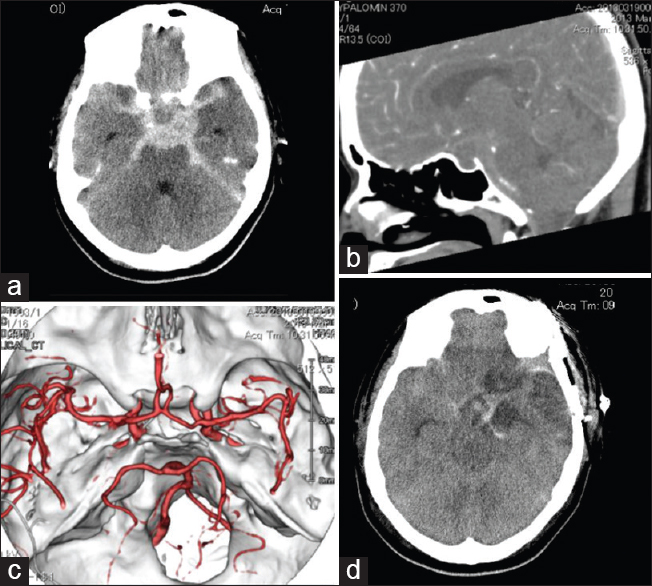
Unruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysm presenting as depression: A case report and review of literature
Date of publication: 01-Aug-2016
Background:Intracranial aneurysms most commonly present following rupture causing subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mental disorders are common among patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms and in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage survivors. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no published report of unruptured intracranial aneurysm presenting as a mental disorder.
Brain abscess caused by Nocardia asiatica
Date of publication: 18-Jul-2016
Background:Nocardia infection of the central nervous system leading to brain abscess is a rare condition but has a high mortality rate. Among the species of Nocardia, only three cases of brain abscess due to Nocardia asiatica infection have been reported.
Neurofibromatosis type 1 and Chiari type 1 malformation: A case report and literature review of a rare association
Date of publication: 07-Jul-2016
Background:The association between neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-I) and Chiari I malformation (CMI) is rare, and not many studies are reported in the literature. Performing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in patients with NF-1 is essential because several cases of Chiari type I are completely asymptomatic. We emphasize the need for inclusion of Chiari I as diagnosis in association with NF-1.
Dural repair using autologous fat: Our experience and review of the literature
Date of publication: 07-Jul-2016
Background:Various materials have been proposed to obliterate dead spaces and to reconstruct dural defects during a neurosurgical approach. This study describes our technique of using the abdominal autologous fat graft and evaluates the complications and characteristics related to the use of this tissue during cranial procedures.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage caused by an undifferentiated sarcoma of the sellar region
Date of publication: 07-Jul-2016
Background:It is rare for patients with pituitary apoplexy to exhibit concomitant subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). Only a handful of patients with pituitary apoplexy have developed such hemorrhagic complications, and histopathological examination revealed pituitary adenoma as the cause of SAH.
Operative surgical nuances of modified extradural temporopolar approach with mini-peeling of dura propria based on cadaveric anatomical study of lateral cavernous structures
Date of publication: 07-Jul-2016
Background:Extradural temporopolar approach (ETA) has been modified as less invasive manner and named as trans-superior orbital fissure (SOF) approach with mini-peeling technique. The present study discusses the operative nuances of this modified technique on the basis of cadaveric study of lateral cavernous structures.
