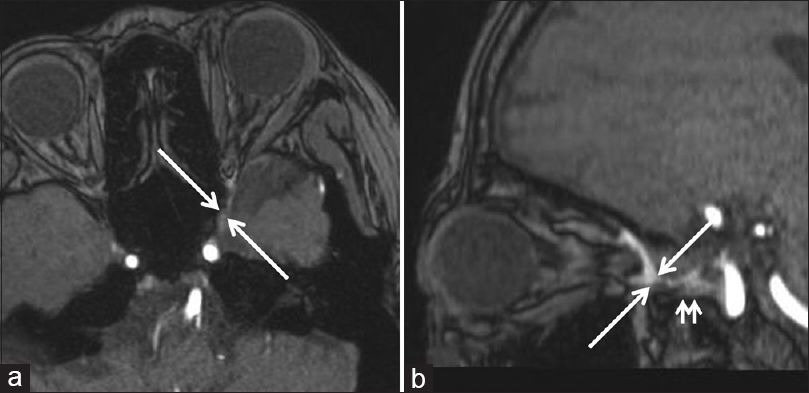
Dural arteriovenous fistula in the superior orbital fissure: A case report
Date of publication: 07-May-2018
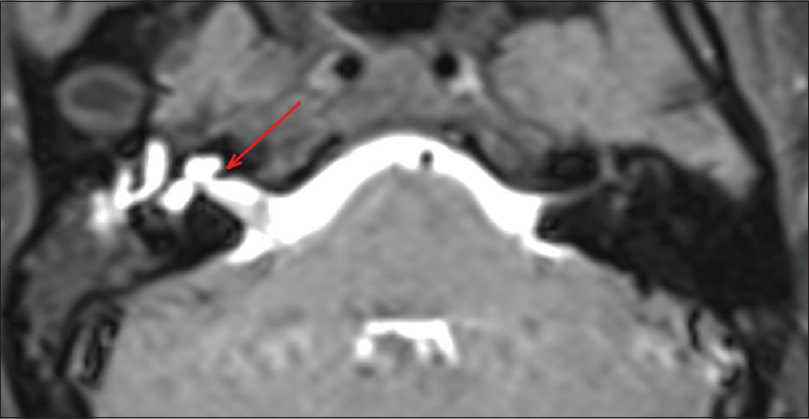
Background:Dural arteriovenous fistulas (dAVFs) are extremely rare in the superior orbital fissure, and they exhibit ocular symptoms similar to the dAVF in the cavernous sinus because of the intraorbital venous congestion. Hence, the distinction of these conditions is imperative because of some inherent differences in endovascular treatment techniques.
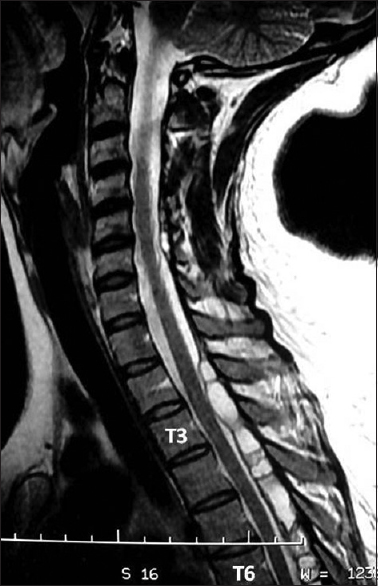
A new surgical technique for the removal of extensive spinal epidural hydatid cyst
Date of publication: 07-May-2018
Background:Extensive spinal epidural hydatidosis may contribute to extensive spinal cord compression. Multilevel laminectomy with surgical excision remains the gold standard for treating these lesions which are typically invasive, and have a high recurrence rate.
