Mesenchymal stem cells in Parkinson’s disease: Motor and nonmotor symptoms in the early posttransplant period
Date of publication: 11-Nov-2020
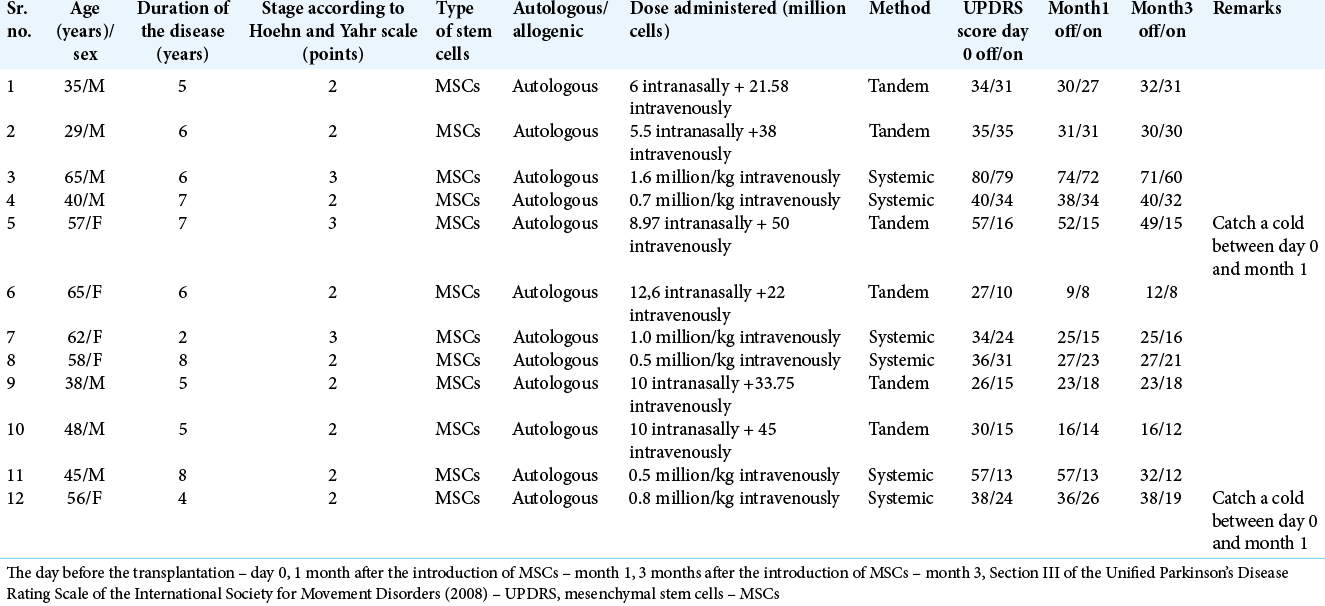
Background: Treatment of patients with Parkinson disease (PD) using autologous mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) is a promising method to influence the pathogenesis of the disease. The aim of this study was to assess the immediate results of the introduction of MSCs on the effectiveness of motor and nonmotor symptoms in patients with PD.
Hemorrhagic complications after decompressive craniectomy
Date of publication: 11-Nov-2020
Background: Decompressive craniectomy (DC) is the preferred surgical management option for lowering refractory intracranial pressure in cases of traumatic brain injury (TBI). A number of randomized controlled trials have demonstrated decreased mortality but increased morbidity following DC for TBI patients. Here, we reviewed the frequency of postoperative hemorrhagic complications following DC correlating with poor outcomes.
