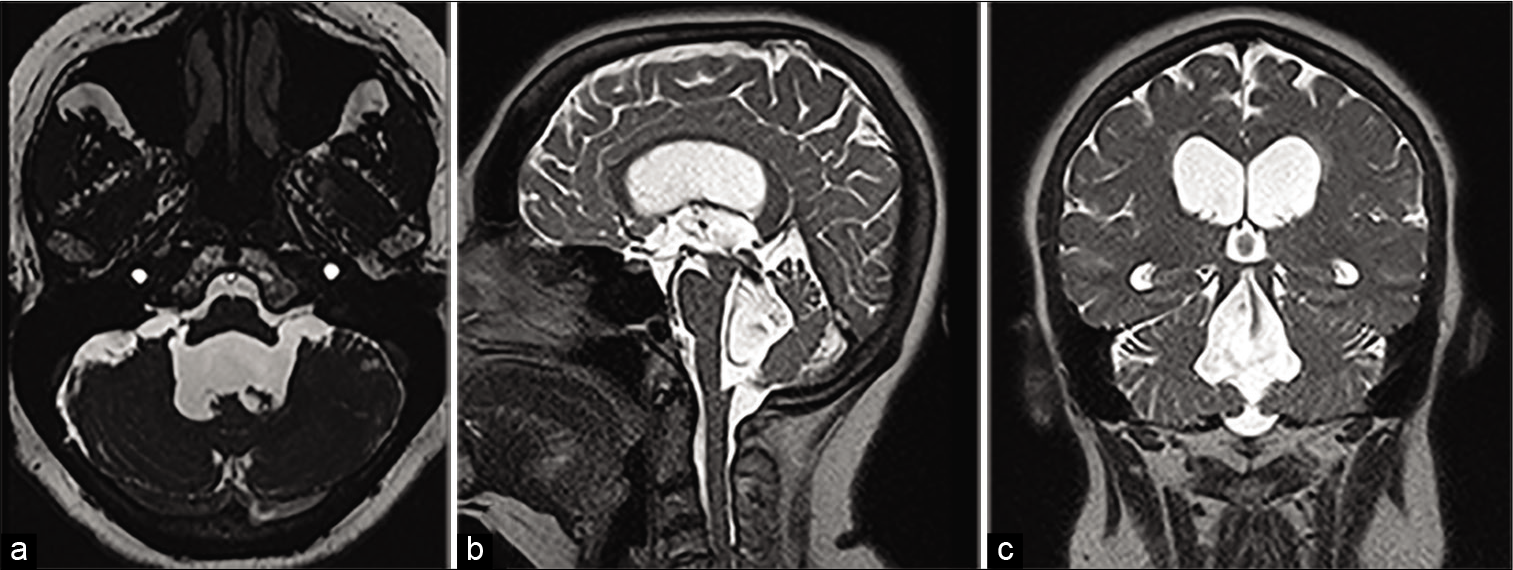
Idiopathic fourth ventricular outlet obstruction misdiagnosed as normal pressure hydrocephalus: A cautionary case
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
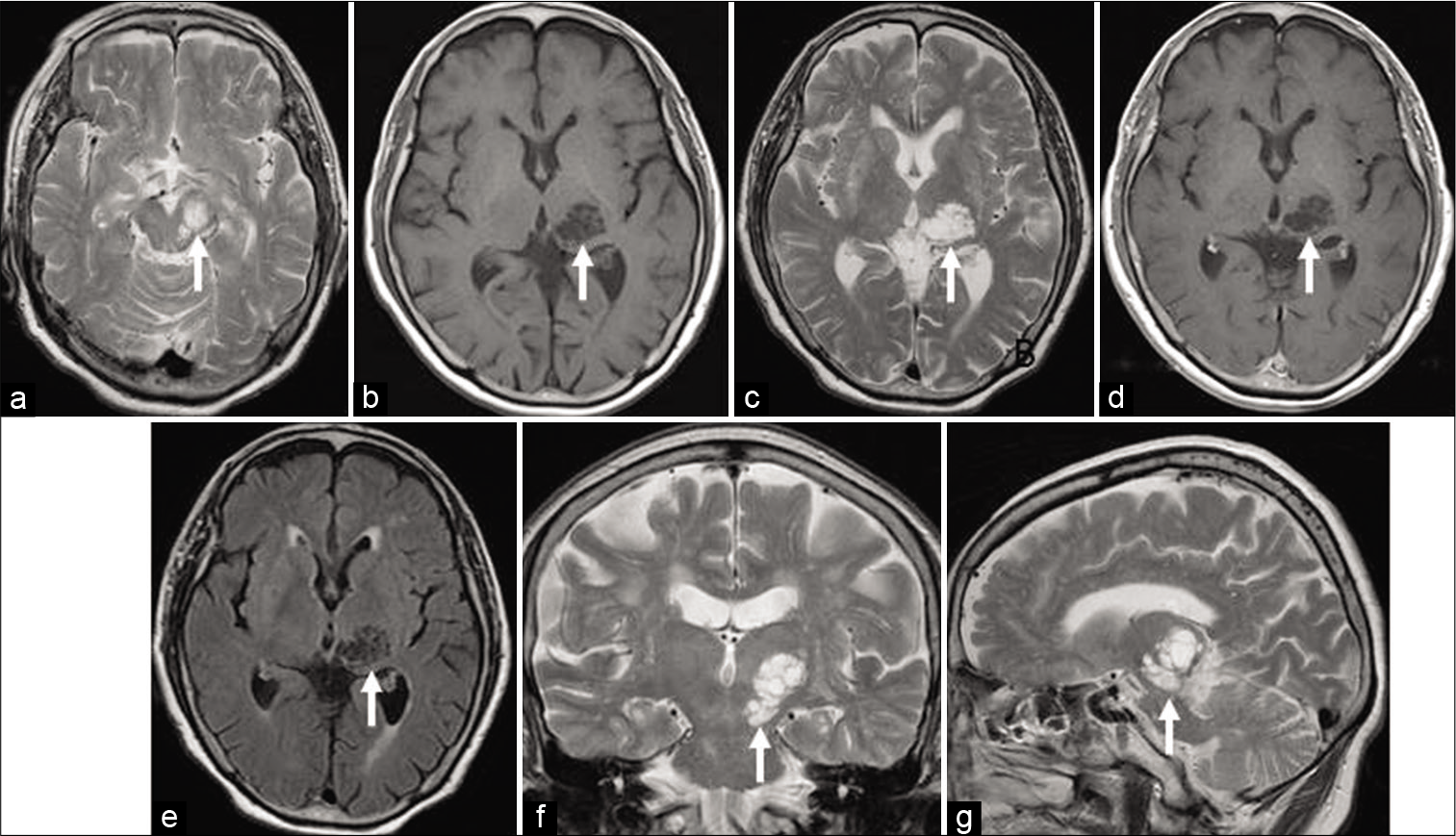
Background: Fourth ventricular outlet obstruction is an infrequent but well-established cause of tetraventricular hydrocephalus characterized by marked dilatation of the ventricular system with ballooning of the foramina of Monro, Magendie, and Luschka. Multiple processes including inflammation, infection, hemorrhage, neoplasms, or congenital malformations are known to cause this pathological obstruction. However, true idiopathic fourth ventricular outlet obstruction is a rare phenomenon with only a limited number of cases reported in the literature.