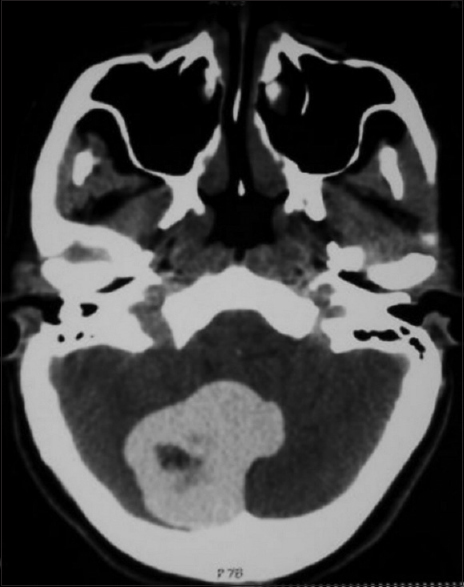
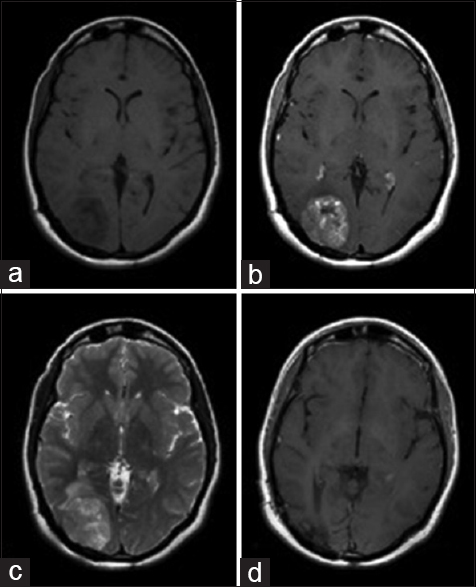
Atypical imaging features of posterior fossa's dermoid cyst: Case report and review of literature
Date of publication: 07-May-2018
Background:Intracranial dermoid cysts are uncommon lesions with characteristic imaging appearances. Symptomatic clinical presentation usually occurs in one of two ways: mass effect or rupture. Radiologically, dermoid cysts typically present as low density masses on computed tomography (CT) scan and are generally hyperintense on T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequences with variable signal on T2-weighted sequences.
The usefulness of indocyanine green during surgery for hypervascular posterior fossa tumors
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2018
Background:Cerebral hemangioblastomas are benign tumors with abundant blood flow that occur mainly in the posterior fossa. Tumor removal en bloc is important in surgical treatment because of the risk of bleeding; however, it is actually rather difficult in practice. Therefore, we propose a surgical strategy for visualizing hypervascular tumors of the posterior fossa utilizing indocyanine green (ICG).
Review of the neurological benefits of phytocannabinoids
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2018
Background:Numerous physical, psychological, and emotional benefits have been attributed to marijuana since its first reported use in 2,600 BC in a Chinese pharmacopoeia. The phytocannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD), and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the most studied extracts from cannabis sativa subspecies hemp and marijuana. CBD and Δ9-THC interact uniquely with the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Through direct and indirect actions, intrinsic endocannabinoids and plant-based phytocannabinoids modulate and influence a variety of physiological systems influenced by the ECS.
Simultaneous cerebrospinal fluid and hematologic metastases in a high-grade ependymoma
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2018
Background:Ependymomas are relatively uncommon tumors that constitute about 7% of all primary intracranial neoplasms. Among these, high-grade ependymomas are locally aggressive and recur most commonly at the primary site following resection. Ependymomas are also known to be the one glial neoplasm that tends to frequently metastasize inside and outside the central nervous system (CNS) that complicates workup and management. Metastasis due to surgical manipulation is common and neurosurgeons should be well-versed in the most effective methods to remove these tumors in order to avoid such metastases.
Utility of magnetic resonance cisternography with intrathecal gadolinium in detection of cerebrospinal fluid fistula associated with Mondini dysplasia in a patient with recurrent meningitis: Case report and literature review
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2018
Background:The intrathecal contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance cisternography (MRC) is a diagnostic method that has been proven effective in selected patients with various disorders of the cerebrospinal system, including the detection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks. The Mondini dysplasia is a malformation of the inner ear characterized by an incomplete cochlear development. The cerebrospinal fistula associated with Mondini dysplasia usually occurs in the first 5–10 years.