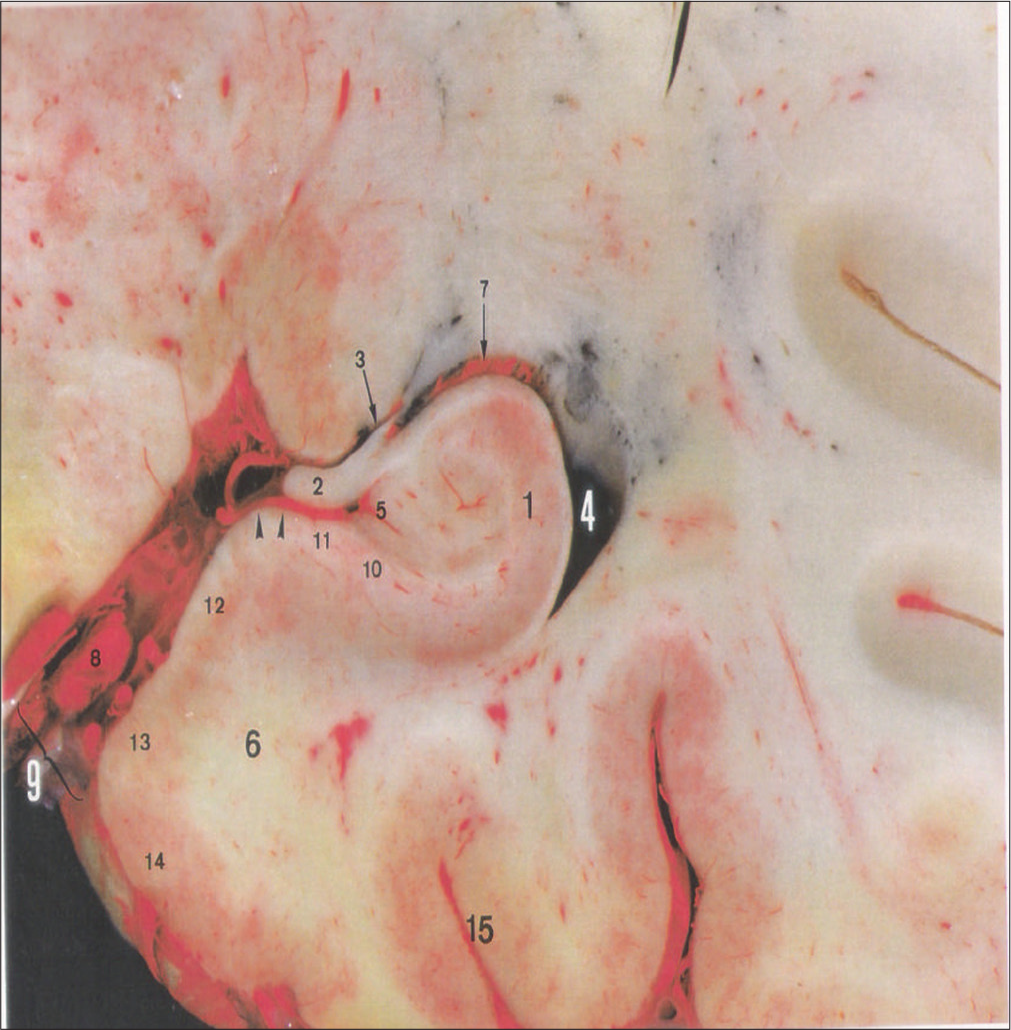
Hippocampal vascularization: Proposal for a new classification
Date of publication: 06-Nov-2020
Background: Anatomy of the hippocampal arterial supply is key to successful surgeries in this area. The goal of the current study is to present the results we obtained from our microsurgical dissections of the temporal lobe and to propose a new classification for the hippocampal arteries (HAs).