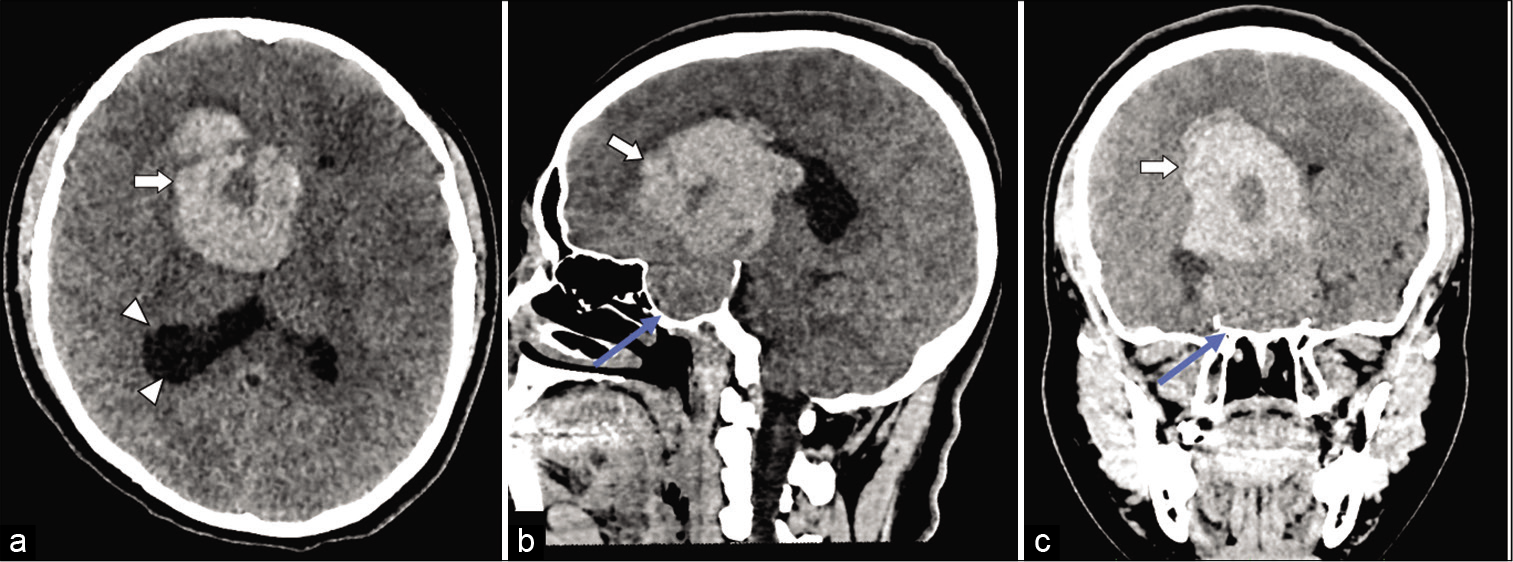
Pituitary macroadenoma apoplexy in a severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2-positive testing: Causal or casual?
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
Background: In December 2019, in Wuhan, a new virus emerged, causing severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) secondary to infection by a type of coronavirus, causing coronavirus disease (COVID-19). The pandemic caused by the new coronavirus has had implications in the central nervous system. COVID-19 is known to be characterized by coagulation activation and endothelial dysfunction, causing ischemic and hemorrhagic vascular syndromes.
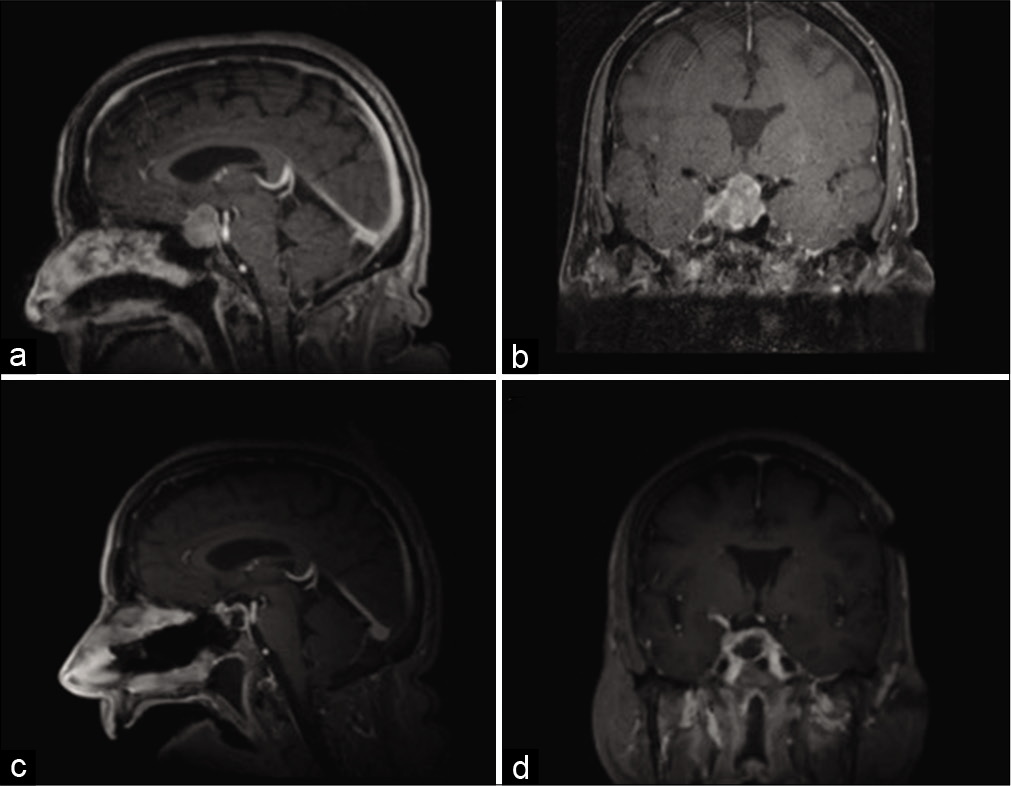
Genetic characterization of a case of sellar metastasis from bronchial carcinoid neuroendocrine tumor
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
Background: Metastasis to the pituitary gland from neuroendocrine tumors is a rare occurrence that may originate from primary tumors the lung, gastrointestinal tract, thyroid, and pancreas, among others. Patients may present with signs of endocrine dysfunction secondary to pituitary involvement, as well as mass effect-related symptoms including headaches and visual deficits. Despite a small but accumulating body of literature describing the clinical and histopathological correlates for pituitary metastases from neuroendocrine tumors, the genetic basis underlying this presentation remains poorly characterized.
