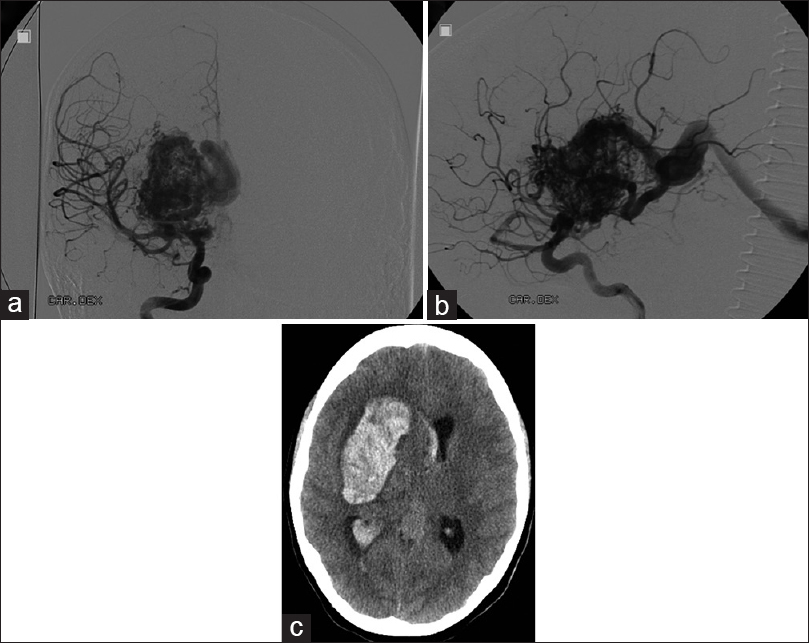
Total temporary occlusion of blood flow for several hours to treat a giant deep arteriovenous malformation: A series of multiple operations to save a young life
Date of publication: 26-Aug-2016
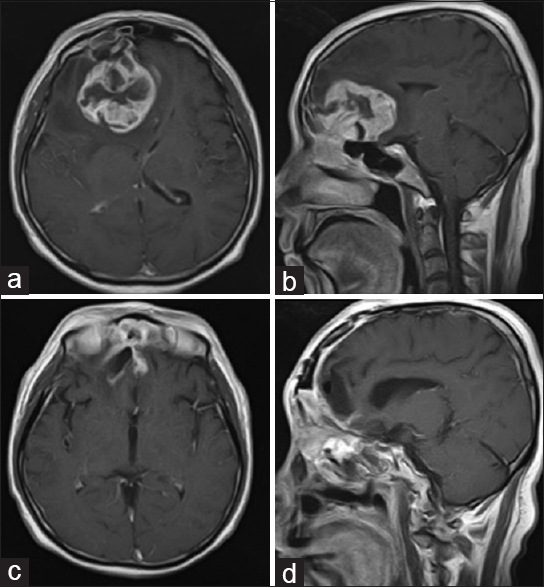
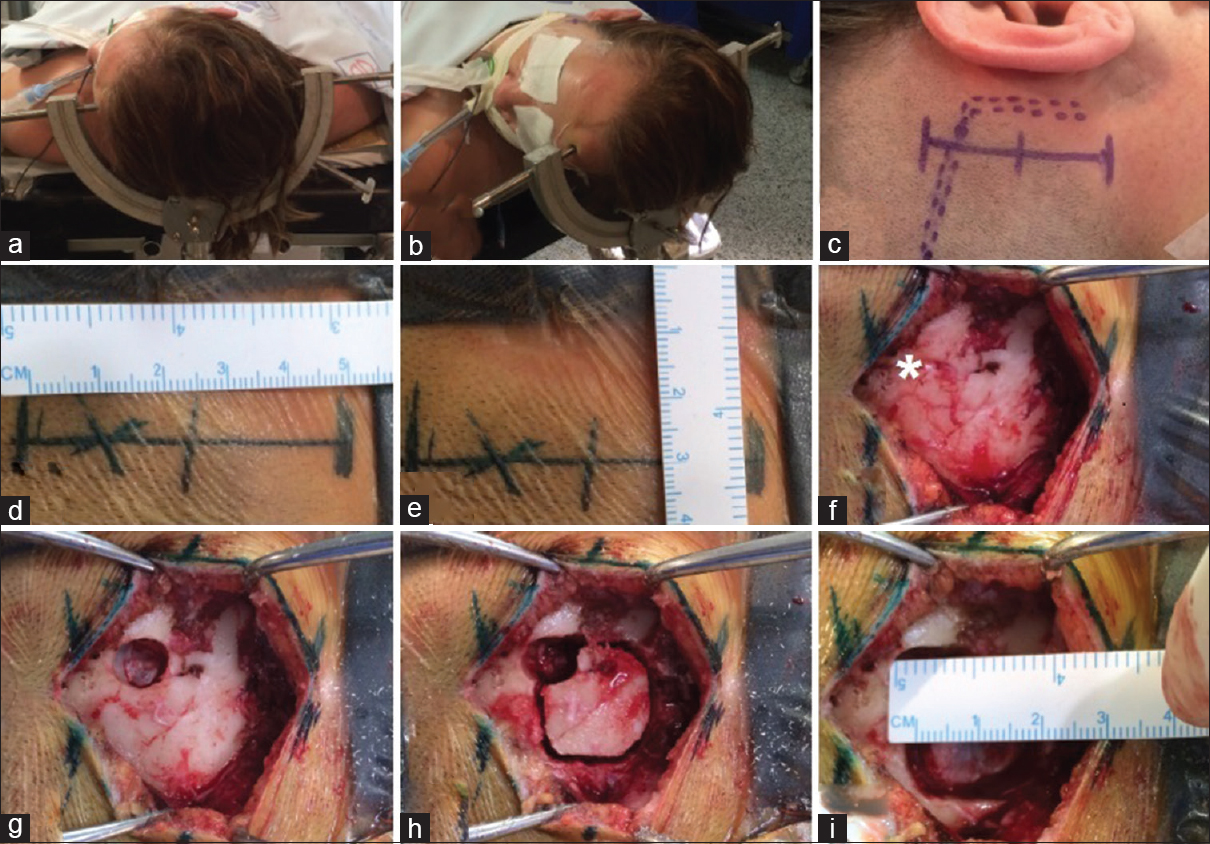
Background:The treatment of giant deep arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) remains challenging.
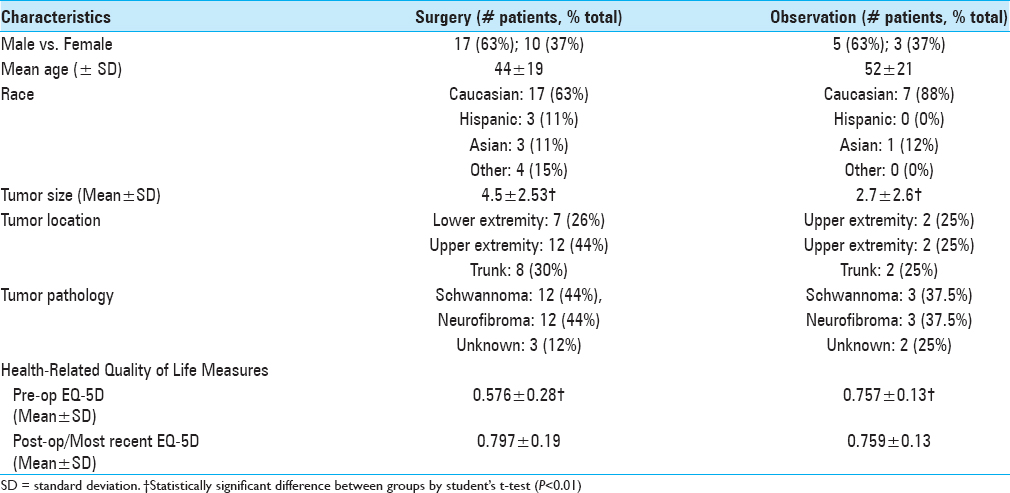
Developing an algorithm for cost-effective, clinically judicious management of peripheral nerve tumors
Date of publication: 26-Aug-2016
Abstract
Peripheral nerve tumors such as neurofibromas and schwannomas have become increasingly identified secondary to improved imaging modalities including magnetic resonance neurogram and ultrasound. Given that a majority of these peripheral nerve tumors are benign lesions, it becomes important to determine appropriate management of such asymptomatic masses. We propose a normal cost-effective management paradigm for asymptomatic peripheral nerve neurofibromas and schwannomas that has been paired with economic analyses. Specifically, our management paradigm identifies patients who would benefit from surgery for asymptomatic peripheral nerve tumors, while providing cost-effective recommendations regarding clinical exams and serial imaging for such patients.