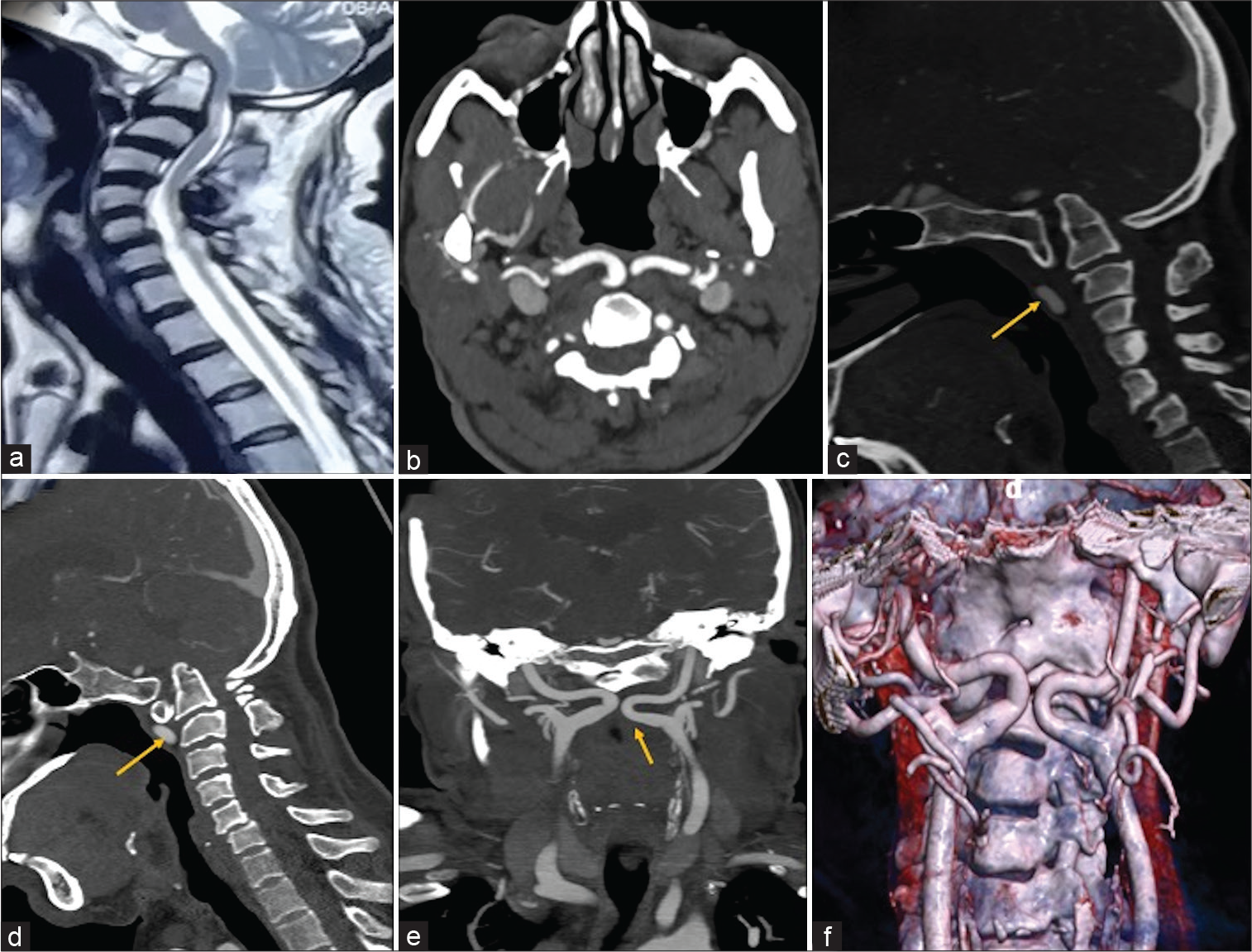
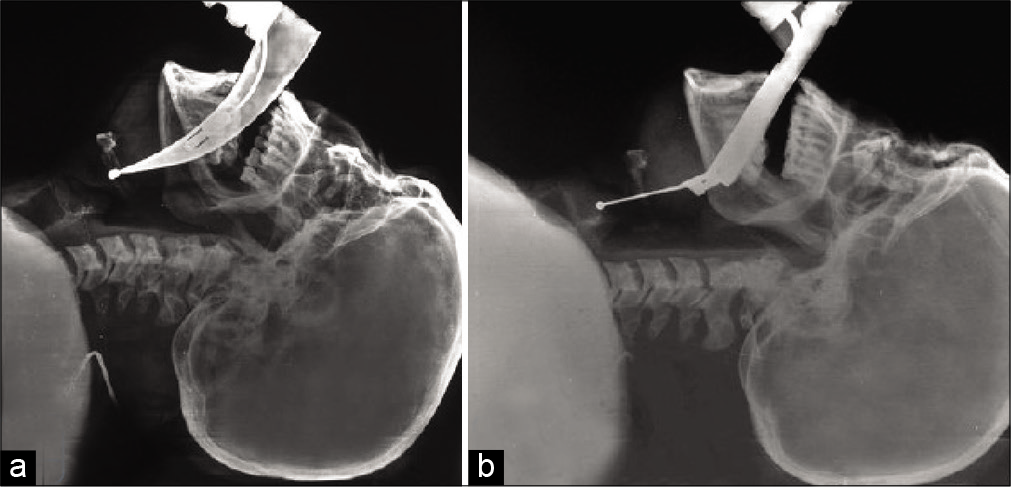
Craniovertebral junction anomaly with kissing carotids
Date of publication: 06-Nov-2020
Background: “Kissing carotids” typically involves the lower C4-C6 retropharyngeal space. Here, we describe a case of “kissing carotids” observed