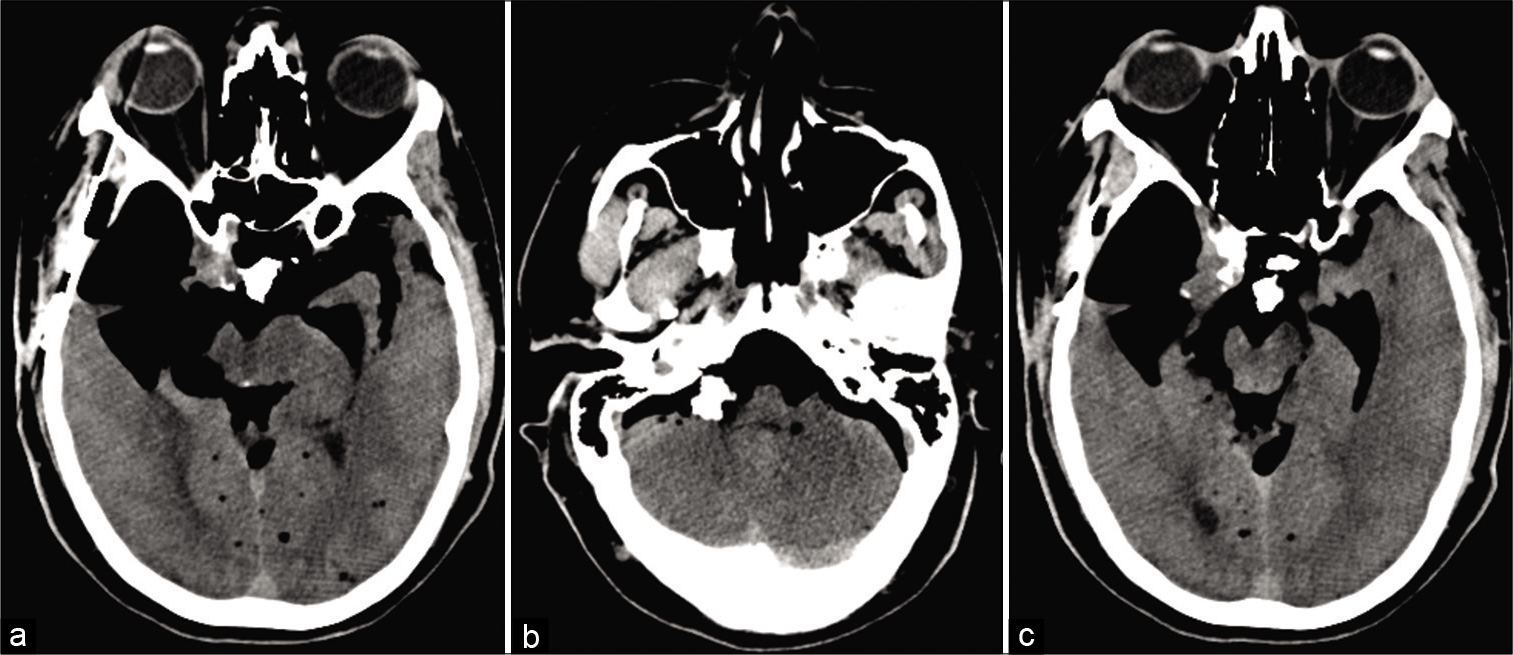
Pneumocephalus causing oculomotor nerve palsy: A case report
Date of publication: 25-Sep-2020
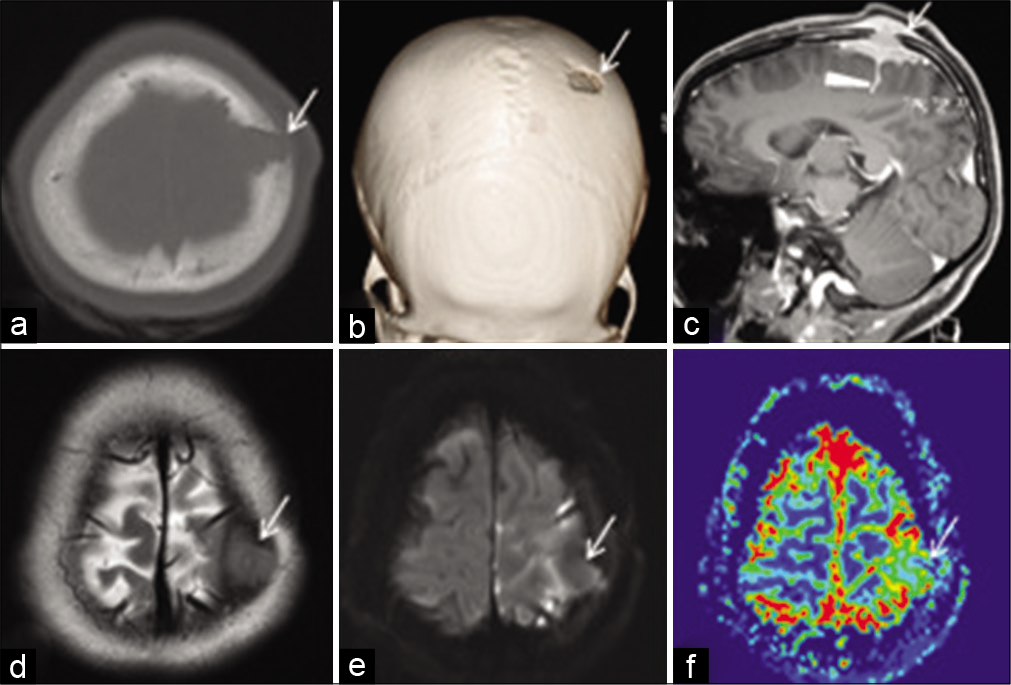
Background: Pneumocephalus, the presence of gas or air within the intracranial cavity, is a common finding after cranial procedures, though patients often remain asymptomatic. Rare cases of cranial nerve palsies in patients with pneumocephalus have been previously reported. However, only two prior reports document direct unilateral compression of the third cranial nerve secondary to pneumocephalus, resulting in an isolated deficit.
Case Report (Precis): Two Telemedicine Consultants Miss Foot Drop: When To See Patients in Person
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Telemedicine has been rapidly adopted due to COVID-19. In the earliest days, most screenings were performed by primary care/internal medicine consultants; referrals to subspecialists were minimized. Now, as the pandemic has evolved over 6 months, secondary telemedicine consultations should be limited, and earlier involvement of appropriate subspecialists should be reconsidered to optimize patient management.
The first 3-D volumetric analysis of mesencephalothalamic giant perivascular spaces showing steady and slow growth over 17 years
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Giant perivascular spaces (PVSs) are very rare condition in the brain and can be associated with neurological symptoms. It often enlarges and causes obstructive hydrocephalus which requires surgical intervention. However, the growth velocity has never been investigated.
Intradural iatrogenic epidermoid cyst at cauda equina: A case report
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Spinal epidermoid accounts for <1% of all primary spinal cord tumors. They occur due to the invagination of epidermal elements into the neural tube during the embryonic period. Even more infrequent are spinal epidermoid cysts that occur without attendant spinal dysraphism (e.g., as occurs with the iatrogenic inoculation of epithelial cells in the subarachnoid space following a lumbar puncture).