Commentary: Metabolic syndrome and the hepatorenal reflex
Date of publication: 26-Aug-2016
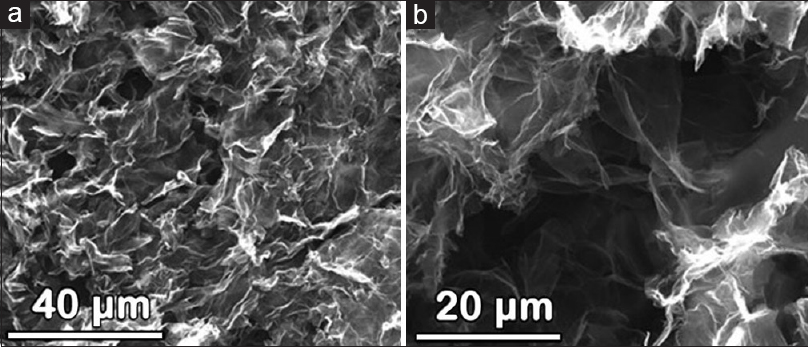
Biocompatibility of reduced graphene oxide nanoscaffolds following acute spinal cord injury in rats
Date of publication: 23-Aug-2016
Background:Graphene has unique electrical, physical, and chemical properties that may have great potential as a bioscaffold for neuronal regeneration after spinal cord injury. These nanoscaffolds have previously been shown to be biocompatible in vitro; in the present study, we wished to evaluate its biocompatibility in an in vivo spinal cord injury model.
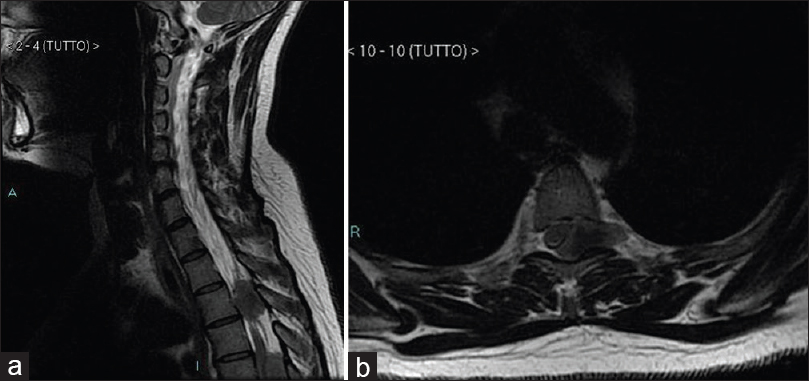
Dorsal extradural meningioma: Case report and literature review
Date of publication: 23-Aug-2016
Background:Extradural spinal mass lesions are most commonly metastatic tumors. Extradural meningiomas are rare, accounting for approximately 2.5–3.5% of spinal meningiomas; intraoperatively, they are easily mistaken for malignant tumors, especially in the en plaque variety, resulting in inadequate surgical treatment.
Olfactory neuroblastoma followed by emergency surgery for symptomatic intradural spinal metastasis: A case report
Date of publication: 23-Aug-2016
Background:Olfactory neuroblastoma (ONB) is a rare, aggressive tumor of the nasal cavity. It may invade the paranasal cavities and anterior skull base locally but may also metastasize to the cervical lymph nodes, lungs, or distant central nervous system.
Surgical variation of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: A technical note and anatomical study
Date of publication: 23-Aug-2016
Background:In this article, the authors described their experience in microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia.
How to compare clinical results of different neurosurgical centers? Is a classification of complications in neurosurgery necessary for this purpose?
