Dorsal extradural meningioma: Case report and literature review
Date of publication: 23-Aug-2016
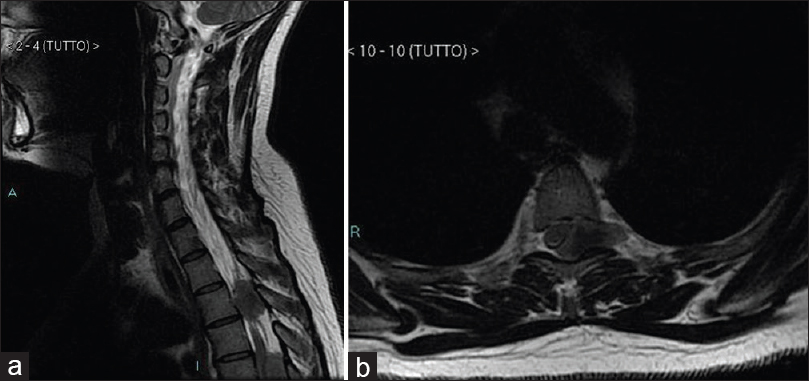
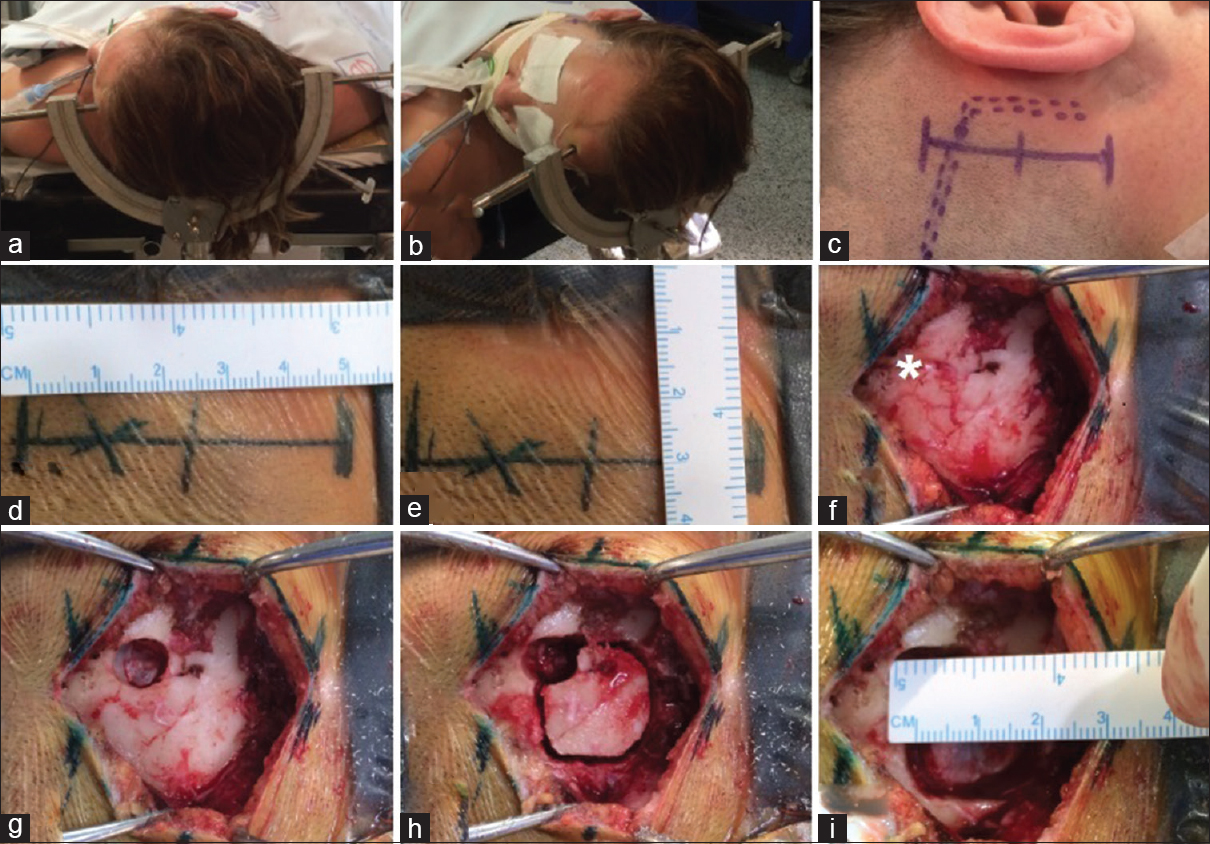
Background:Extradural spinal mass lesions are most commonly metastatic tumors. Extradural meningiomas are rare, accounting for approximately 2.5–3.5% of spinal meningiomas; intraoperatively, they are easily mistaken for malignant tumors, especially in the en plaque variety, resulting in inadequate surgical treatment.