Rosai-Dorfman disease of cranial and spinal origin - A case series
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
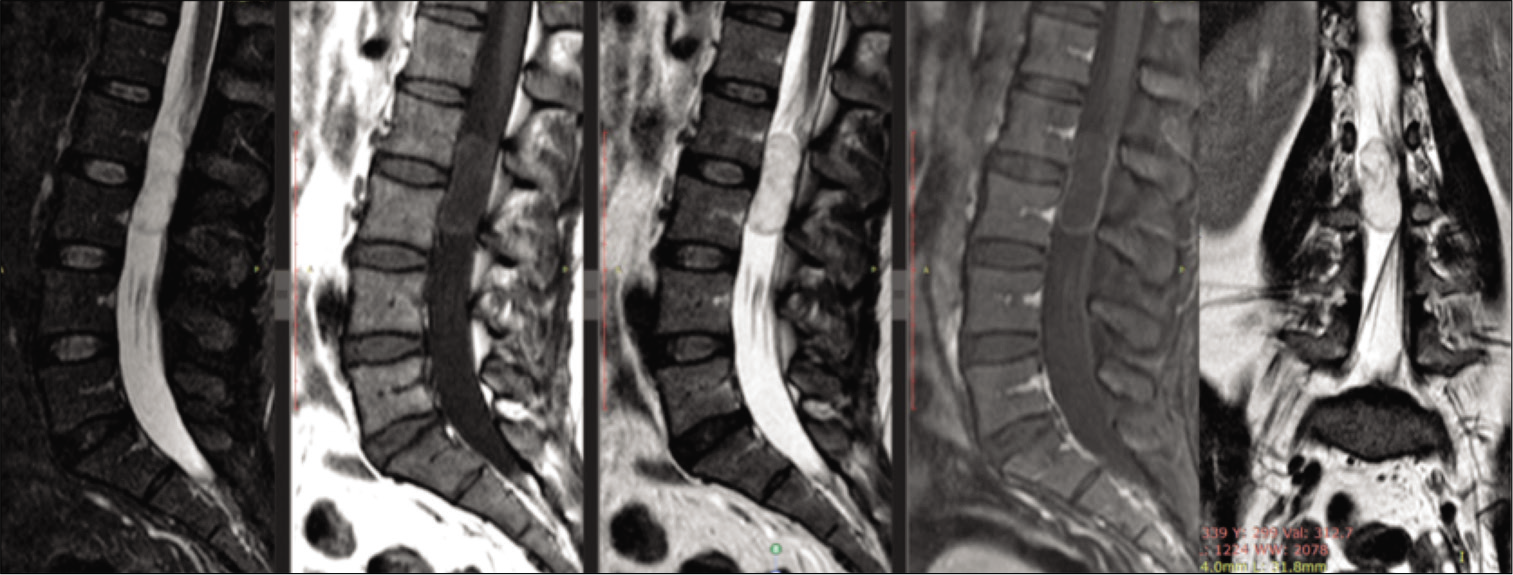
Background: Rosai-Dorfman disease (RDD) is an idiopathic nonneoplastic lymphadenopathy disorder which is characterized by lymph node enlargement, but it may also presents primarily involving a variety of extranodal sites, including central nerves system and craniospinal axis. This study reports five cases of craniospinal RDD, with review of epidemiology, clinical presentation, imaging, and histopathological features with current management strategies.
