Combined simultaneous endoscopic endonasal and microscopic transventricular surgery using a port retractor system for giant pituitary adenoma: A technical case report
Date of publication: 08-Mar-2021
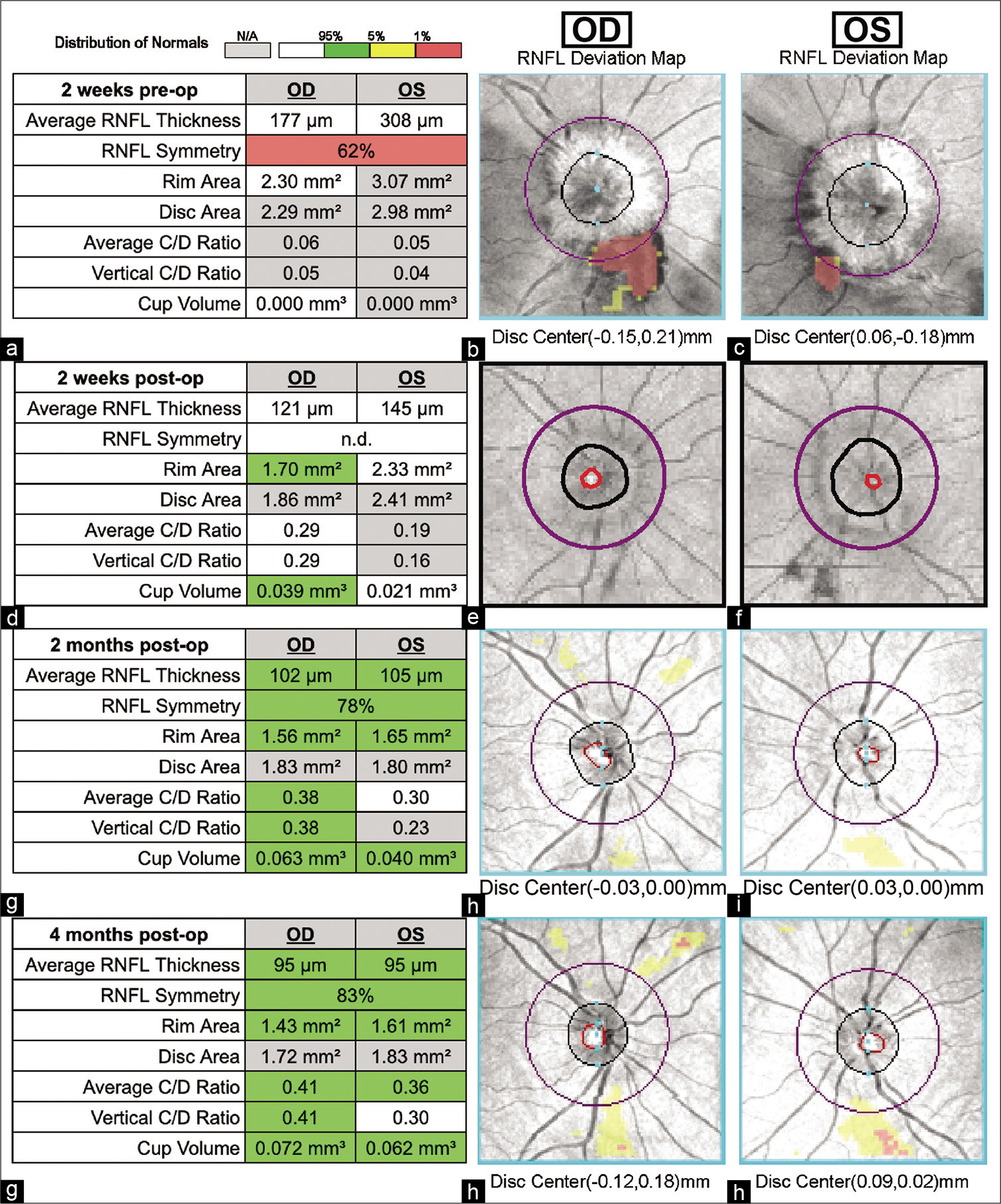
Background: We report a case of a giant pituitary adenoma with marked extension into the third ventricle that was successfully removed using combined simultaneous endoscopic endonasal surgery (EES) and microscopic transventricular port surgery.
