Large central lumbar disc herniation causing acute cauda equina syndrome with loss of evoked potentials during prone positioning for surgery
Date of publication: 19-Mar-2018
Background:Few studies in the literature discuss operative positioning for lumbar surgery precipitating acute cauda equina syndromes (CES).
How to compare outcomes and complications in neurosurgery: We must make the mission possible!
Date of publication: 19-Mar-2018
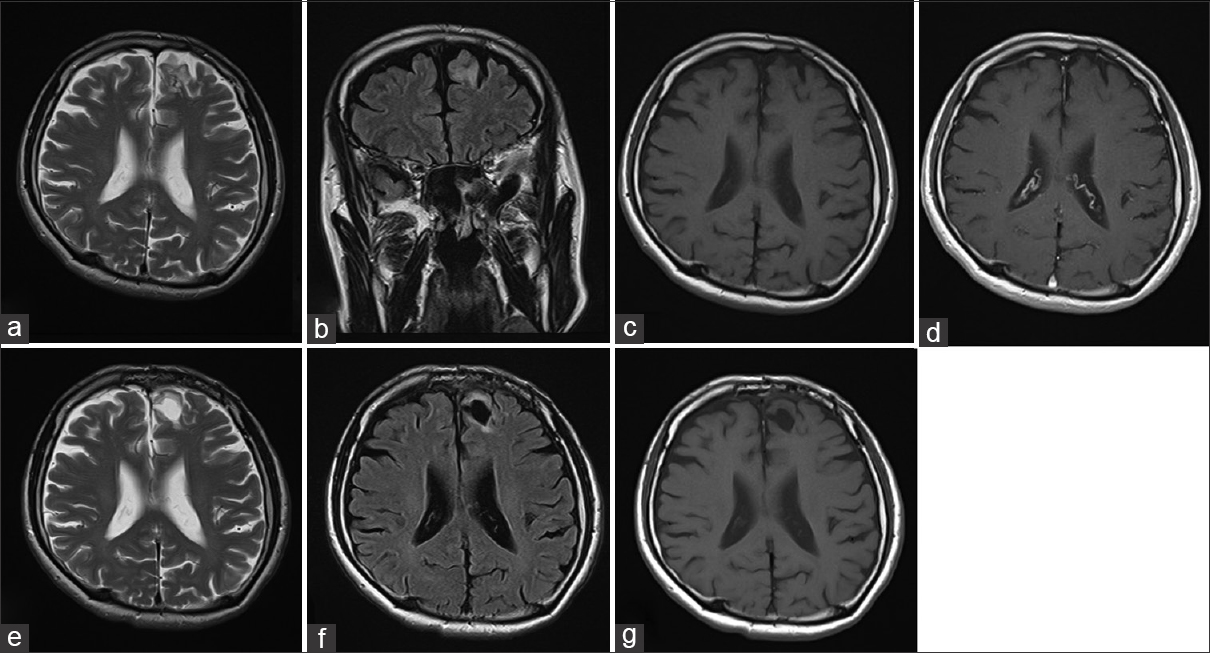
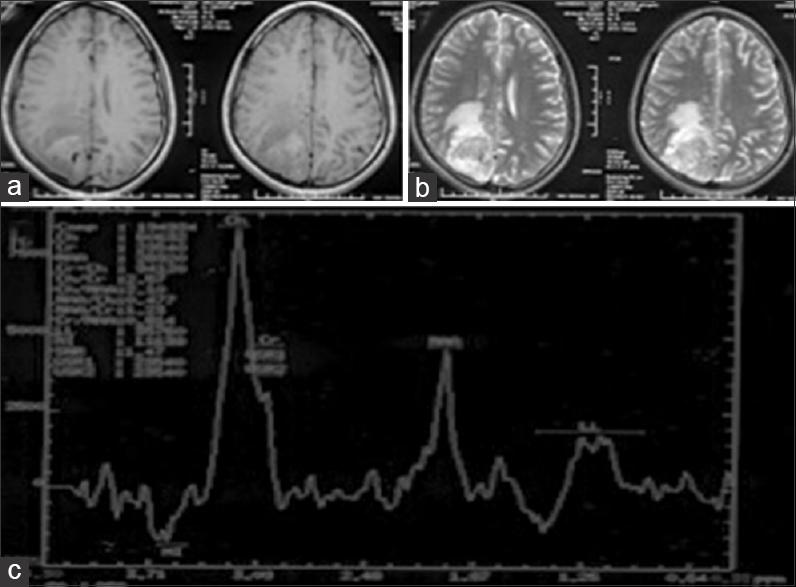
Multinodular and vacuolating neuronal tumor: A case report and literature review
Date of publication: 19-Mar-2018
Background:Multinodular and vacuolated neuronal tumor (MVNT) is a benign neuronal tumor that is newly recognized as architectural appearance that may be related to ganglion cell tumors in 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System. Herein, we report a case of MVNT in a 60-year-old man with a thorough literature review.