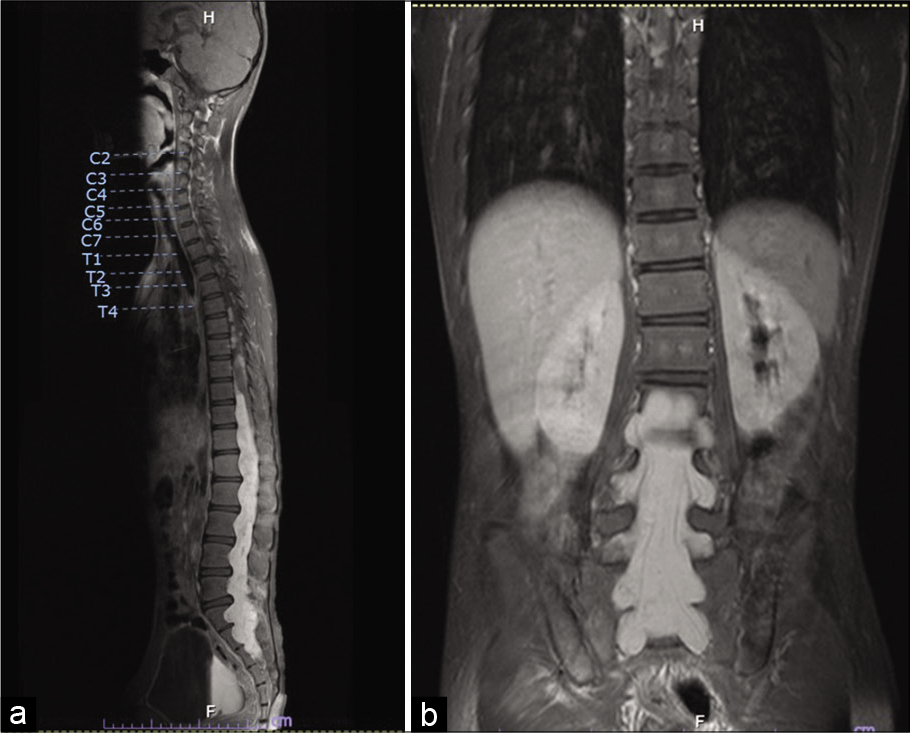
Image report: Extensive disseminated thoracolumbosacral myxopapillary ependymoma
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Myxopapillary ependymoma occurs more frequently in adults, but is found in the first two decades of life in around 8–20% of patients. Tumors are usually benign with low likelihood for dissemination.
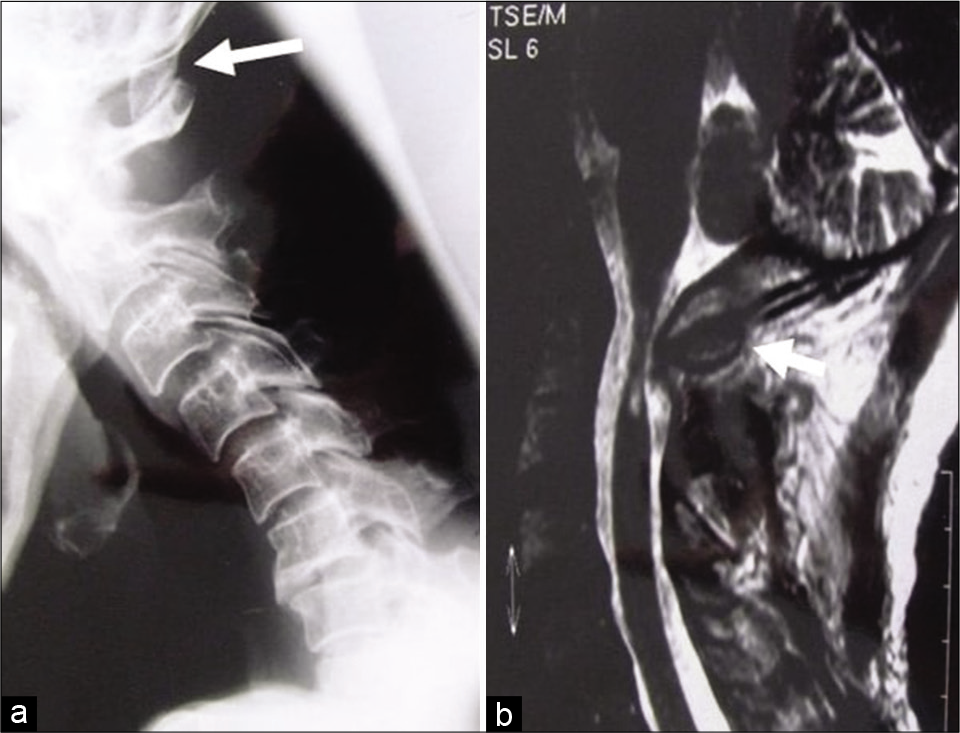
Foramen magnum osteochondroma causing myelopathy in a patient with hereditary multiple exostoses
Date of publication: 18-Sep-2020
Background: Osteochondromas are commonly occurring benign bone tumors which may be either a solitary lesion or occur due to association with hereditary multiple exostoses (HMEs). There have been several reported cases of spinal osteochondromas, but intracranial lesions are rare.