Review of the neurological benefits of phytocannabinoids
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2018
Background:Numerous physical, psychological, and emotional benefits have been attributed to marijuana since its first reported use in 2,600 BC in a Chinese pharmacopoeia. The phytocannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD), and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the most studied extracts from cannabis sativa subspecies hemp and marijuana. CBD and Δ9-THC interact uniquely with the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Through direct and indirect actions, intrinsic endocannabinoids and plant-based phytocannabinoids modulate and influence a variety of physiological systems influenced by the ECS.
Simultaneous cerebrospinal fluid and hematologic metastases in a high-grade ependymoma
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2018
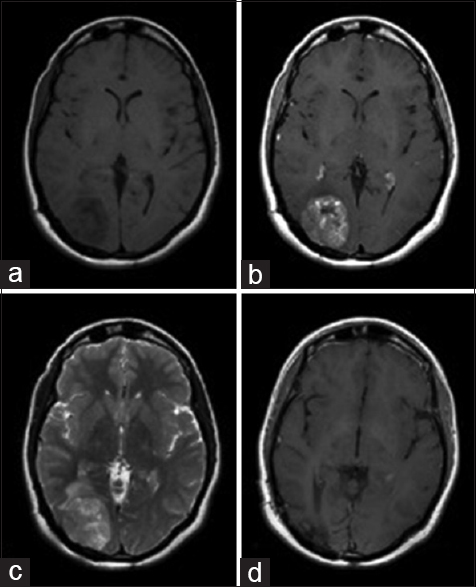
Background:Ependymomas are relatively uncommon tumors that constitute about 7% of all primary intracranial neoplasms. Among these, high-grade ependymomas are locally aggressive and recur most commonly at the primary site following resection. Ependymomas are also known to be the one glial neoplasm that tends to frequently metastasize inside and outside the central nervous system (CNS) that complicates workup and management. Metastasis due to surgical manipulation is common and neurosurgeons should be well-versed in the most effective methods to remove these tumors in order to avoid such metastases.
Utility of magnetic resonance cisternography with intrathecal gadolinium in detection of cerebrospinal fluid fistula associated with Mondini dysplasia in a patient with recurrent meningitis: Case report and literature review
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2018
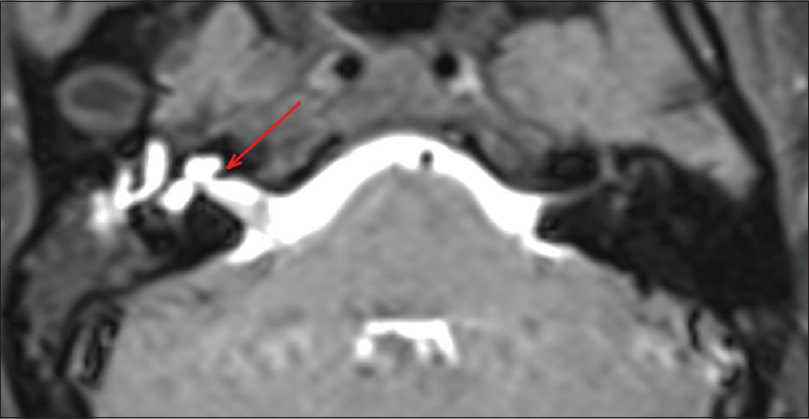
Background:The intrathecal contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance cisternography (MRC) is a diagnostic method that has been proven effective in selected patients with various disorders of the cerebrospinal system, including the detection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks. The Mondini dysplasia is a malformation of the inner ear characterized by an incomplete cochlear development. The cerebrospinal fistula associated with Mondini dysplasia usually occurs in the first 5–10 years.