Date of publication: 16-Aug-2016
Interventional magnetic resonance imaging-guided subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease: Patient selection
Date of publication: 02-Aug-2016
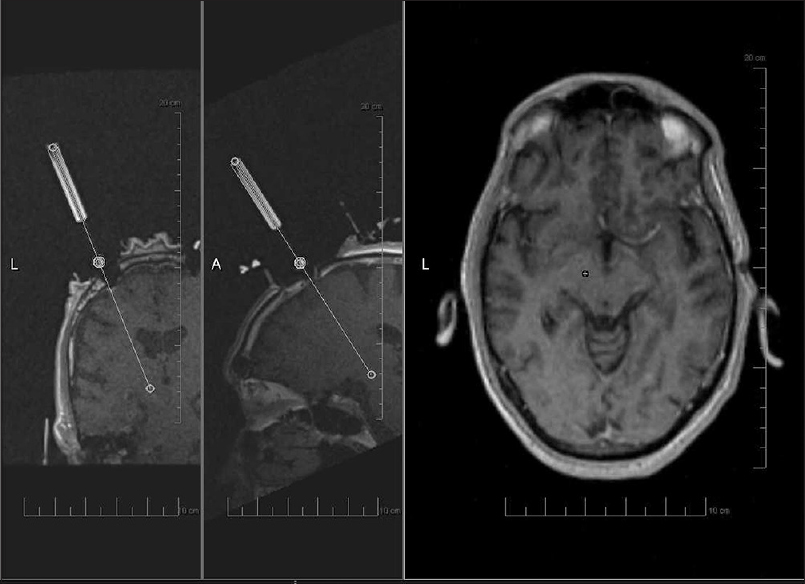
Background:Interventional magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI) guided deep brain stimulation (DBS) for Parkinson's disease (PD) has been shown to be effective. The costs of a dedicated intraoperative MRI may be prohibitive. The procedure can also be performed in a diagnostic scanner, however this presents challenges for utilization of time when the scanner is used both as a diagnostic and an interventional unit. This report outlines our novel methodology for patient selection for implantation in a diagnostic MR scanner, as an attempt to streamline the use of resources. A retrospective review of our outcomes is also presented.
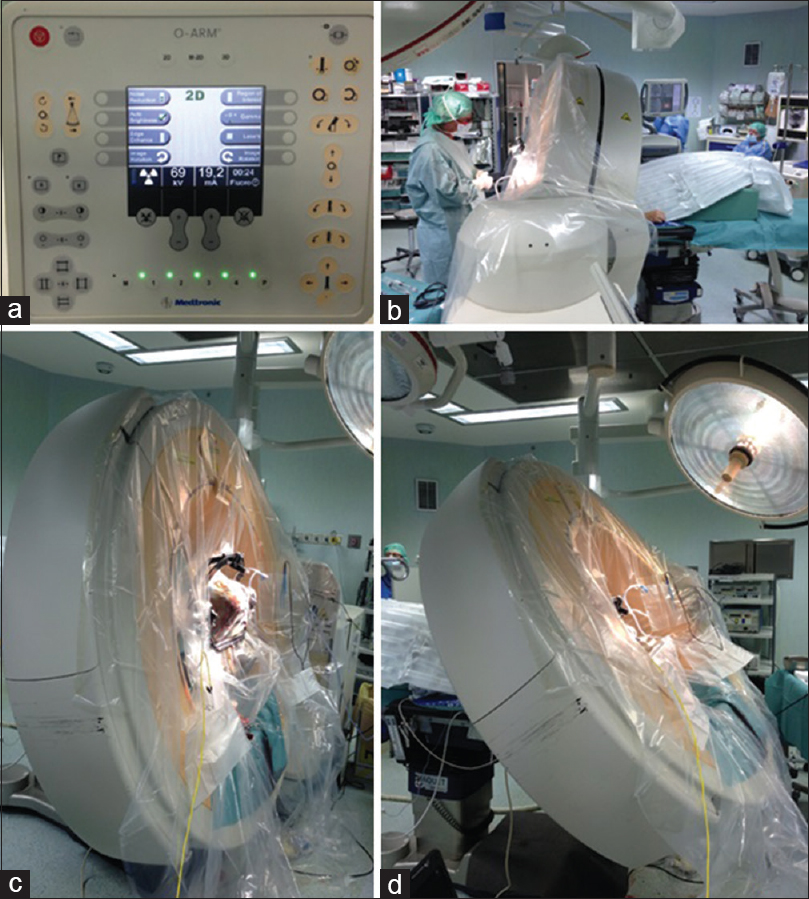
The pros and cons of intraoperative CT scan in evaluation of deep brain stimulation lead implantation: A retrospective study
Date of publication: 02-Aug-2016
Background:Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is an established therapy for movement disorders, such as Parkinson's disease (PD), dystonia, and tremor. The efficacy of DBS depends on the correct lead positioning. The commonly adopted postoperative radiological evaluation is performed with computed tomography (CT) scan and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).