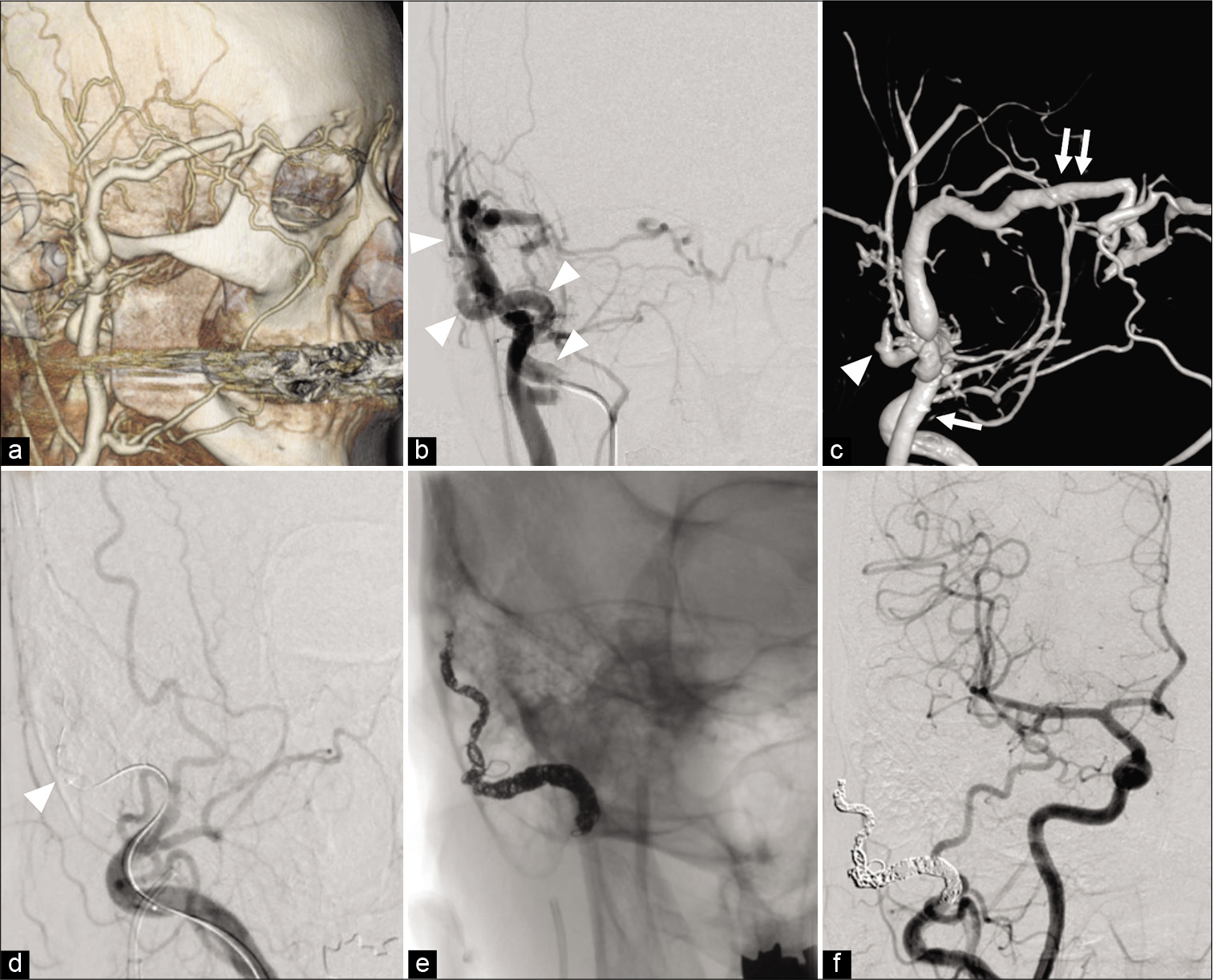
The usefulness of temporary balloon occlusion during transarterial embolization for scalp arteriovenous fistula
Date of publication: 08-Mar-2021
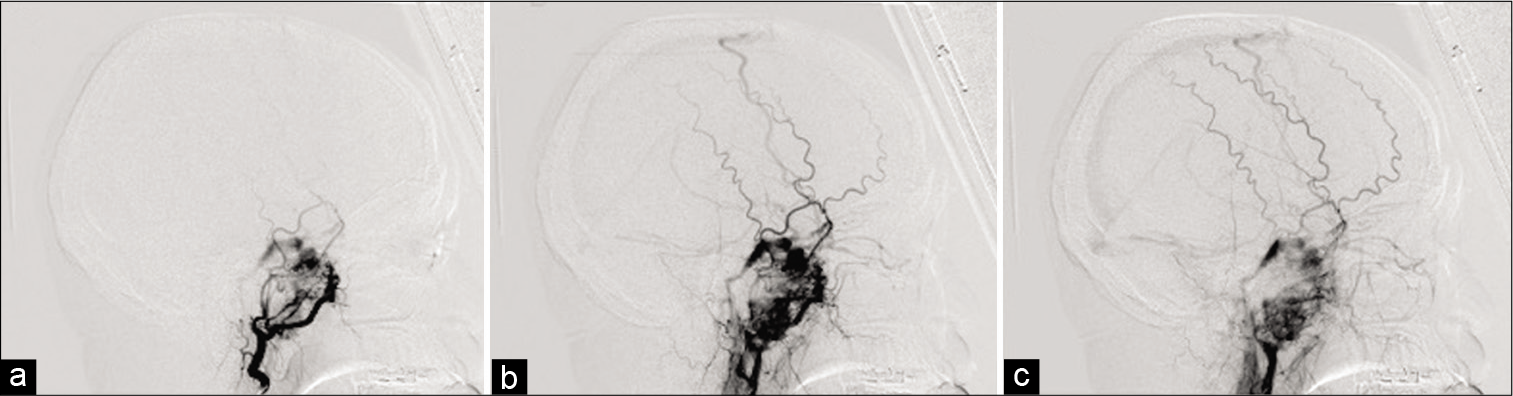
Background: We present two cases of scalp arteriovenous fistula (sAVF) treated by transarterial embolization with the aid of a temporary balloon occlusion (TBO) to detect precise vasculature.
