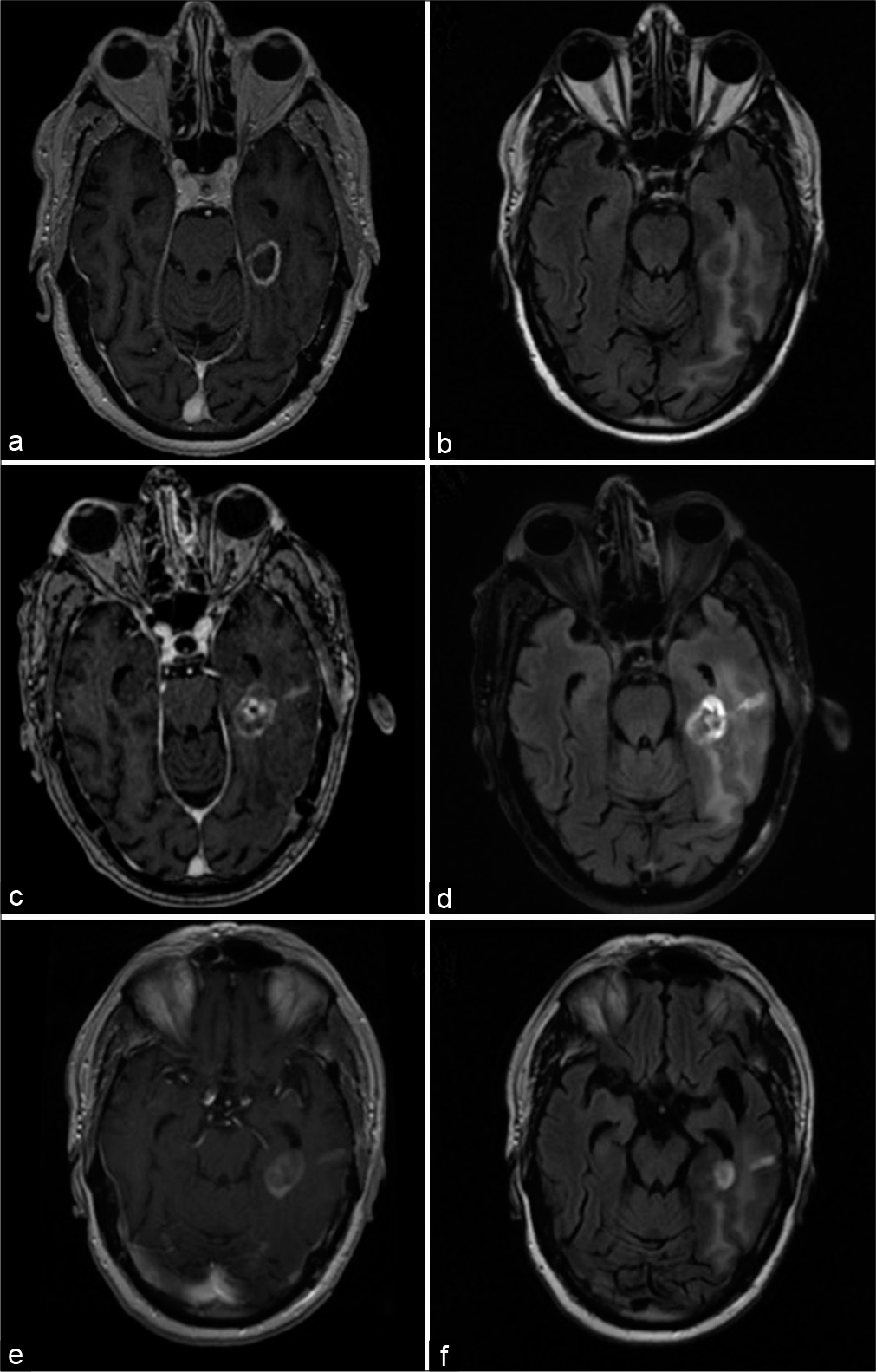
Oversized primary intrapulmonary schwannoma: A case report and a review of the literature
Date of publication: 08-Aug-2020
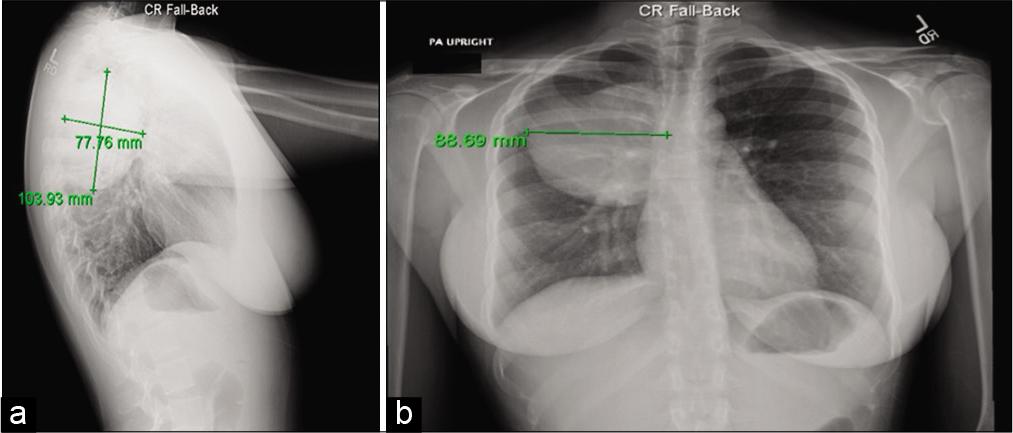
Background: Schwannomas, also known as neurilemommas, are benign, well-circumscribed encapsulated peripheral nerve sheath tumors with rather indolent evolution. Made up of cells closely related to normal myelinating Schwann cells, these neoplasms may arise from the peripheral nervous system as well as from spinal or cranial nerves. They are mostly found in the base of the skull, neck, chest wall, posterior mediastinum, posterior spinal roots, cerebellopontine angle, retroperitoneum, and flexor surfaces of the