Olfactory neuroblastoma followed by emergency surgery for symptomatic intradural spinal metastasis: A case report
Date of publication: 23-Aug-2016
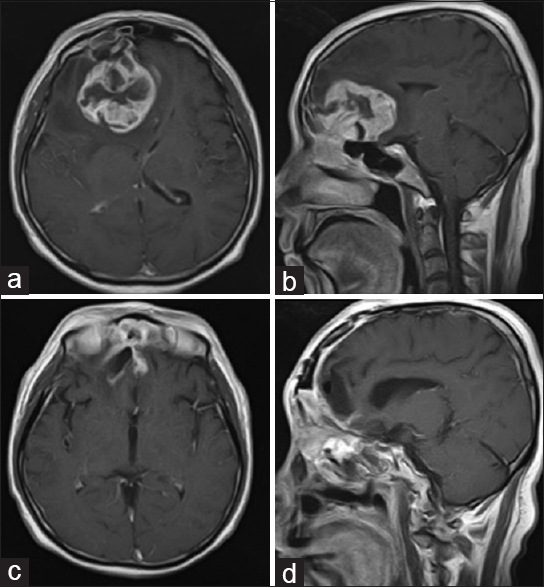
Background:Olfactory neuroblastoma (ONB) is a rare, aggressive tumor of the nasal cavity. It may invade the paranasal cavities and anterior skull base locally but may also metastasize to the cervical lymph nodes, lungs, or distant central nervous system.
Surgical variation of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: A technical note and anatomical study
Date of publication: 23-Aug-2016
Background:In this article, the authors described their experience in microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia.
How to compare clinical results of different neurosurgical centers? Is a classification of complications in neurosurgery necessary for this purpose?
Date of publication: 16-Aug-2016
Interventional magnetic resonance imaging-guided subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease: Patient selection
Date of publication: 02-Aug-2016
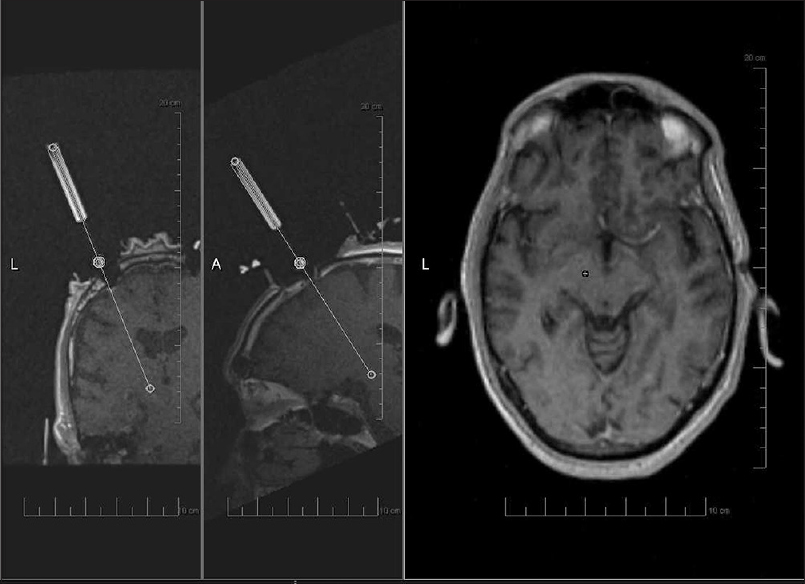
Background:Interventional magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI) guided deep brain stimulation (DBS) for Parkinson's disease (PD) has been shown to be effective. The costs of a dedicated intraoperative MRI may be prohibitive. The procedure can also be performed in a diagnostic scanner, however this presents challenges for utilization of time when the scanner is used both as a diagnostic and an interventional unit. This report outlines our novel methodology for patient selection for implantation in a diagnostic MR scanner, as an attempt to streamline the use of resources. A retrospective review of our outcomes is also presented.