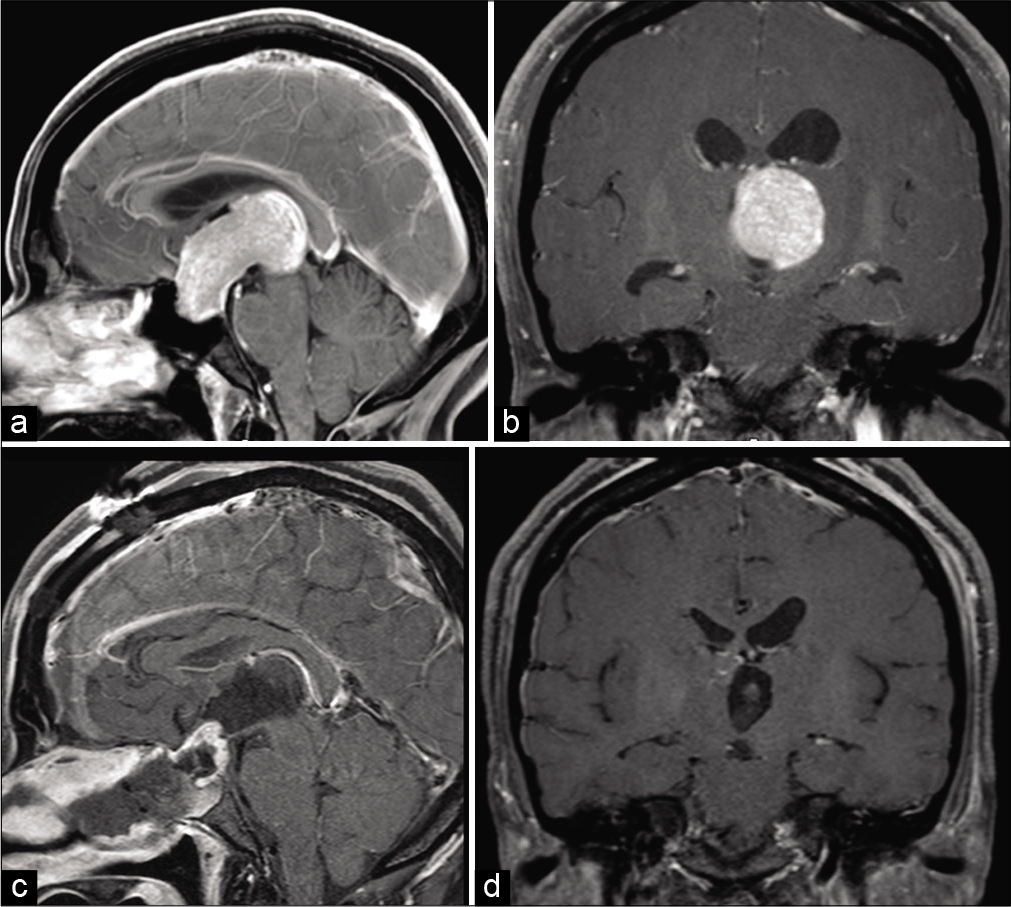
A rare diagnosis of an extraventricular neurocytoma
Date of publication: 08-Mar-2021
Background: Extraventricular neurocytoma (EVN) is an extremely rare neoplasm of the central nervous system. As reported, it arises in a variety of locations, but mainly within the cerebral hemispheres. Despite its histological similarity with central neurocytoma (CN), EVN occurs outside the ventricular system and, in 2007, was recognized by the World Health Organization as a separate entity.