extremities. The incidence rate of spinal schwannoma is 0.3–0.5/100,000 cases per year with an average age of 50 at diagnosis. We report a case of intrapulmonary schwannoma, adding a review of the literature.
Computed tomography perfusion imaging after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage can detect cerebral vasospasm and predict delayed cerebral ischemia after endovascular treatment
Date of publication: 08-Aug-2020
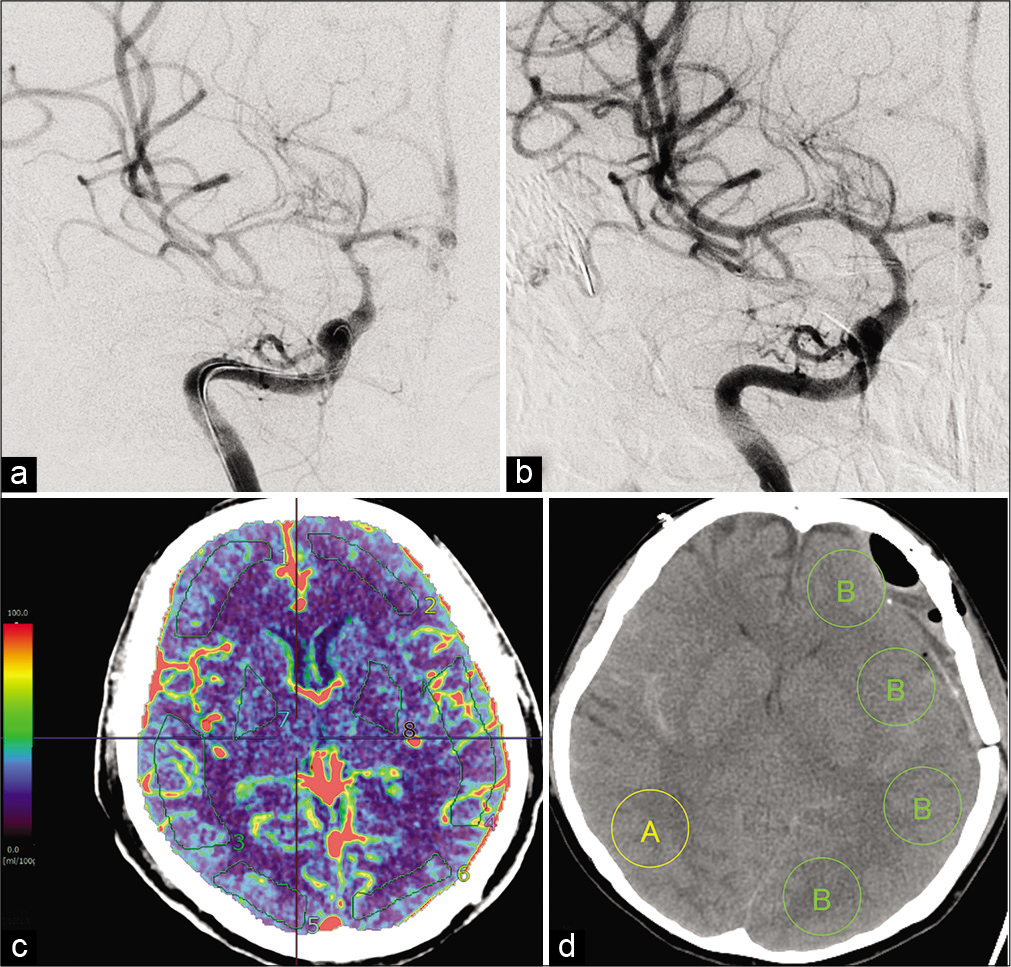
Background: Endovascular treatment (ET) can improve angiographic cerebral vasospasm (CV) after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage, but was unrelated to clinical outcomes in previous analyses. Appropriate detection of CV and precise