at the C1-C2 level in conjunction with basilar invagination (BI).
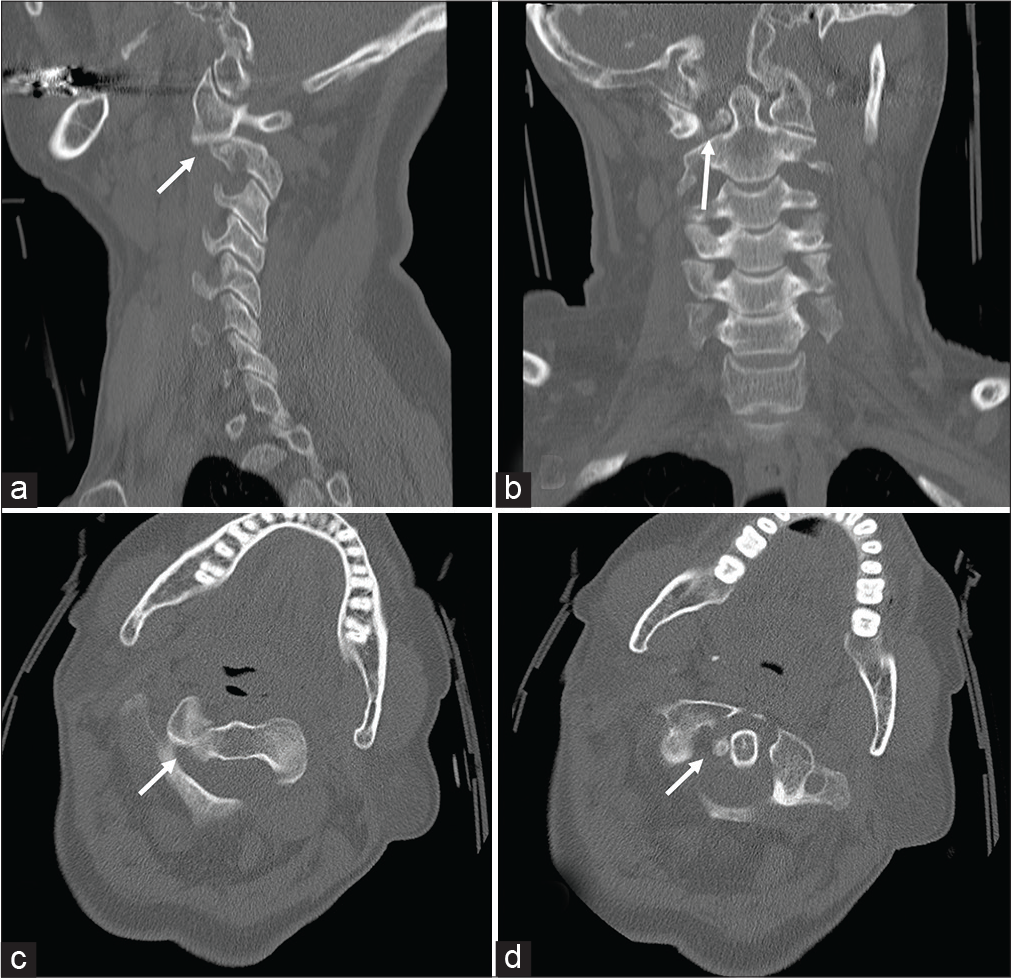
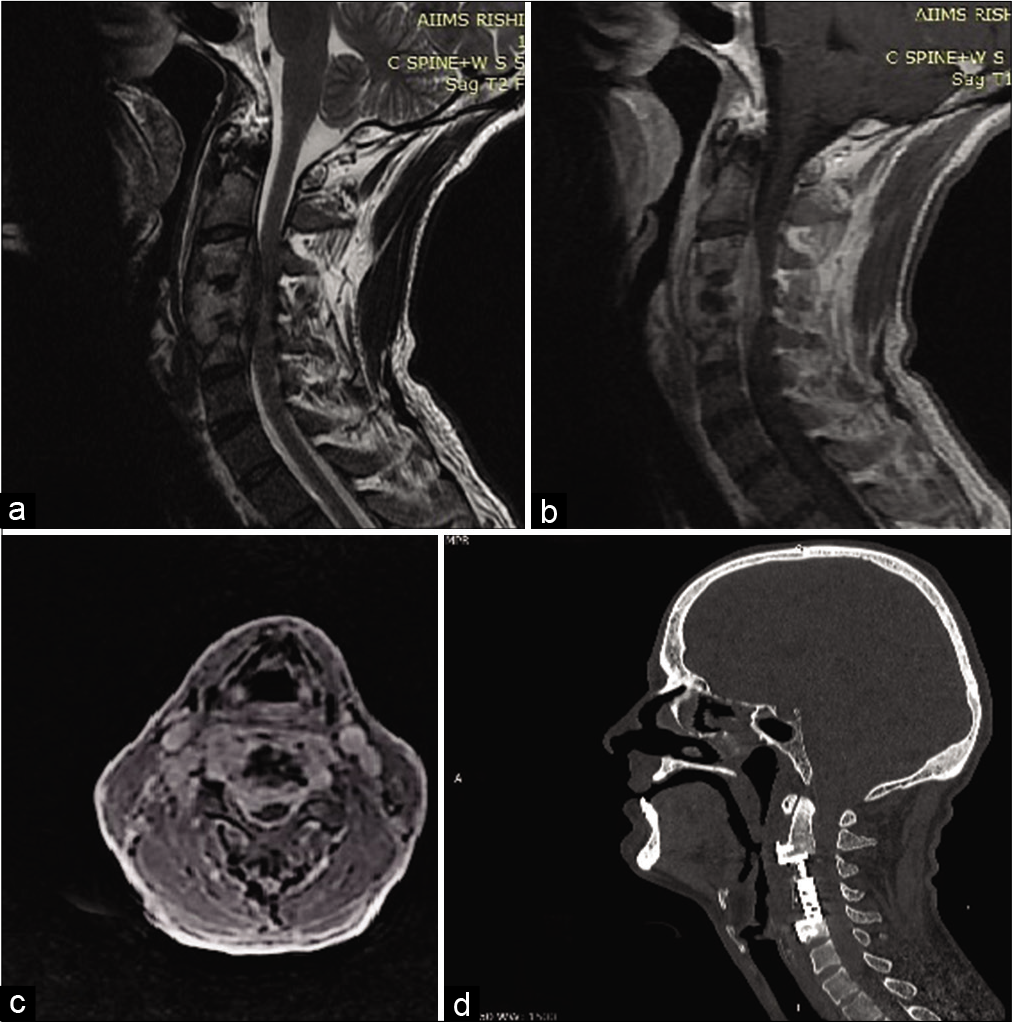
Traumatic atlantoaxial rotatory subluxation in adults – A case report and literature review
Date of publication: 06-Nov-2020
Background: Traumatic atlantoaxial rotatory subluxation (AARS) is extremely rare in adult versus pediatric populations. Patients usually present with post-traumatic neck pain and torticollis. Surgical management aims at reducing the deformity and stabilizing the spine utilizing external orthotics, and/or internal reduction/fixation.