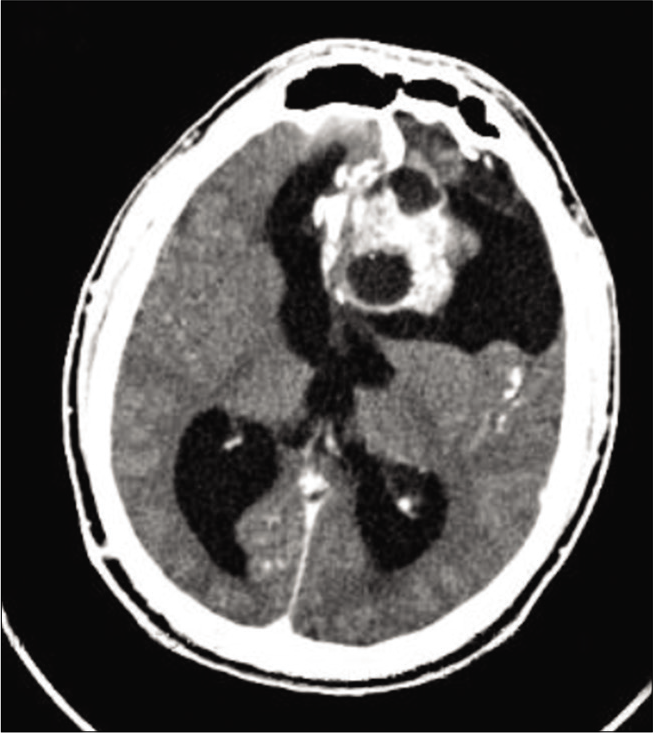
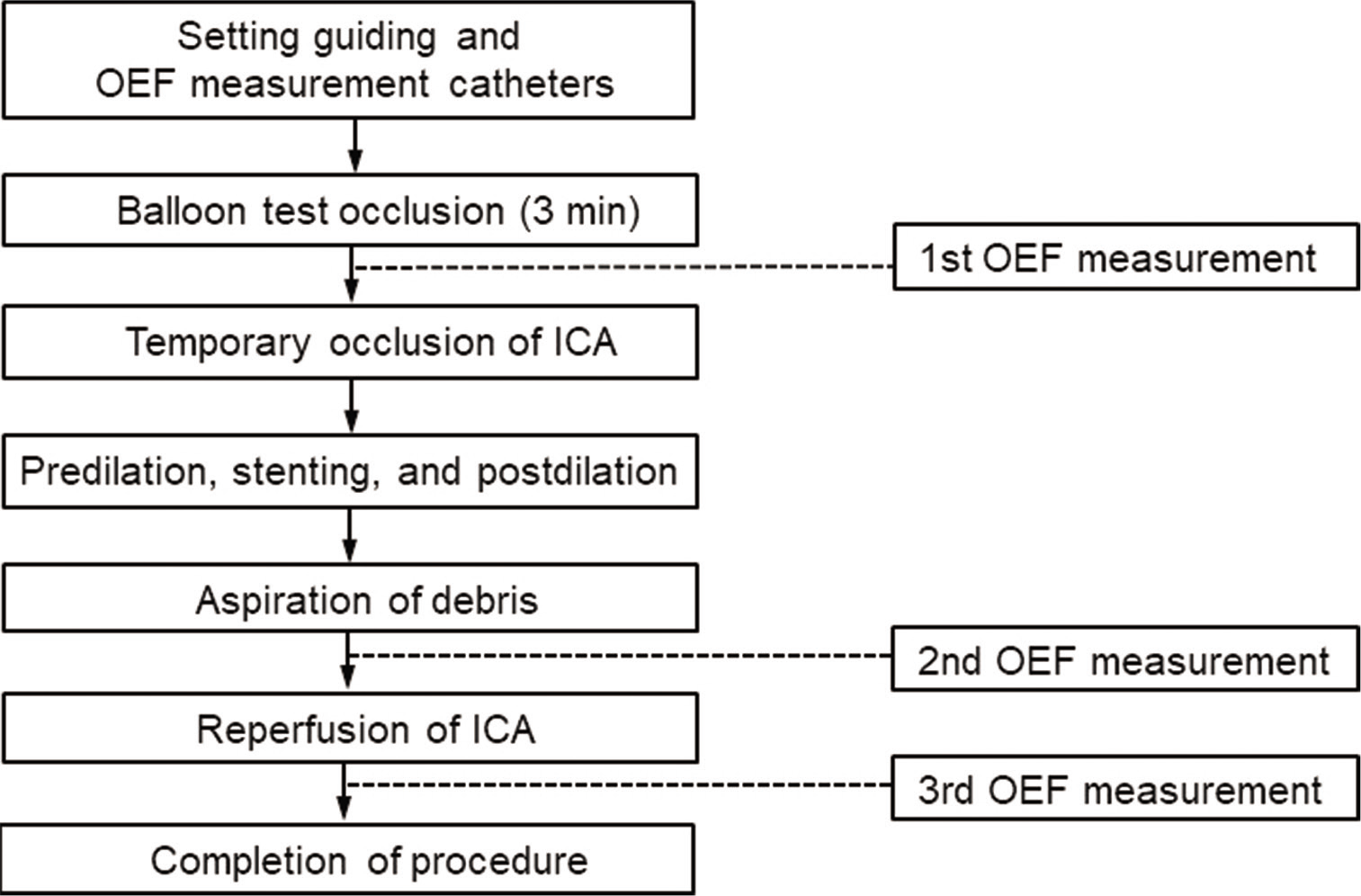
Analysis of postprocedural microembolic infarctions and global oxygen extraction fraction during balloon-protected carotid artery stenting: Preliminary study
Date of publication: 08-Mar-2021
Background: Atherosclerotic carotid stenosis with impaired cerebral perfusion is a risk factor for cerebral ischemia. In major carotid stenoocclusive diseases, increased oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) is associated with ischemic stroke. Balloon-protected carotid artery stenting (CAS) is valuable for high-grade carotid stenosis. However, while balloon-protected CAS can effectively reduce the occurrence of ischemic complications by blocking carotid flow, cerebral hypoperfusion may result in simultaneous cerebral ischemia. We sought to evaluate whether increased OEF during balloon-protected CAS can predict postprocedural microembolic infarction (MI).