indications for ET are required. This study investigated whether changes in computed tomography perfusion (CTP) parameter can determine indications for ET in CV and predict its effectiveness.
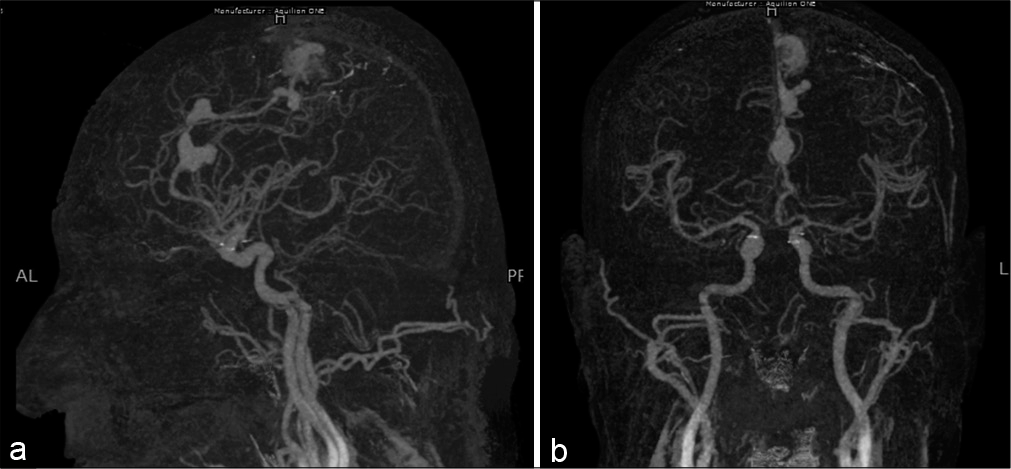
Arteriovenous malformation with associated multiple flow-related distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysms: A case report with poor outcomes
Date of publication: 08-Aug-2020
Background: Low-grade arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) associated with multiple flow-related distal anterior cerebral artery (DACA) aneurysms are rare occurrences. Here, we present a case of a frontal AVM with three associated DACA aneurysms arising from a single feeder.