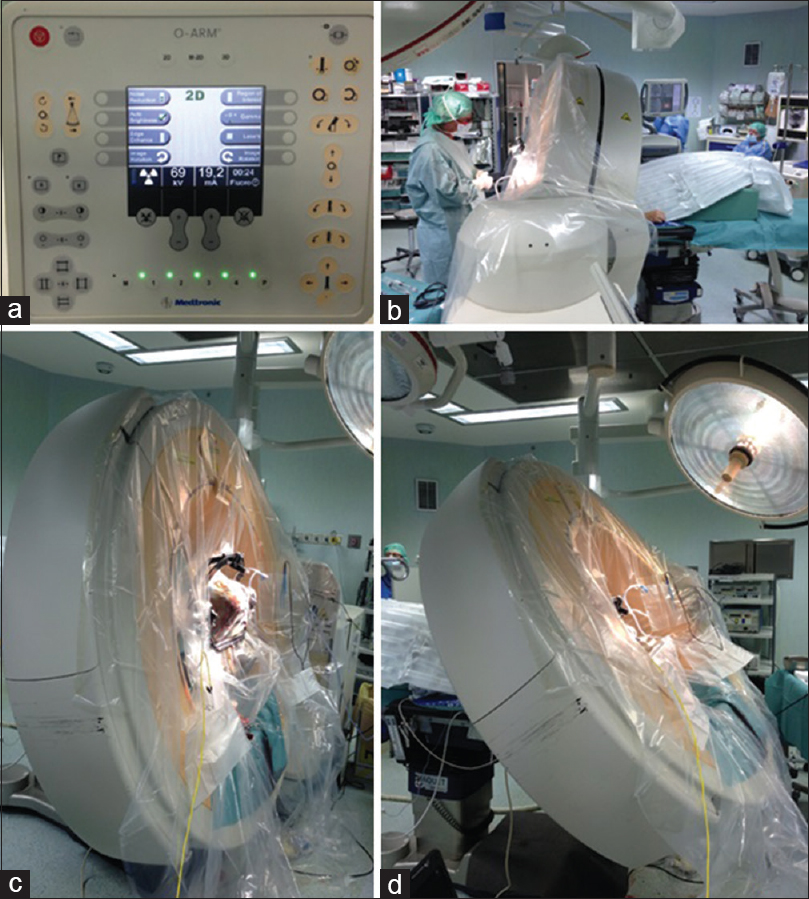
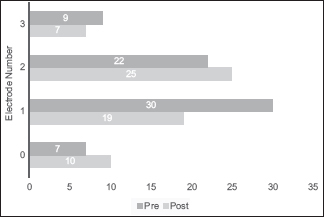
The pros and cons of intraoperative CT scan in evaluation of deep brain stimulation lead implantation: A retrospective study
Date of publication: 02-Aug-2016
Background:Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is an established therapy for movement disorders, such as Parkinson's disease (PD), dystonia, and tremor. The efficacy of DBS depends on the correct lead positioning. The commonly adopted postoperative radiological evaluation is performed with computed tomography (CT) scan and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Rapid assessment of gait and speech after subthalamic deep brain stimulation
Date of publication: 02-Aug-2016
Background:Describe a rapid assessment for patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease (PD) and deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus reporting worsening speech and/or gait problems.
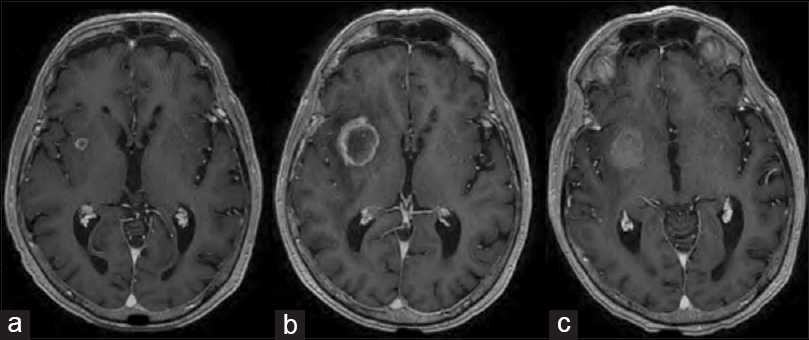
Bevacizumab for the treatment of post-stereotactic radiosurgery adverse radiation effect
Date of publication: 02-Aug-2016
Background:Adverse radiation effect (ARE) is one of the complications of stereotactic radiosurgery. Its treatment with conventional medications, such as corticosteroids, vitamin E, and pentoxifylline carries a high risk of failure, with up to 20% of lesions refractory to such medications. In addition, deep lesions and those occurring in patients with significant medical comorbidities may not be suitable for surgical resection. Bevacizumab is an antiangiogenic monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor, a known mediator of cerebral edema. It can be used to successfully treat ARE.
Intrathecal baclofen therapy for spasticity: A compliance-based study to indicate effectiveness
Date of publication: 02-Aug-2016
Background:Intrathecal baclofen (ITB) therapy using a programmable battery-based pump is a well-recognized option in the treatment of patients with refractory spasticity. Improvements in clinical scale scores for muscle spasticity among this heterogeneous group of patients may not reflect the functional benefits of this therapeutic option. The aim of our study is to report the efficacy of ITB therapy by setting the patient's compliance at the 2-year follow-up after pump implantation as an indicator of treatment efficacy, as appreciated by the patients or their caregivers.
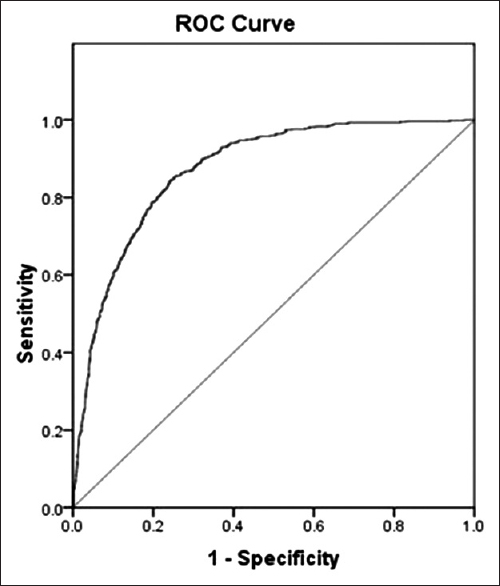
Clinical outcome prediction in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage – Alterations in brain–body interface
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2016
Background:Brain–body associations are essential in influencing outcome in patients with ruptured brain aneurysms. Thus far, there is scarce literature on such important relationships.