Successful management of an intraluminal superior sagittal sinus meningioma causing elevated intracranial pressure using gamma knife radiosurgery in subacute setting: A case report
Date of publication: 08-Mar-2021
Background: Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery (GKRS) facilitates precisely focused radiation to an intracranial target while minimizing substantial off-target radiation in the surrounding normal tissue. Meningiomas attached to or invading the superior sagittal sinus may result in sinus occlusion and are often impossible to completely resect safely. The authors describe successful management of a patient with a meningioma located completely inside the posterior aspect of the superior sagittal sinus.
Four-dimensional digital subtraction angiography for exploration of intraosseous arteriovenous fistula in the sphenoid bone
Date of publication: 02-Mar-2021
Background: Intraosseous arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is a rare clinical entity that typically presents with symptoms from their effect on surrounding structures. Here, we report a case of intraosseous AVF in the sphenoid bone that presented with bilateral abducens palsy.
A case with bilateral thalamic infarction manifesting mutism – Cerebral blood flow and neural fibers evaluation
Date of publication: 02-Mar-2021
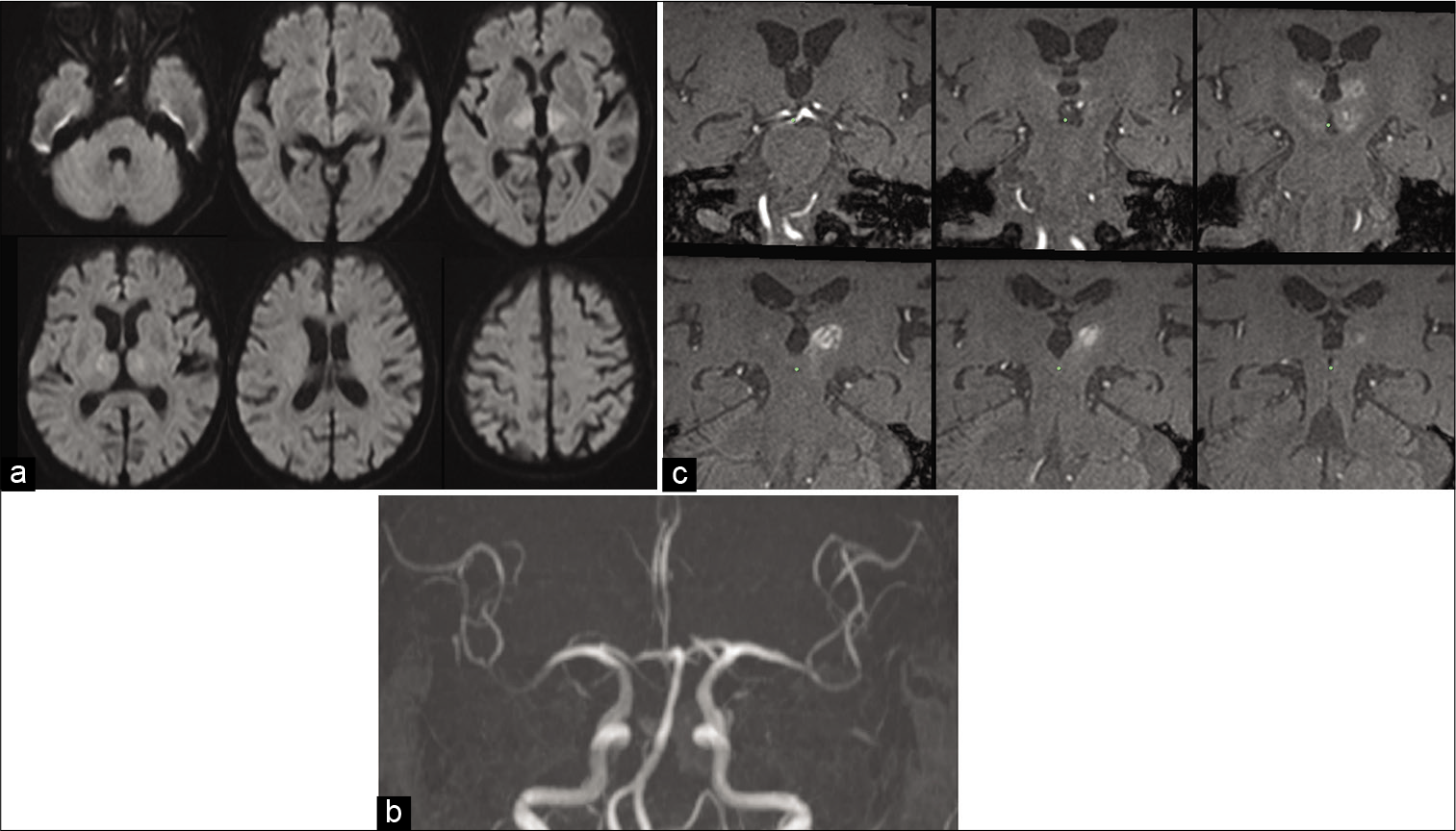
Background: Acute bilateral thalamic infarction is rare, and occlusion of the artery of percheron (AOP) may be one of its reasons. AOP occlusion results in an acute disturbance of consciousness, but mutism due to AOP occlusion is rare. We described a mutism patient with bilateral thalamic infarction presumably due to AOP occlusion. We also performed cerebral blood flow (CBF) evaluation by N-isopropyl-p-[123I]-iodoamphetamine single-photon emission computed tomography (123I-IMP-SPECT) as well as neural fiber evaluation by diffusion tensor tractography, discussing the mechanism of mutism.