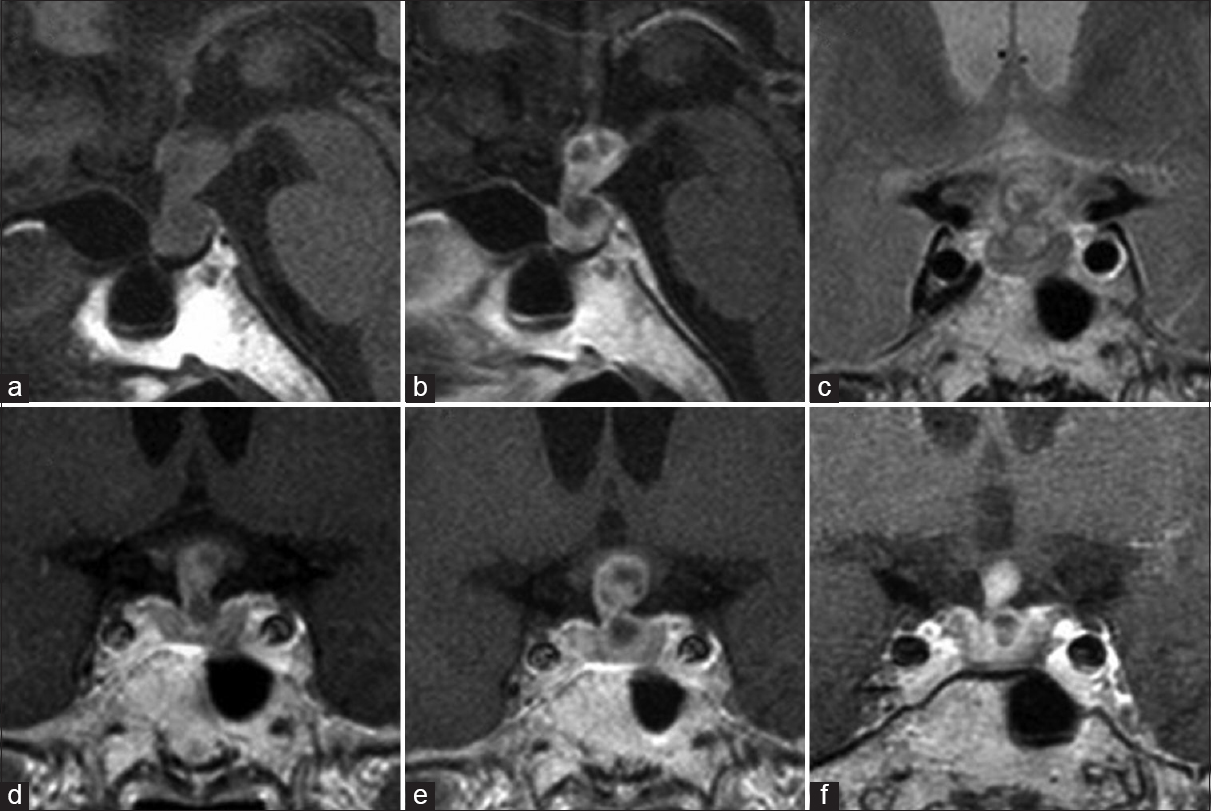
Xanthomatous hypophysitis associated with autoimmune disease in an elderly patient: A rare case report
Date of publication: 07-Jul-2016
Background:Xanthomatous hypophysitis (XH) is an extremely rare form of primary hypophysitis characterized by infiltration of the pituitary gland by mixed types of inflammatory cells, including foamy cells, plasma cells, and small mature lymphocytes. XH manifests as varying degrees of hypopituitarism. Although several previous reports have denied a possible contribution of autoimmune mechanism, the exact pathogenesis of XH remains unclear.
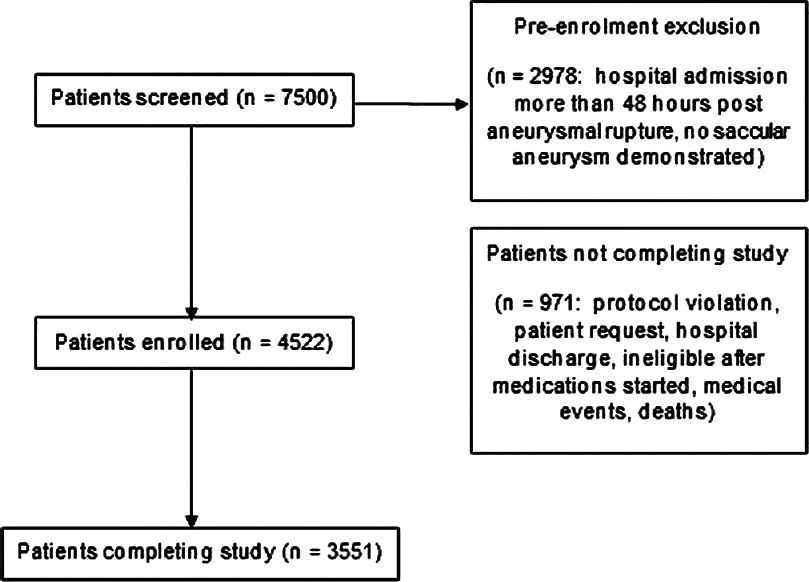
Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage prognostic decision-making algorithm using classification and regression tree analysis
Date of publication: 07-Jul-2016
Background:Classification and regression tree analysis involves the creation of a decision tree by recursive partitioning of a dataset into more homogeneous subgroups. Thus far, there is scarce literature on using this technique to create clinical prediction tools for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).