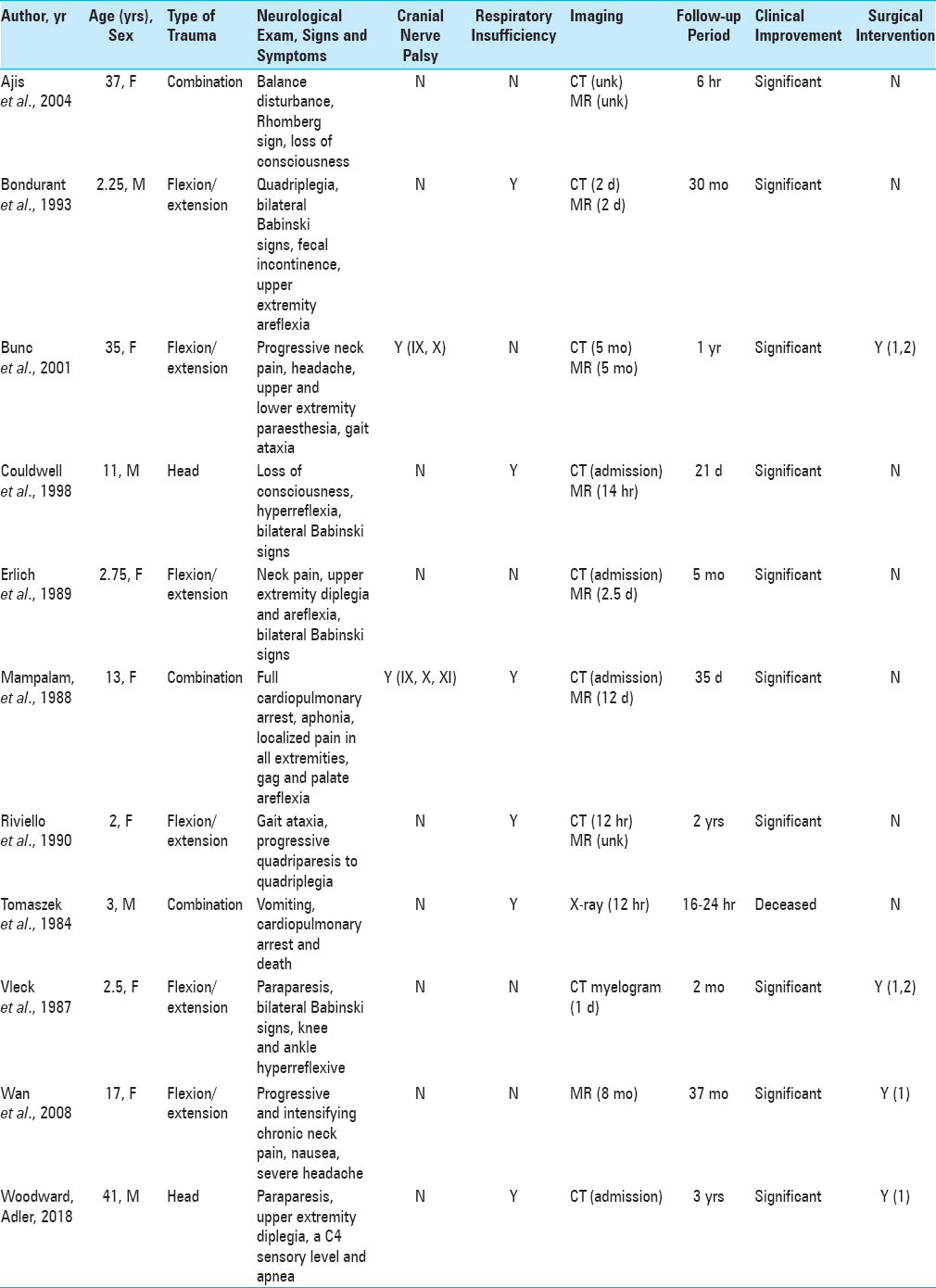
Chiari I malformation with acute neurological deficit after craniocervical trauma: Case report, imaging, and anatomic considerations
Date of publication: 23-Apr-2018
Background:In patients with Chiari I malformation (CMI), the occurrence of acute neurologic deficit after craniocervical trauma is rare. However, the pathologic potential of exacerbating anatomic overcrowding of the posterior fossa has immense clinical consequences and prompt recognition is essential.