Chiari I malformation with acute neurological deficit after craniocervical trauma: Case report, imaging, and anatomic considerations
Date of publication: 23-Apr-2018
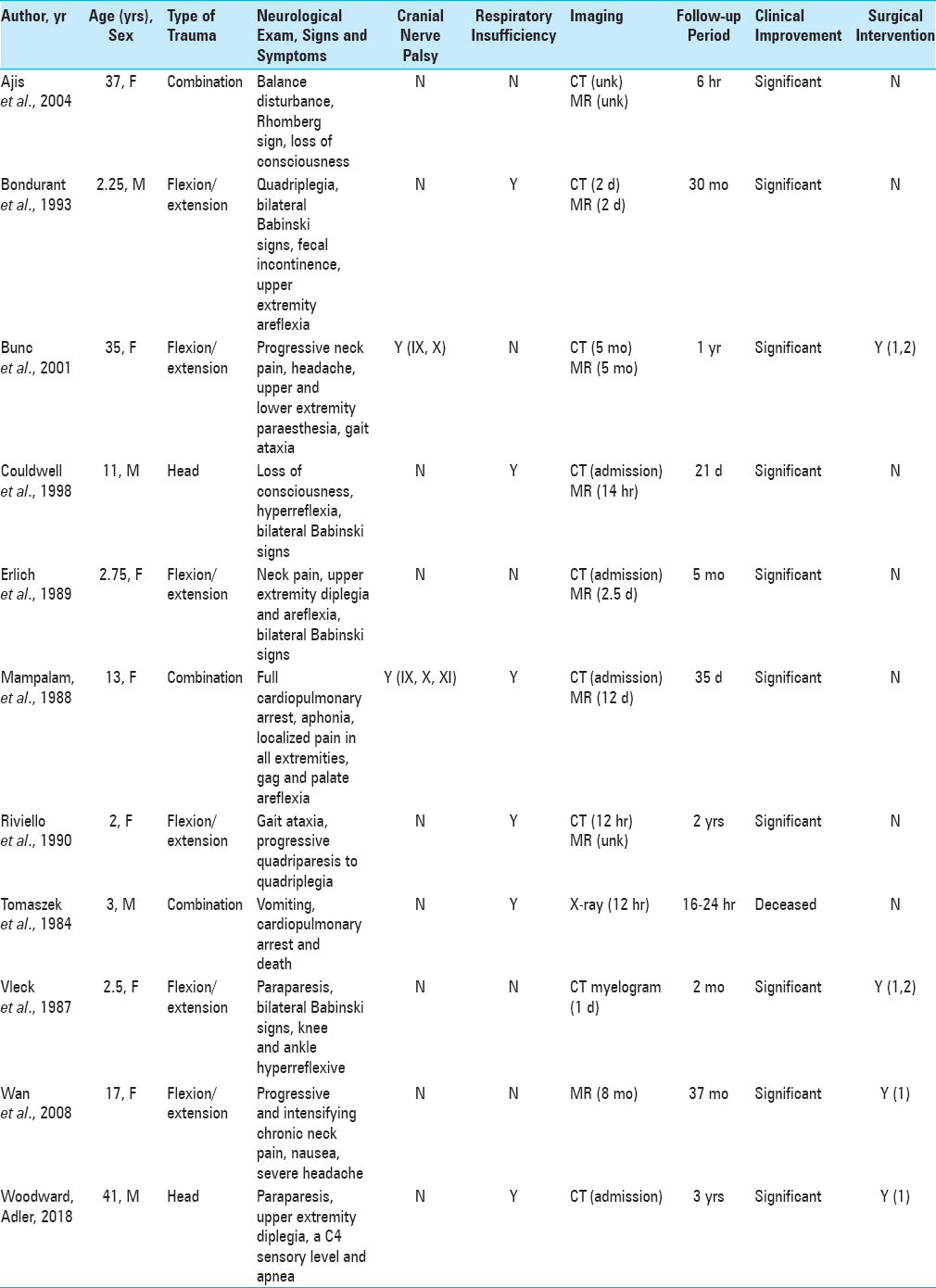
Background:In patients with Chiari I malformation (CMI), the occurrence of acute neurologic deficit after craniocervical trauma is rare. However, the pathologic potential of exacerbating anatomic overcrowding of the posterior fossa has immense clinical consequences and prompt recognition is essential.