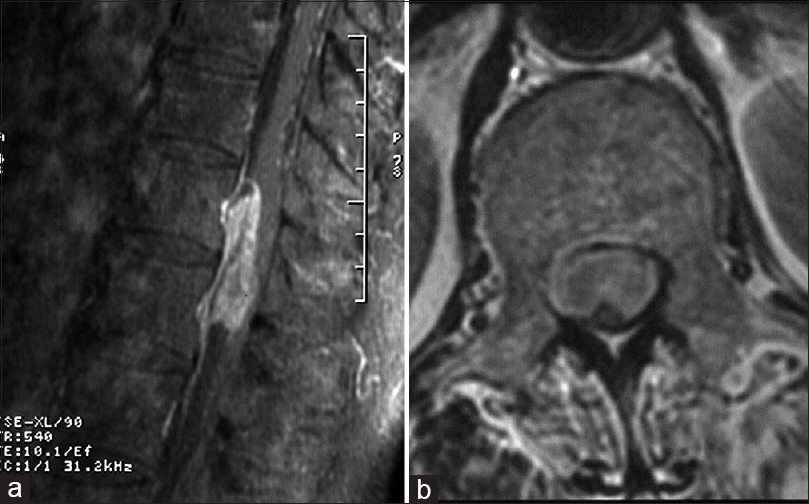
Multicentric spinal cord and brain glioblastoma without previous craniotomy
Date of publication: 07-Jul-2016
Background:Glioblastoma multiforme (GBS) is a highly malignant glioma that rarely presents as an infratentorial tumor. Multicentric gliomas lesions are widely separated in site and/or time and its incidence has been reported between 0.15 and 10%. Multicentric gliomas involving supratentorial and infratentorial region are even more rare. In most cases, infratentorial disease is seen after surgical manipulation or radiation therapy and is usually located in the cerebellum or cervical region.
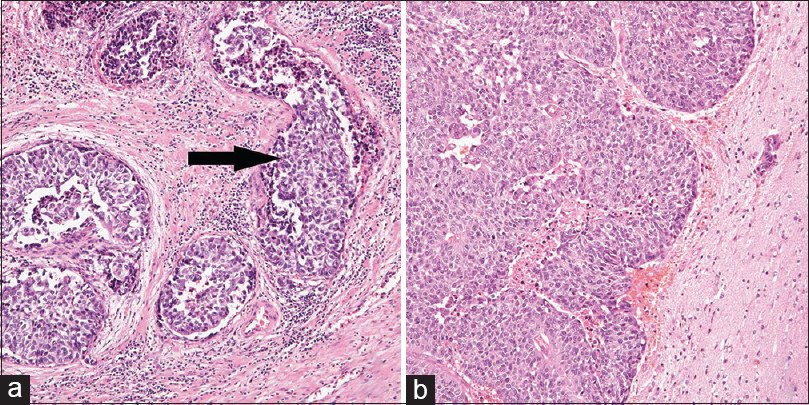
Metastatic brain tumor from urothelial carcinoma of the prostatic urethra
Date of publication: 07-Jul-2016
Background:Urothelial carcinoma occurs in the bladder, upper urinary tract, and lower urinary tract, including prostatic urethra. A majority of the reported cases of intracranial metastasis from urothelial carcinoma originates from the bladder and upper urinary tract. Brain metastasis from urothelial carcinoma of the prostatic urethra has not yet been reported in the literature.