Prognosis of spinal infections managed by minimal debridement: A case series in two tertiary centers
Date of publication: 02-Mar-2021
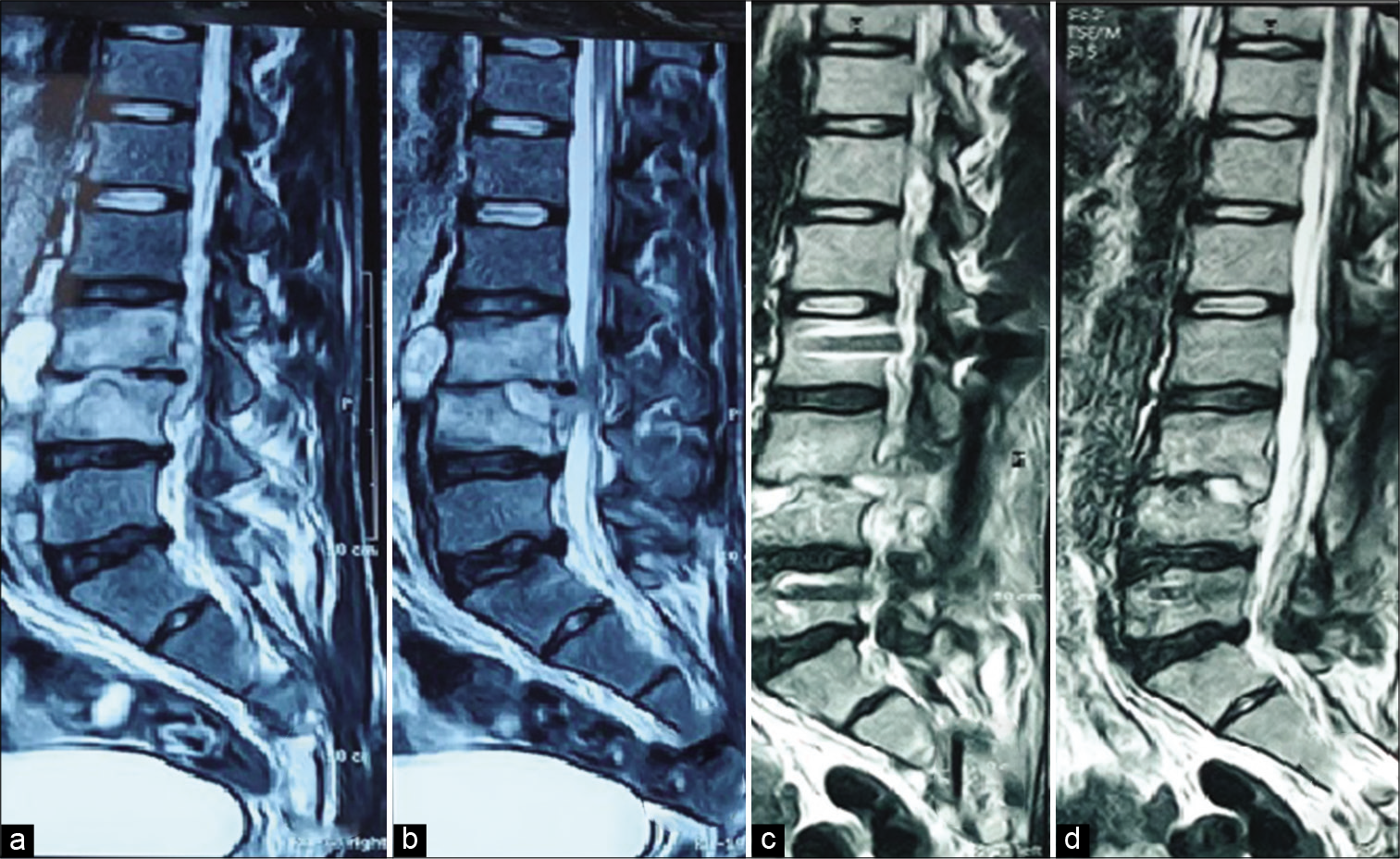
Background: Spinal infections can be challenging in their management and include spondylitis, epidural abscess, and spondylodiscitis. Usual treatment is conservative through antimicrobials or surgery to decompress neural tissue, debride all infected tissues, and fix if needed. We propose the concept of surgery without formal debridement aiming at neural protection.