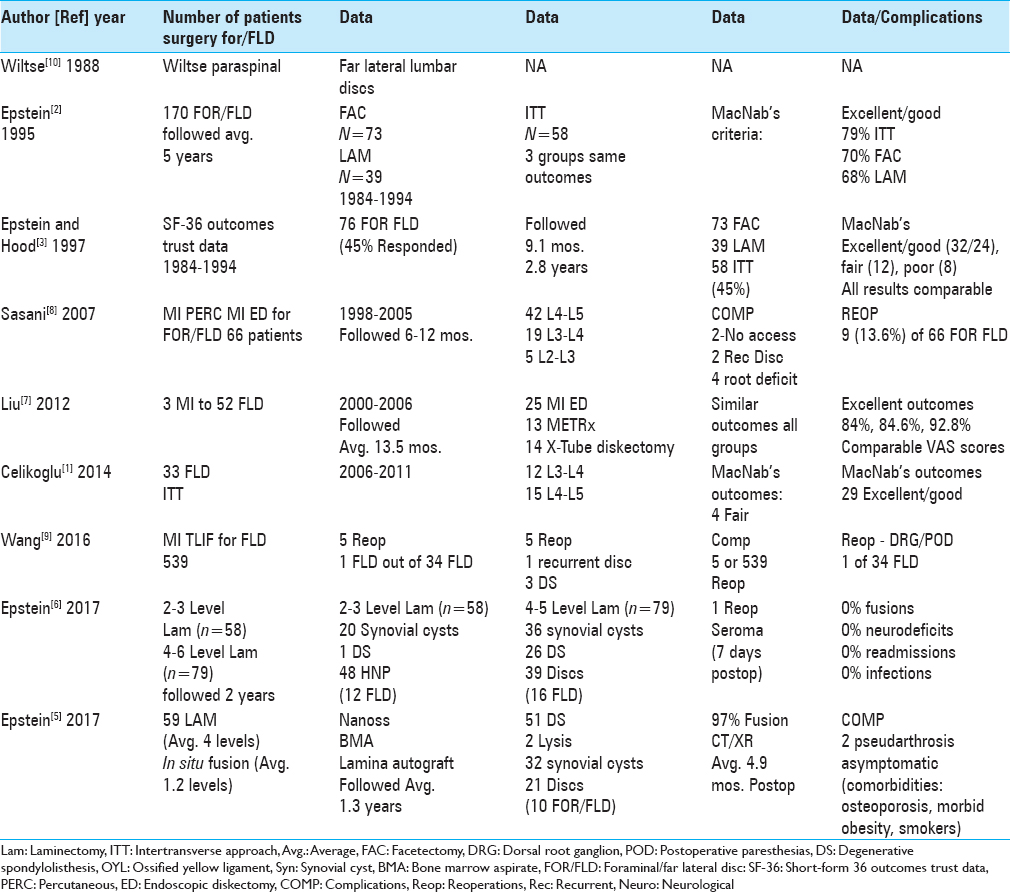
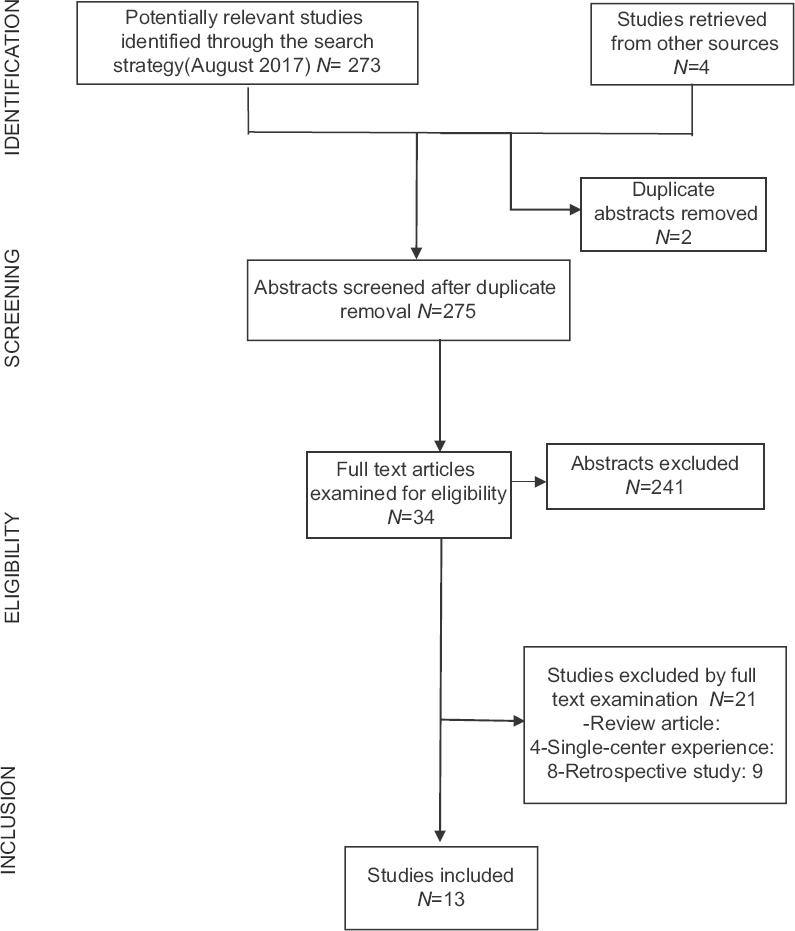
Case presentation and short perspective on management of foraminal/far lateral discs and stenosis
Date of publication: 23-Apr-2018
Background:The management of lumbar foraminal/far lateral discs (FOR/FLD) with stenosis remains controversial. Operative choices should be based on each patient's preoperative dynamic X-ray findings, magnetic resonance (MR), and computed tomography (CT) studies. Here we reviewed several options for decompression alone vs. decompression with fusion.
