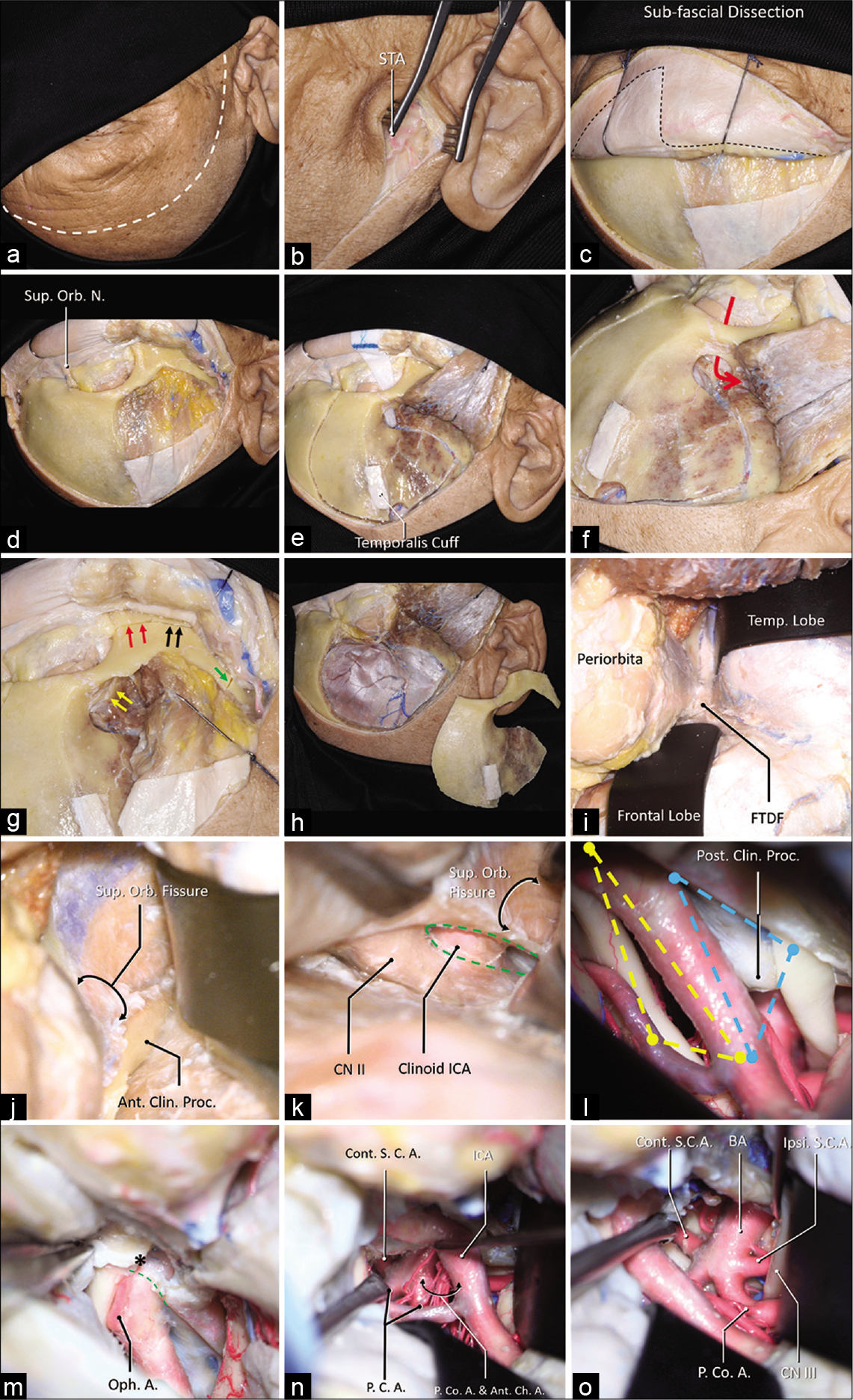
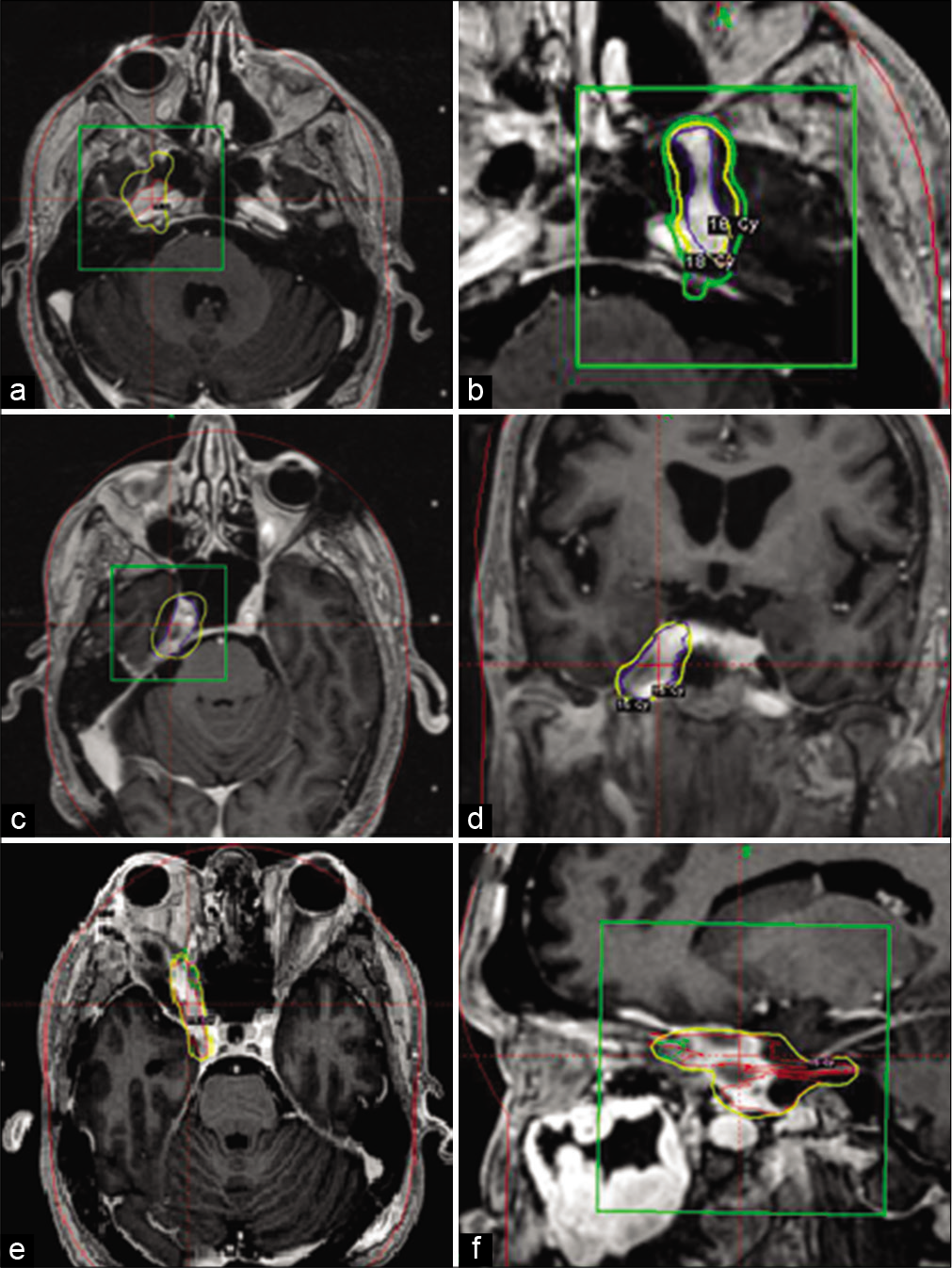
The anterior incisural width as a preoperative indicator for intradural space evaluation: An anatomical investigation
Date of publication: 25-Jul-2020
Background: The opticocarotid triangle (OCT) and the carotico-oculomotor triangle (COT) are two anatomical triangles used in accessing the interpeduncular region. Our objective is to evaluate if the anterior incisural width (AIW) is an indicator to predict the intraoperative exposure through both triangles.
Neurosurgical management of perineural metastases: A case series and review of the literature
Date of publication: 25-Jul-2020
Background: Perineural invasion (PNI) and spread are one of the grimmest prognostic factors associated with primary skin and head-and-neck cancers, yet remain an often confused, and underreported, phenomenon. Adding complexity to reaching a diagnosis and treating perineural spread (PNS) is the finding that patients may have no known primary tumor, history of skin cancer, and/or incidental PNI in the primary tumor. These delays in diagnosis and treatment are further compounded by an already slow disease process and often require multidisciplinary care with combinations of stereotactic radiosurgery, surgical resection, and novel treatments such as checkpoint inhibitors.