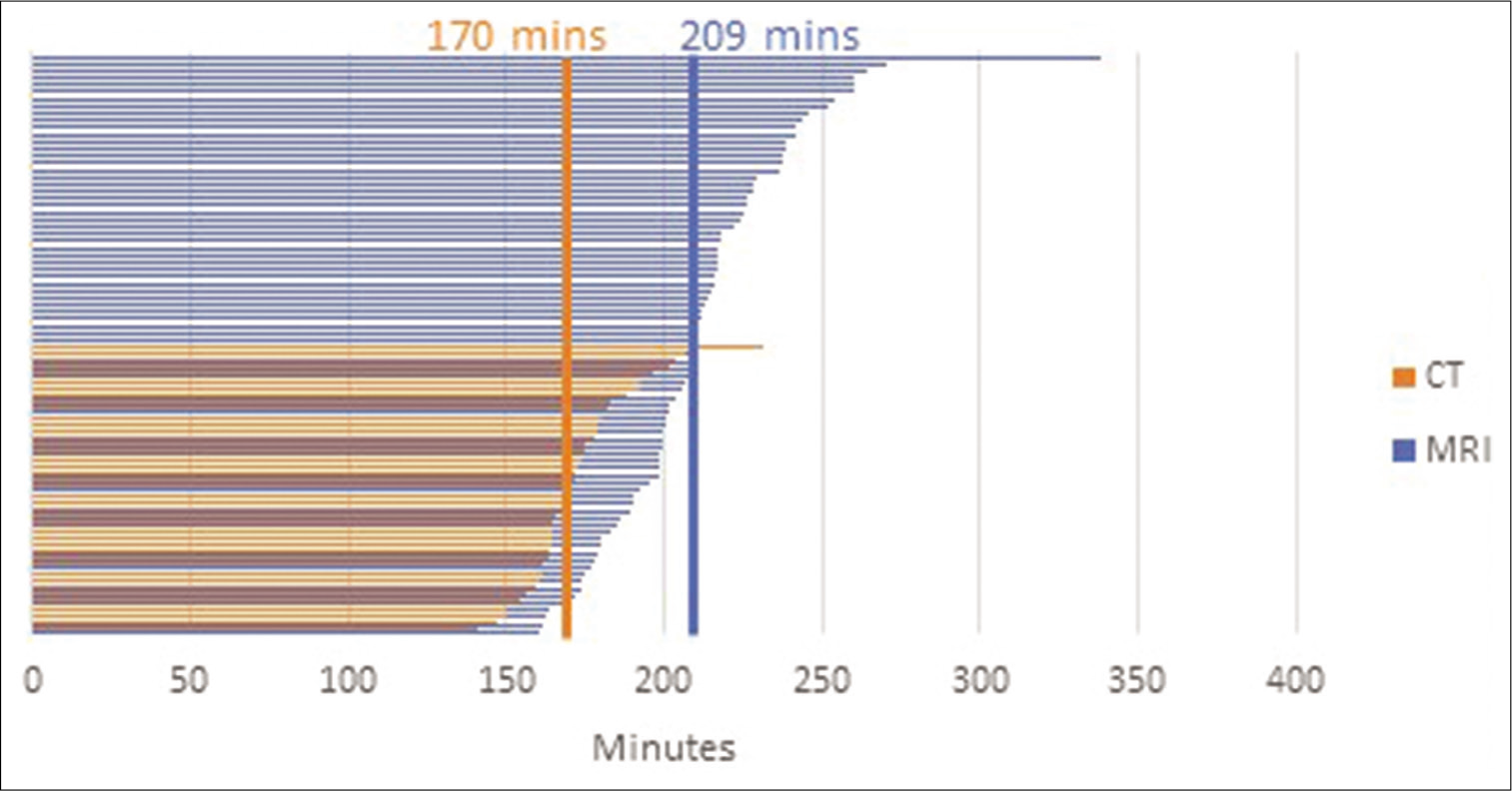
Influence of stereotactic imaging on operative time in deep brain stimulation
Date of publication: 02-Mar-2021
Background: Various techniques are used across institutions for implantation of deep brain stimulation (DBS) leads. The most used techniques for each step include preoperative MRI fused to in-frame CT, intraoperative fluoroscopy, and postoperative CT, but postimplantation MRI also is used, as it was at our center. We present the quality assurance study performed at our institution after a change from postimplantation MRI performed across the hospital to postimplantation in room CT.