Laser interstitial thermal therapy in neuro-oncology applications
Date of publication: 08-Aug-2020
Background: Laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) is a minimally invasive surgical treatment for multiple intracranial pathologies that are of growing interest to neurosurgeons and their patients and is emerging as an effective alternative to standard of care open surgery in the neurosurgical armamentarium. This option was initially considered for those patients with medical comorbidities and lesion-specific characteristics that confer excessively high risk for resection through a standard craniotomy approach but indications are changing.
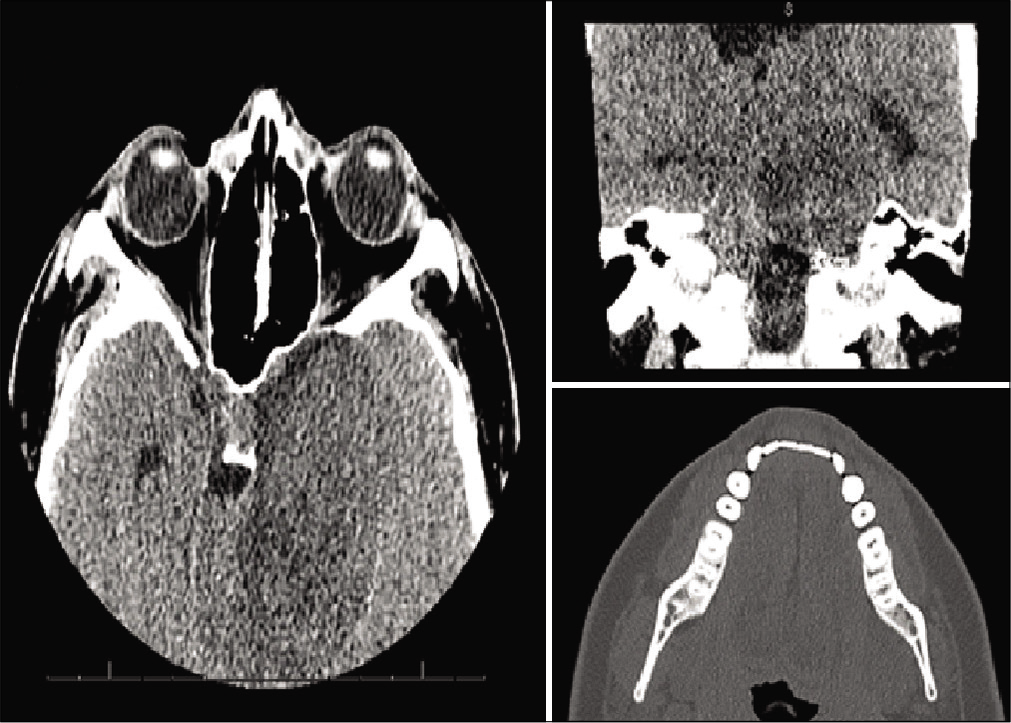
Trigeminal schwannoma presenting with malocclusion: A case report and review of the literature
Date of publication: 08-Aug-2020
Background: Trigeminal schwannomas are rare tumors of the trigeminal nerve. Depending on the location, from which they arise along the trigeminal nerve, these tumors can present with a variety of symptoms that include, but are not limited to, changes in facial sensation, weakness of the masticatory muscles, and facial pain.