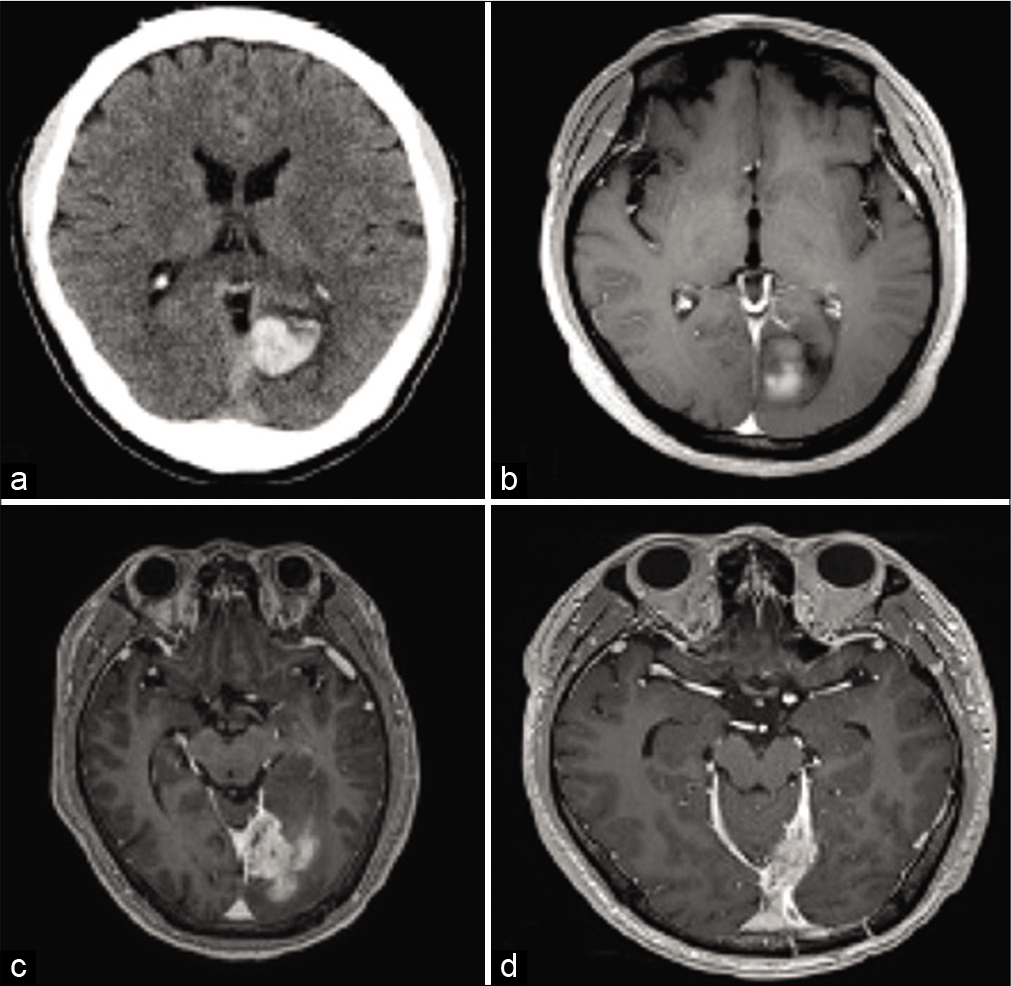
Brainstem abscess treated conservatively
Date of publication: 25-Jul-2020
Background: Brainstem abscess is a rare condition with a variety of treatment approaches. In this paper, we report an unusual case of a brainstem abscess with a positive outcome in an immunocompetent patient who was treated with antibiotic therapy.