Comparison of TruView and King Vision video laryngoscopes in subaxial cervical spine injury: A randomized controlled trial
Date of publication: 06-Nov-2020
Background: Airway management with cervical spine immobilization poses a particular challenge for intubation in the absence of neck extension and risks neurological damage in cases of unstable cervical spine injuries. Here, with manual inline stabilization (MILS) in patients with cervical spine injuries, we compared the safety/efficacy of intubation utilizing the TruView versus King Vision video laryngoscopes.
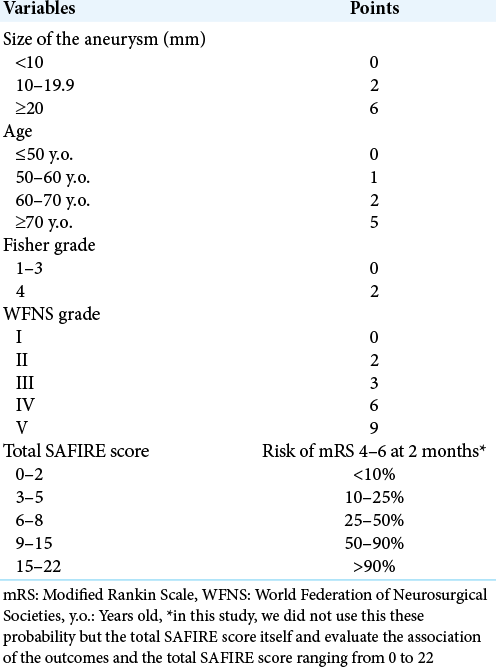
Easily created prediction model using deep learning software (Prediction One, Sony Network Communications Inc.) for subarachnoid hemorrhage outcomes from small dataset at admission
Date of publication: 06-Nov-2020
Background: Reliable prediction models of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) outcomes are needed for decision-making of the treatment. SAFIRE score using only four variables is a good prediction scoring system. However, making such prediction models needs a large number of samples and time-consuming statistical analysis. Deep learning (DL), one of the artificial intelligence, is attractive, but there were no reports on prediction models for SAH outcomes using DL. We herein made a prediction model using DL software, Prediction One (Sony Network Communications Inc., Tokyo, Japan) and compared it to SAFIRE score.
Primary anaplastic lymphoma kinase-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma of cervical spine presenting with quadriplegia: A case report and literature review
Date of publication: 06-Nov-2020
Background: An anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) involving the cervical spine and leading to quadriplegia is very rare.
IDH1-mutant primary intraventricular gliosarcoma: Case report and systematic review of a rare location and molecular profile
Date of publication: 06-Nov-2020
Background: Gliosarcoma (GS) is classified as an IDH-wild-type variant of glioblastoma (GBM). While GS is already an unusual presentation of GBM, IDH1-mutant cases are especially rare. We present an IDH1-mutant primary intraventricular GS case report and a systematic review of the molecular profile in GS correlating to the prognostic and pathogenesis of IDH1/2 mutations.