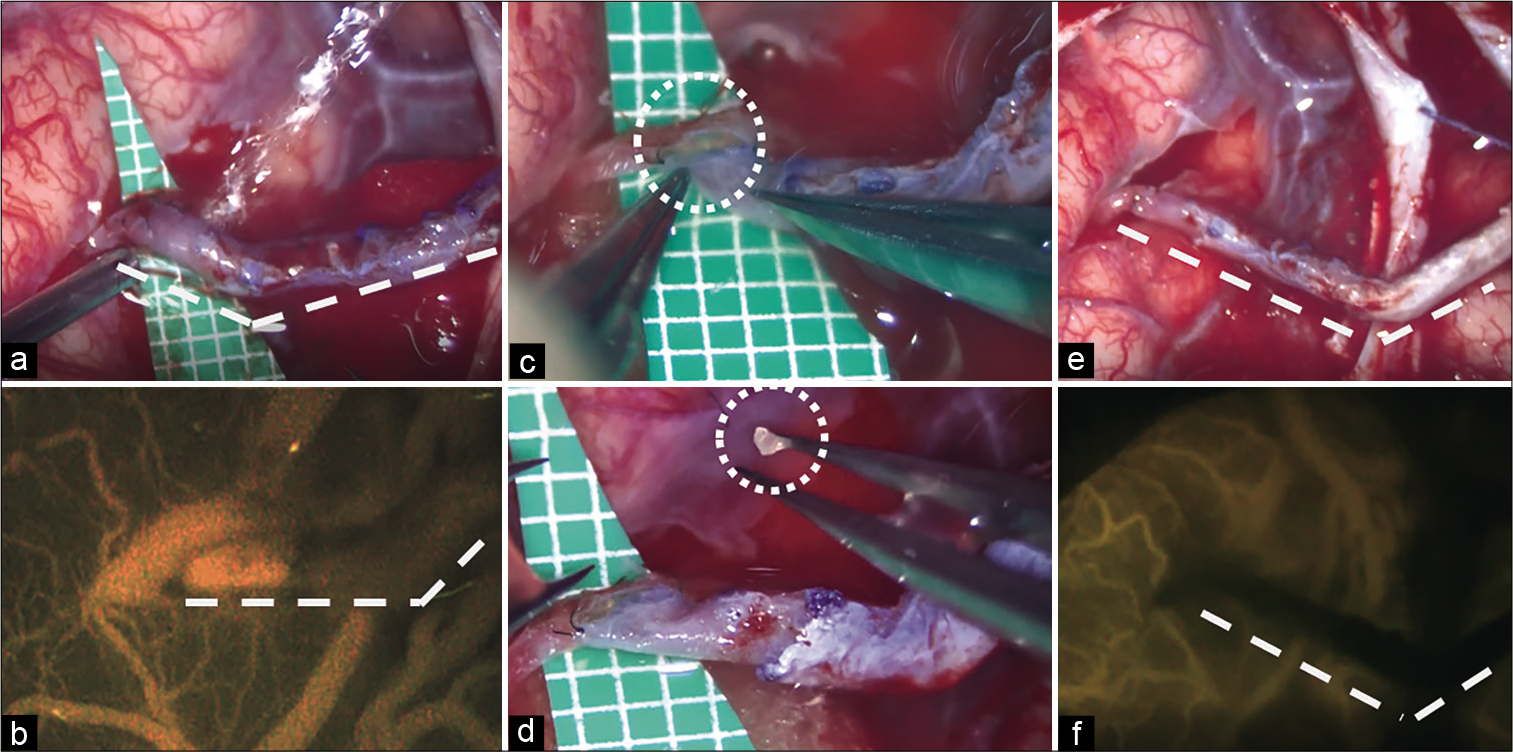
Delayed reopening of a superficial temporal artery to middle cerebral artery bypass graft occluded by a white thrombus during surgery
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2020
Background: To the authors’ knowledge, reopening of a superficial temporal artery to middle cerebral artery (STA-MCA) bypass graft occluded by a white thrombus during the procedure and was observed several months after the surgery is relatively rare.