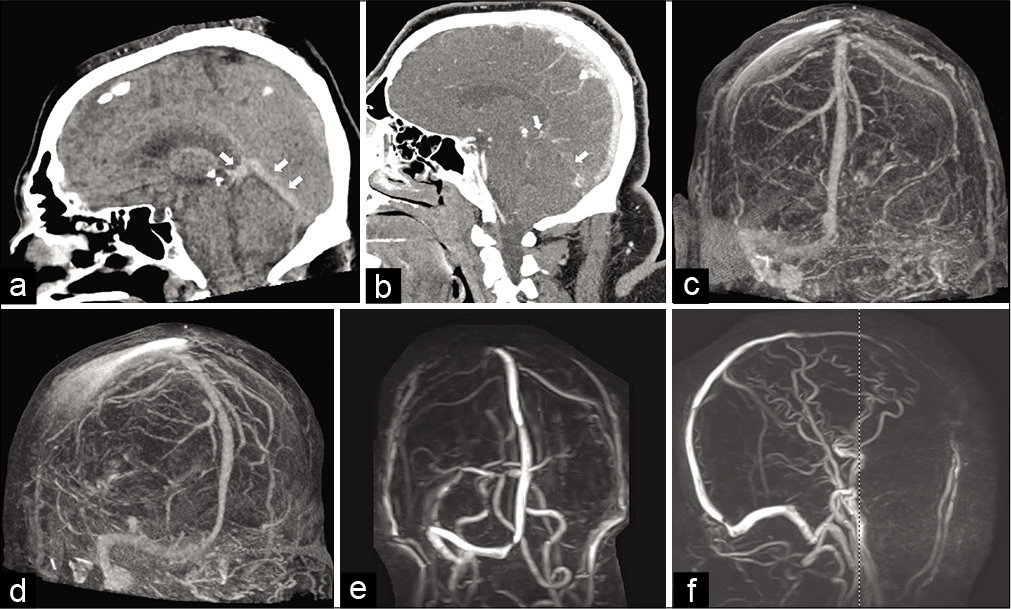
Therapeutic options for primary meningeal angiosarcoma: A case report
Date of publication: 25-Jul-2020
Background: Primary angiosarcoma (AS) of the central nervous system (PACNS) is an extremely rare malignancy. The meninges represent an uncommon site of origin of PACNS. This report describes a recurrent meningeal PACNS treated with surgery, radiotherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, and paclitaxel at different stages of the disease.
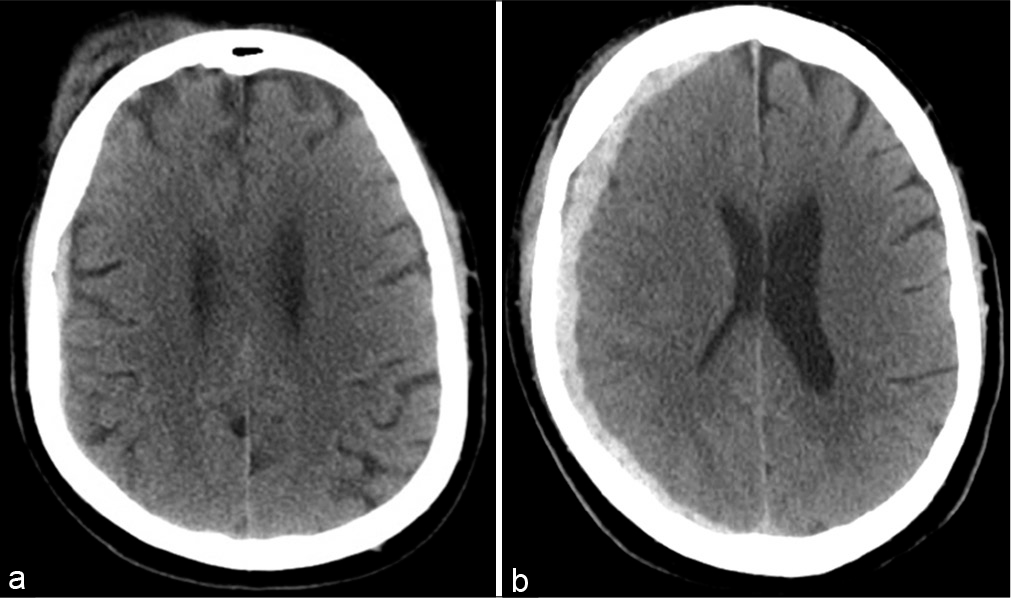
Arteriovenous malformation presenting as traumatic subdural hematoma: A case report
Date of publication: 25-Jul-2020
Background: Brain arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are congenital aberrant connections between afferent arteries and draining veins with no intervening capillary bed or neural parenchyma. Other than seizures, the most common initial presentation of AVM is hemorrhage, which is typically intraparenchymal, subarachnoid, or intraventricular, and very rarely subdural.