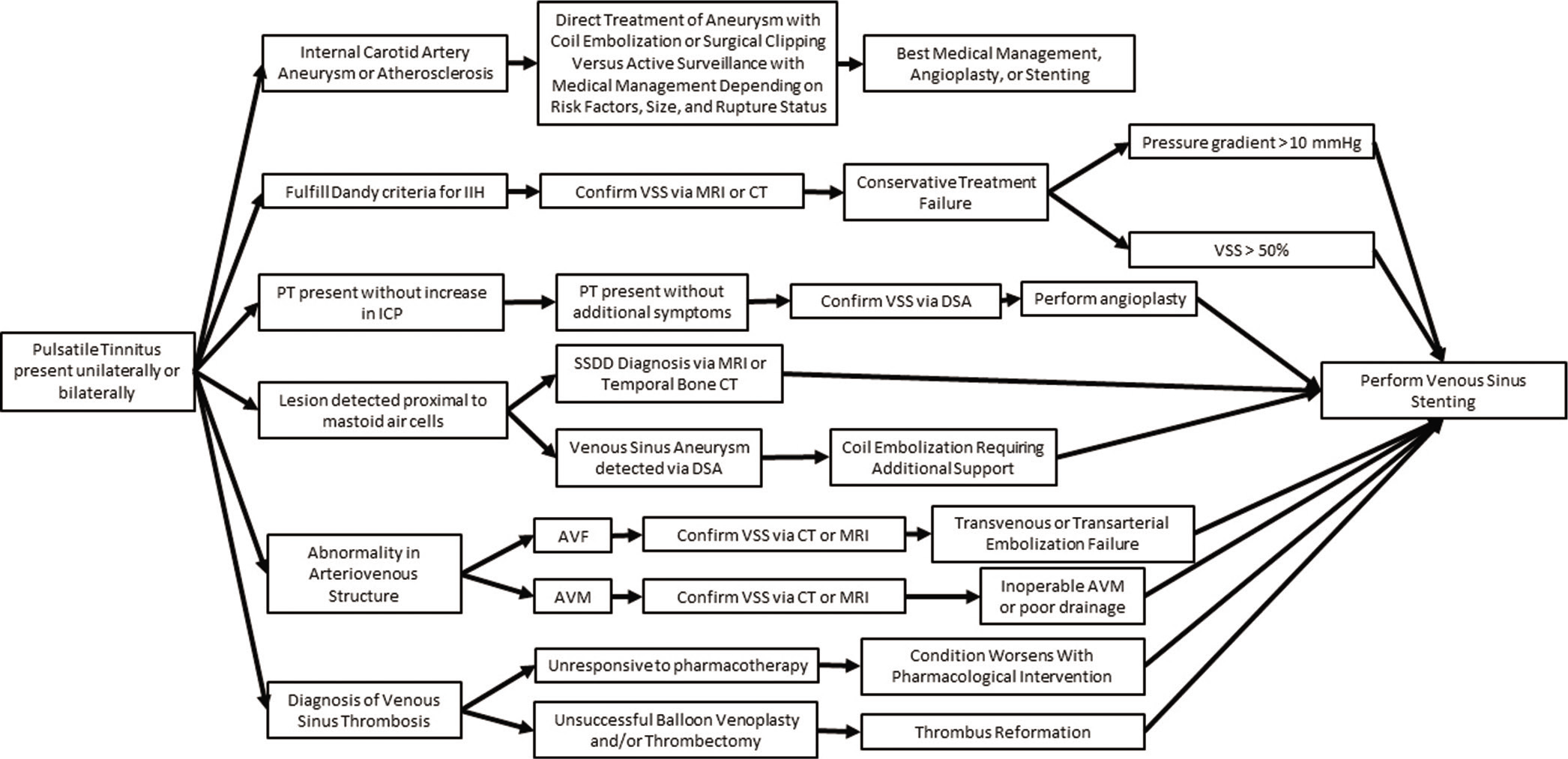
Venous sinus stenting for intractable pulsatile tinnitus: A review of indications and outcomes
Date of publication: 02-Mar-2021
Background: Pulsatile tinnitus presents as a unique variation of tinnitus in which a conscious perception of the heartbeat is localized to the ears in either unilateral or bilateral fashion. The sensation is typically caused by an increase in turbulent blood flow in the affected ear, in most cases, due to a structural abnormality of the venous sinuses – the most common of which being stenosis. Herein, we discuss the etiology of pulsatile tinnitus followed by indications for treatment of various pathologies which have been successfully treated with venous sinus stenting and have led to resolution of auditory symptoms.