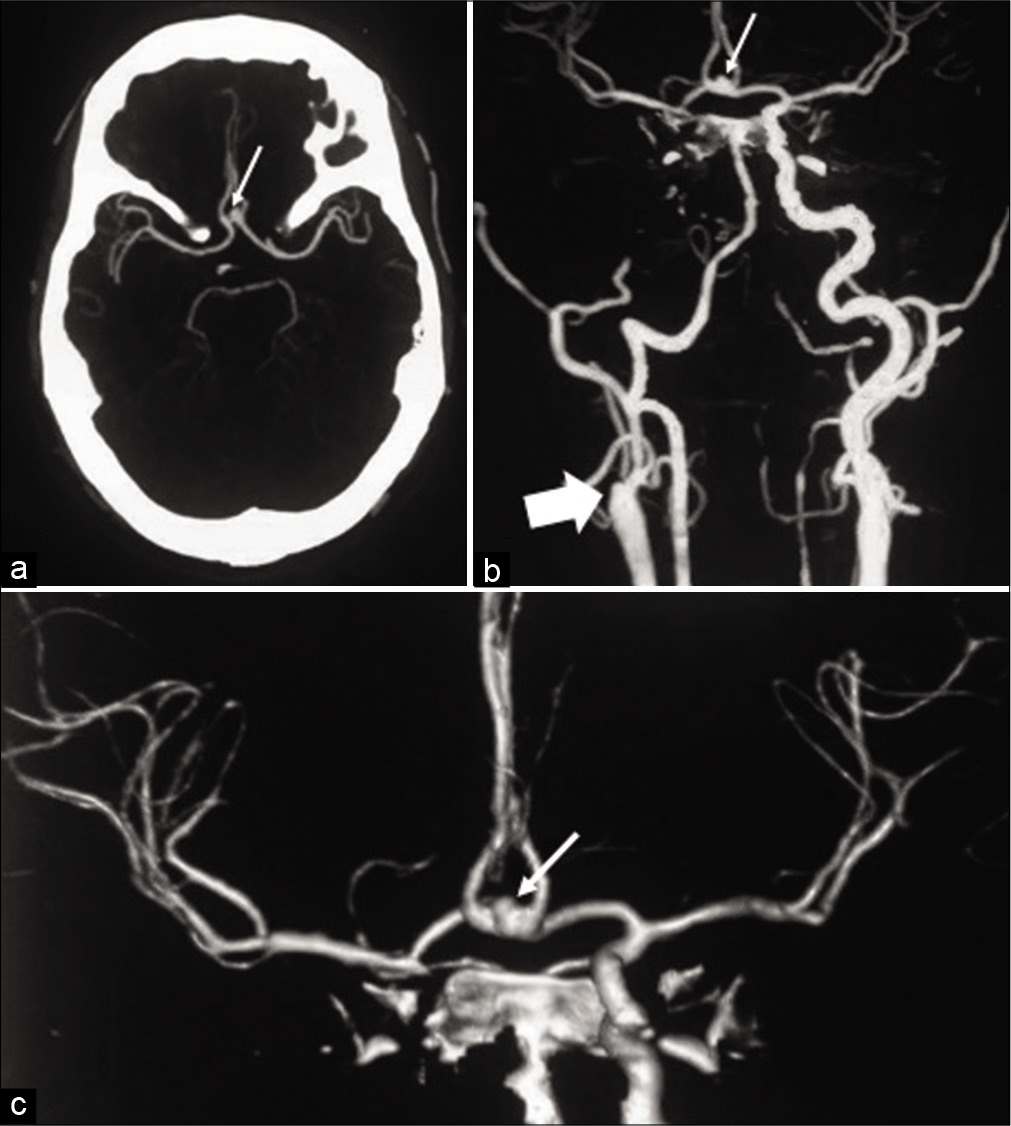
Unilateral absence of the internal carotid artery associated with anterior communicating artery aneurysms: Systematic review and a proposed management algorithm
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2020
Background: Absence or hypoplasia of the internal carotid artery (ICA) is a rare congenital anomaly that is mostly unilateral and highly associated with other intracranial vascular anomalies, of which saccular aneurysm is the most common. Blood flow to the circulation of the affected side is maintained by collateral pathways, some of which include the anterior communicating artery (Acom) as part of their anatomy. Therefore, temporary clipping during microsurgery on Acom aneurysms in patients with unilateral ICA anomalies could jeopardize these collaterals and place the patient at risk of ischemic damage. In this paper, we review the literature on cases with a unilaterally absent ICA associated with Acom aneurysms and provide an illustrative case.