Ambiguity in the Dural Tail Sign on MRI
Date of publication: 19-Mar-2018
Background:Meningiomas give rise to the dural tail sign (DTS) on contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CEMRI). The presence of DTS does not always qualify for a meningioma, as it is seen in only 60-72% of cases. This sign has been described in various other lesions like lymphomas, metastasis, hemangiopericytomas, schwannomas and very rarely glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). The characteristics of dural-based GBMs are discussed here, as only eleven such cases are reported in the literature till date. Here we discuss the unique features of this rare presentation.
Cranial autologous bone flap resorption after a cranioplasty: A case report
Date of publication: 19-Mar-2018
Background:Craniectomies and cranioplasty are common neurosurgical procedures performed after brain trauma, ischemia, tumor resection, or infection. Post-cranioplasty autologous bone flap resorption may occur in patients after delayed cranial reconstruction. The occurrence is usually low when bone flaps are stored in subcutaneous abdominal tissue. We report a unique case of post-cranioplasty cranial bone flap.
Internal auditory canal exostosis: A technical case report
Date of publication: 19-Mar-2018
Background:Exostoses of the internal auditory canal is a rare finding that may present with disabling symptoms of dizziness, hearing loss, and vestibular dysfunction based on the extent of cranial nerve compression. The purpose of this case report is to discuss the presentation and outcomes in a patient who presented with this disorder.
Lower complication and reoperation rates for laminectomy rather than MI TLIF/other fusions for degenerative lumbar disease/spondylolisthesis: A review
Date of publication: 07-Mar-2018
Background:Utilizing the spine literature, we compared the complication and reoperation rates for laminectomy alone vs. instrumented fusions including minimally invasive (MI) transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) for the surgical management of multilevel degenerative lumbar disease with/without degenerative spondylolisthesis (DS).
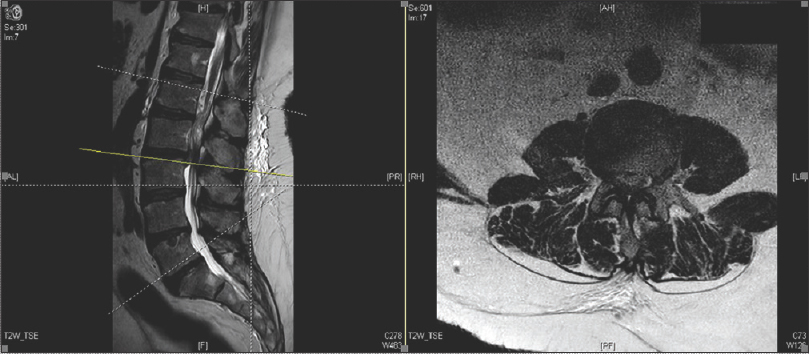
Spinal case of the month with short perspective: How would you treat this L3-L4 synovial cyst?