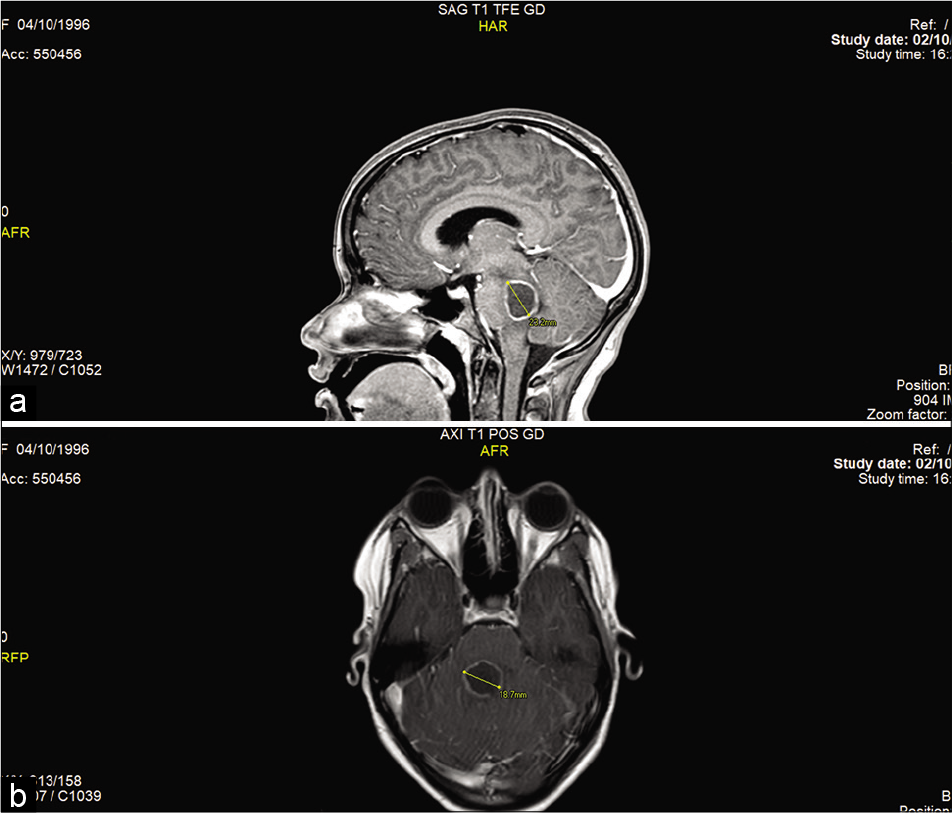
Giant tumefactive perivascular spaces: A case report
Date of publication: 18-Jul-2020
Background: Perivascular spaces are interstitial fluid-filled regions located deep to the pia mater. They play roles in lymphatic drainage and the central nervous system immunological function. When they enlarge, they are referred to as giant tumefactive perivascular spaces. Often misdiagnosed as cystic neoplasms, they require a high degree of clinical suspicion and key radiological features to be accurately diagnosed. We describe an interesting case in which a man presented with worsening headache, subsequently found on neuroimaging to have this phenomenon.
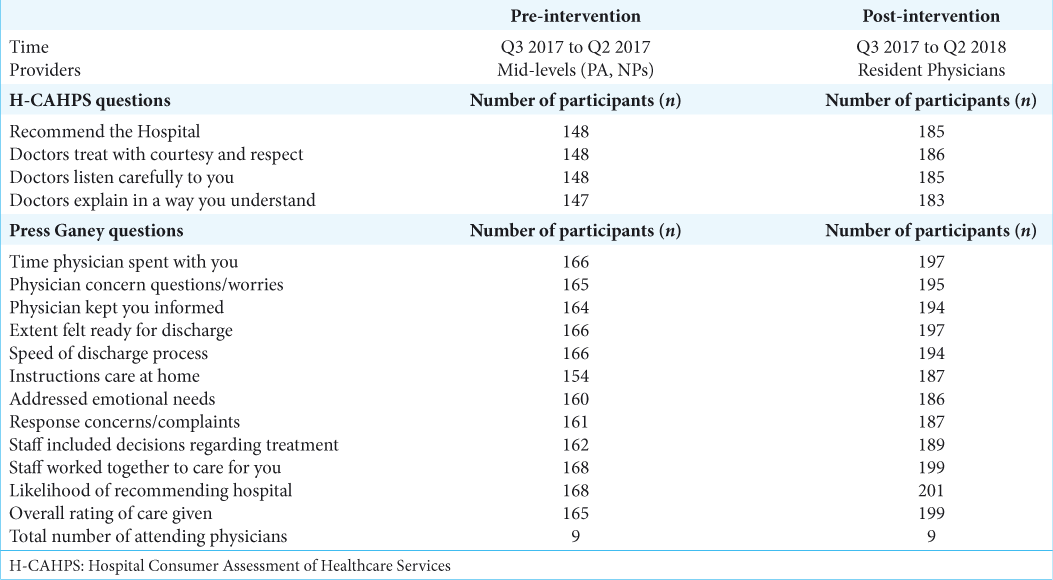
The use of hospital consumer assessment of healthcare services and the Press Ganey medical practice surveys in guiding surgical patient care practices
Date of publication: 18-Jul-2020
Background: Patient satisfaction questionaries have become popular in the past decade after the institution of the Patient Care and Affordable Care Act of 2010. This study evaluated whether the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Services (H-CAHPS) and Press Ganey scores improved after institutional changes to the rounding system.