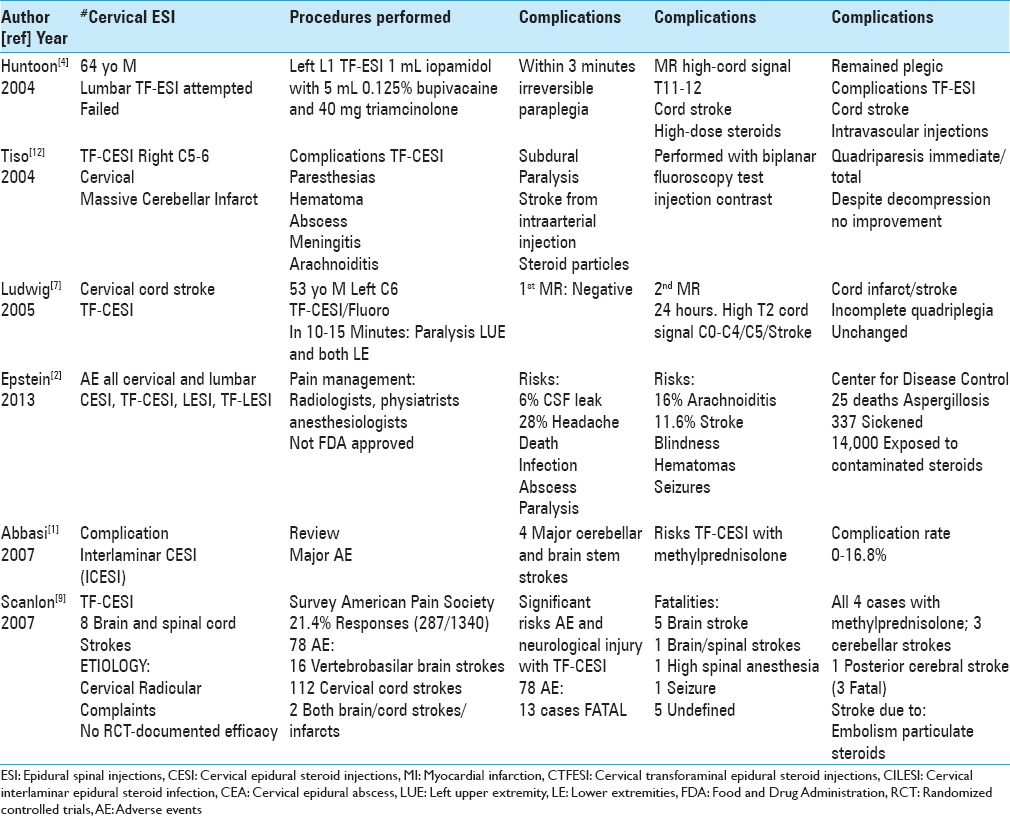
Major risks and complications of cervical epidural steroid injections: An updated review
Date of publication: 23-Apr-2018
Background:Too many patients, with or without significant cervical disease, unnecessarily undergo cervical epidural steroid injections (CESIs). These include interlaminar (ICESI) and transforaminal ESI (TF-CESI) injections that are not Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved, have no documented long-term efficacy, and carry severe risks and complications.
Carotid artery stenting vs. carotid endarterectomy in the management of carotid artery stenosis: Lessons learned from randomized controlled trials
Date of publication: 16-Apr-2018
Background:Carotid artery stenosis, both symptomatic and asymptomatic, has been well studied with several multicenter randomized trials. The superiority of carotid endarterectomy (CEA) to medical therapy alone in both symptomatic and asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis has been well established in previous trials in the 1990s. The consequent era of endovascular carotid artery stenting (CAS) has offered another option for treating carotid artery stenosis. A series of randomized trials have now been conducted to compare CEA and CAS in the treatment of carotid artery disease. The large number of similar trials has created some confusion due to inconsistent results. Here, the authors review the trials that compare CEA and CAS in the management of carotid artery stenosis.
Epidural abscess presenting as severe depression with suicidal ideations: Case report
Date of publication: 16-Apr-2018
Background:Epidural abscess (EDA) is an uncommon form of intracranial infection that generally presents with fever, headache, and focal neurologic deficit. Imaging generally reveals a lentiform collection with diffusion restriction on diffusion weighted image. We present an interesting case in which a patient with EDA presented with three weeks of depression with suicidal ideations. The patient displayed no notable infectious signs and the imaging was suggestive of chronic subdural hematoma (SDH) rather than EDA.
Occipital artery to extracranial vertebral artery anastomosis for bilateral vertebral artery stenosis at the origin: A case report
Date of publication: 16-Apr-2018
Background:Revascularization of posterior circulation is essential in patients with severe bilateral vertebral artery (VA) stenosis despite administering maximal medical treatment, due to the high mortality of posterior circulation stroke.