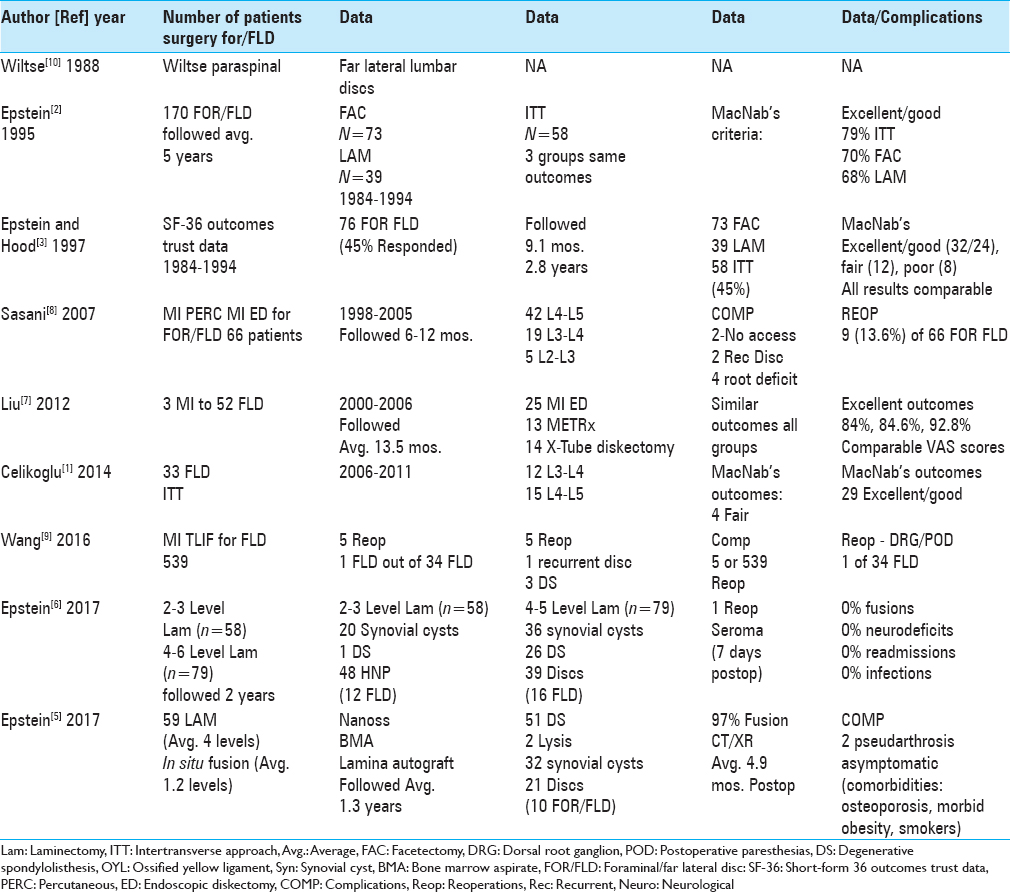
Case presentation and short perspective on management of foraminal/far lateral discs and stenosis
Date of publication: 23-Apr-2018
Background:The management of lumbar foraminal/far lateral discs (FOR/FLD) with stenosis remains controversial. Operative choices should be based on each patient's preoperative dynamic X-ray findings, magnetic resonance (MR), and computed tomography (CT) studies. Here we reviewed several options for decompression alone vs. decompression with fusion.