Mechanical venous thrombectomy and prolonged infusion of tissue plasminogen activator for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: Video case report
Date of publication: 18-Jul-2020
Background: Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) is a rare and often misdiagnosed condition with mortality rates ranging from 6 to 10%. Diagnosis and monitoring are typically achieved through noninvasive imaging, including computed tomography or magnetic resonance venography. The current standard of treatment is systemic anticoagulation. However, in patients who continue to decline neurologically or do not show sufficient response to or have absolute contraindications to systemic anticoagulation, endovascular treatments are an alternative. Endovascular options are poorly studied and specific devices have not been developed, partially due to the rare nature of the disease. Here, we present a case report detailing the treatment of extensive CVST from the vein of Galen to the sigmoid sinus using mechanical thrombectomy and local infusions of unfractionated heparin (UFH) and tissue plasminogen activator.
Cerebrospinal fluid fistula in a patient with chronic constipation related to an autonomic dysfunction and revealed by bacterial meningitis – A case report
Date of publication: 18-Jul-2020
Background: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) fistula represents a rare neurosurgical entity that can be defined as a communication between the subarachnoid space and nasal fossa or less commonly the ear cavity. It can be spontaneous without an evident etiology or secondary following a skull base surgery or trauma. The early diagnosis of spontaneous forms remains a challenge as clinical signs (e.g., unilateral rhinorrhea) can be absent or neglected by patients and can result in meningitis.
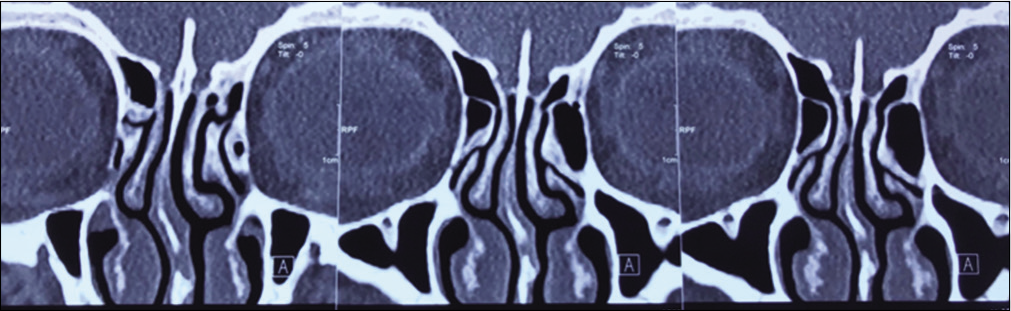
Fulminant presentation of a SMARCB1-deficient, anterior cranial fossa tumor in adult
Date of publication: 18-Jul-2020
Background: Malignant atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor (ATRT) usually develops in children. ATRTs are rare in adults, with only one case in the literature describing involvement of the anterior skull base. These primary intracranial tumors are characterized molecularly as SMARCB1 (INI1) deficient. Different types of such SMARCB1-deficient tumors exist in adulthood, usually in the form of extracranial tumors. Very few cases of such a new entity, named SMARCB1-deficient sinonasal carcinoma have been described with intracranial penetration and involvement of the anterior cranial fossa.