Date of publication: 07-Mar-2018
Background:In this new section, Case of the Month with Short Perspective from Surgical Neurology International, we want to see how various spine surgeons would approach different spinal pathologies. In this first case, an elderly male presented with 3 years of lower back pain and progressive neurogenic claudication with bilateral radiculopathy that had exacerbated over the prior 6 months. An outside physician performed a magnetic resonance (MR) study of the lumbar spine that showed a massive synovial cyst filling the spinal canal (e.g., large bilateral cysts) at the L3-L4 level with grade I spondylolisthesis. The MR and CT studies also both demonstrated moderate L2-L3, and severe L3-L4 stenosis.
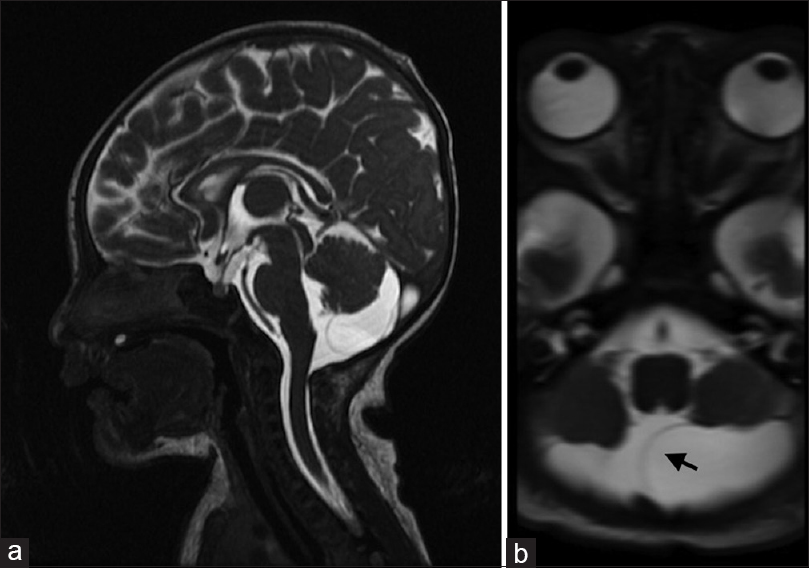
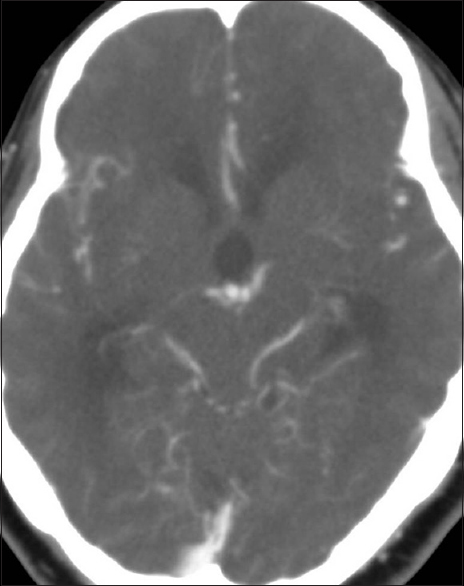
Rare case of a rapidly enlarging symptomatic arachnoid cyst of the posterior fossa in an infant: A case report and review of the literature
Date of publication: 07-Mar-2018
Background:Intracranial arachnoid cysts are space-occupying lesions that typically remain stable or decrease in size over time. Cysts in infants younger than 1 year of age are remarkably different from those in older children and adults in terms of cyst localization and enlargement. Arachnoid cysts of the posterior fossa (PFACs) are very rare in infants and do not typically grow or present with clinical symptoms, such that surgical treatment is generally considered to be unnecessary. Here, we describe an extremely rare case of an infant with a rapidly enlarging symptomatic PFAC that was successfully treated with surgery.
Obstructive hydrocephalus and facial nerve palsy secondary to vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia: Case Report
Date of publication: 07-Mar-2018
Background:Symptomatic hydrocephalus due to vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia is a rare occurrence.