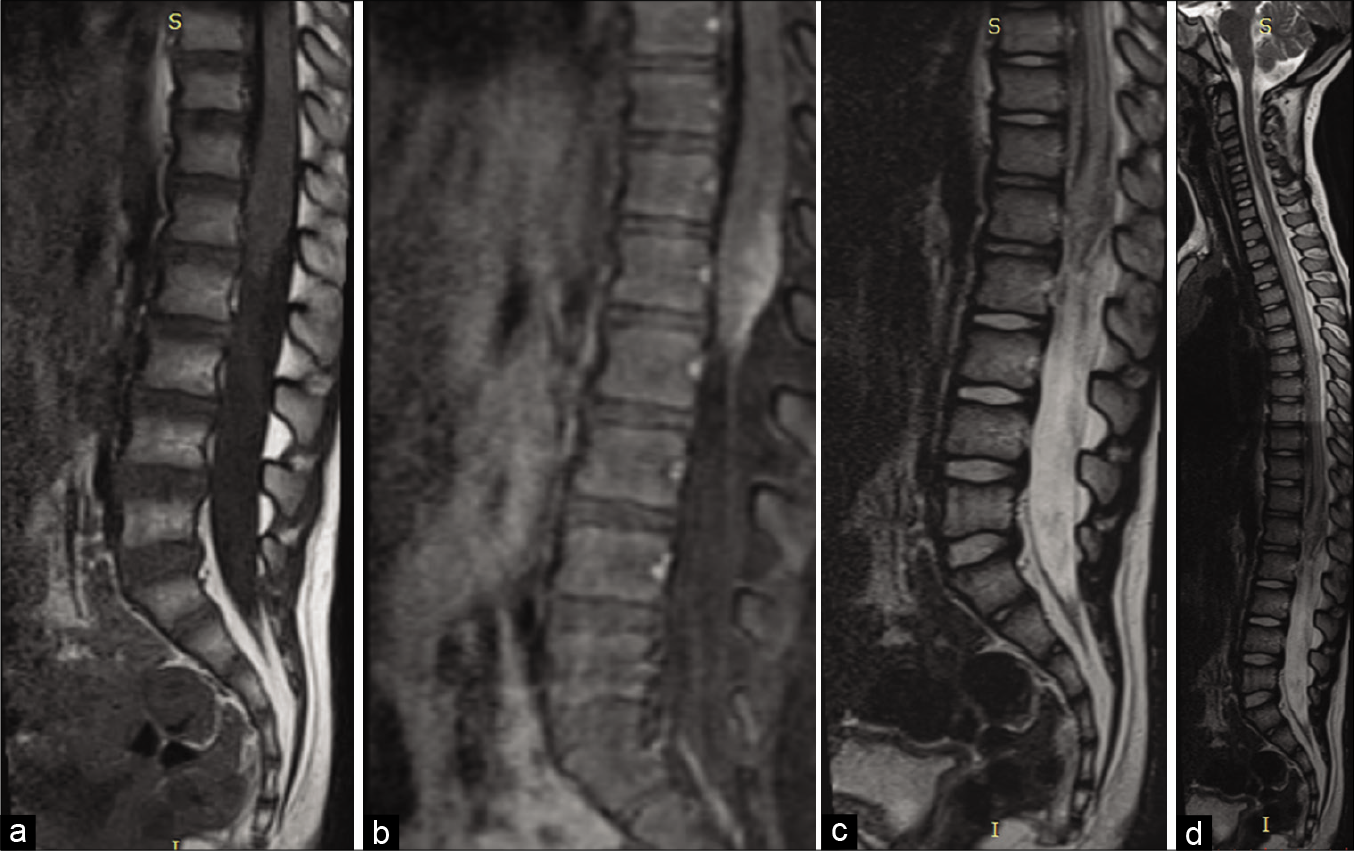
Intramedullary spinal schistosomiasis in a child with acute myelopathy: A case report
Date of publication: 06-Nov-2020
Background: Neuroschistosomiasis is defined as an infection of the nervous system caused by Schistosoma mansoni. Neuroschistosomiasis is an important differential diagnostic consideration in pediatric patients presenting with myelopathy. Surgical excision combined with antiparasitic drugs typically provides a satisfactory outcome and often results in neurological recovery.