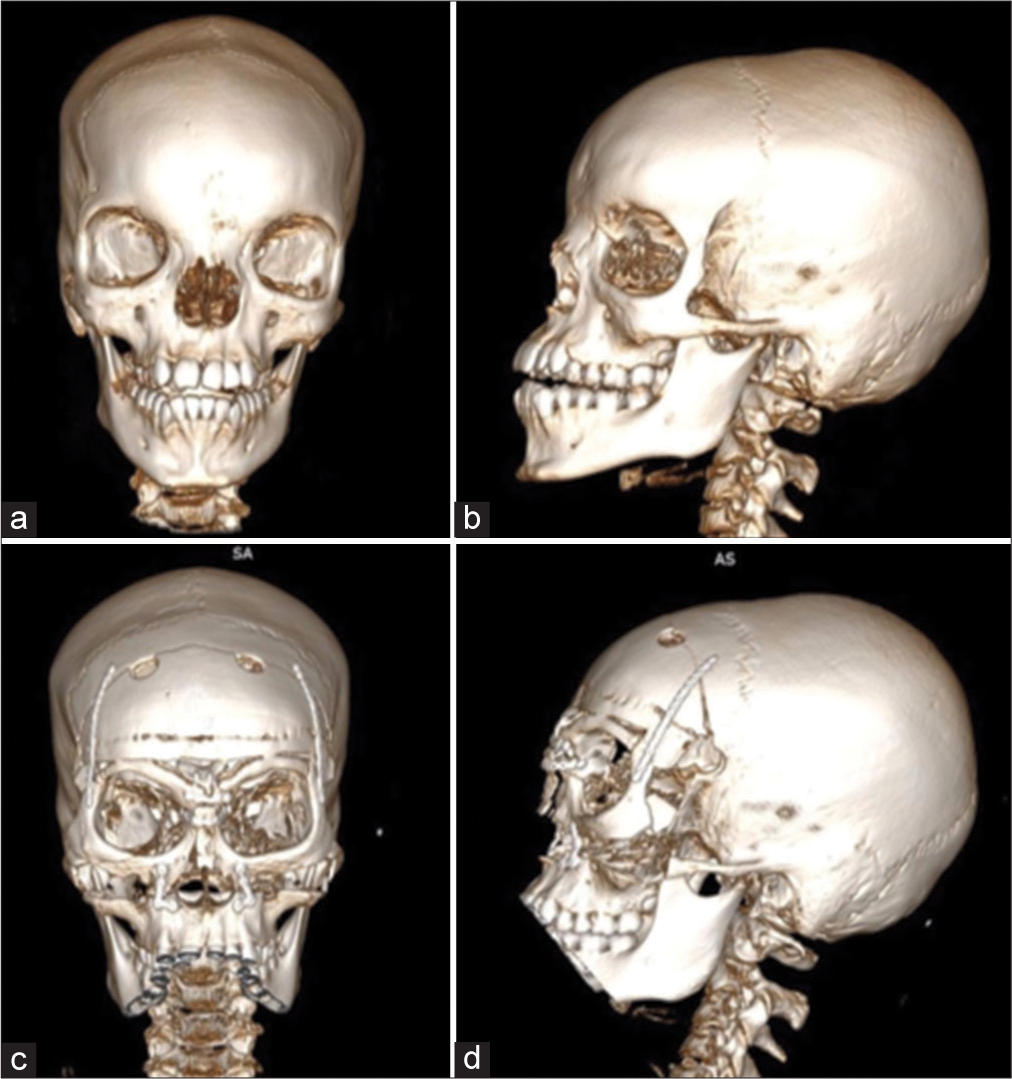
Isolated hypertelorism: Late surgical correction using the box osteotomy technique
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2024
Background: Orbital hypertelorism is a rare congenital condition caused by craniofacial malformations. It consists of complete orbital lateralization, characterized by an increase in distance (above the 95th percentile) of the inner canthal (ICD), outer canthal, and interpupillary distances. It can be approached surgically, and the main techniques are box osteotomy and facial bipartition. The surgical procedure is usually performed before the age of 8. We describe here two patients who underwent late surgical correction using the box osteotomy technique.
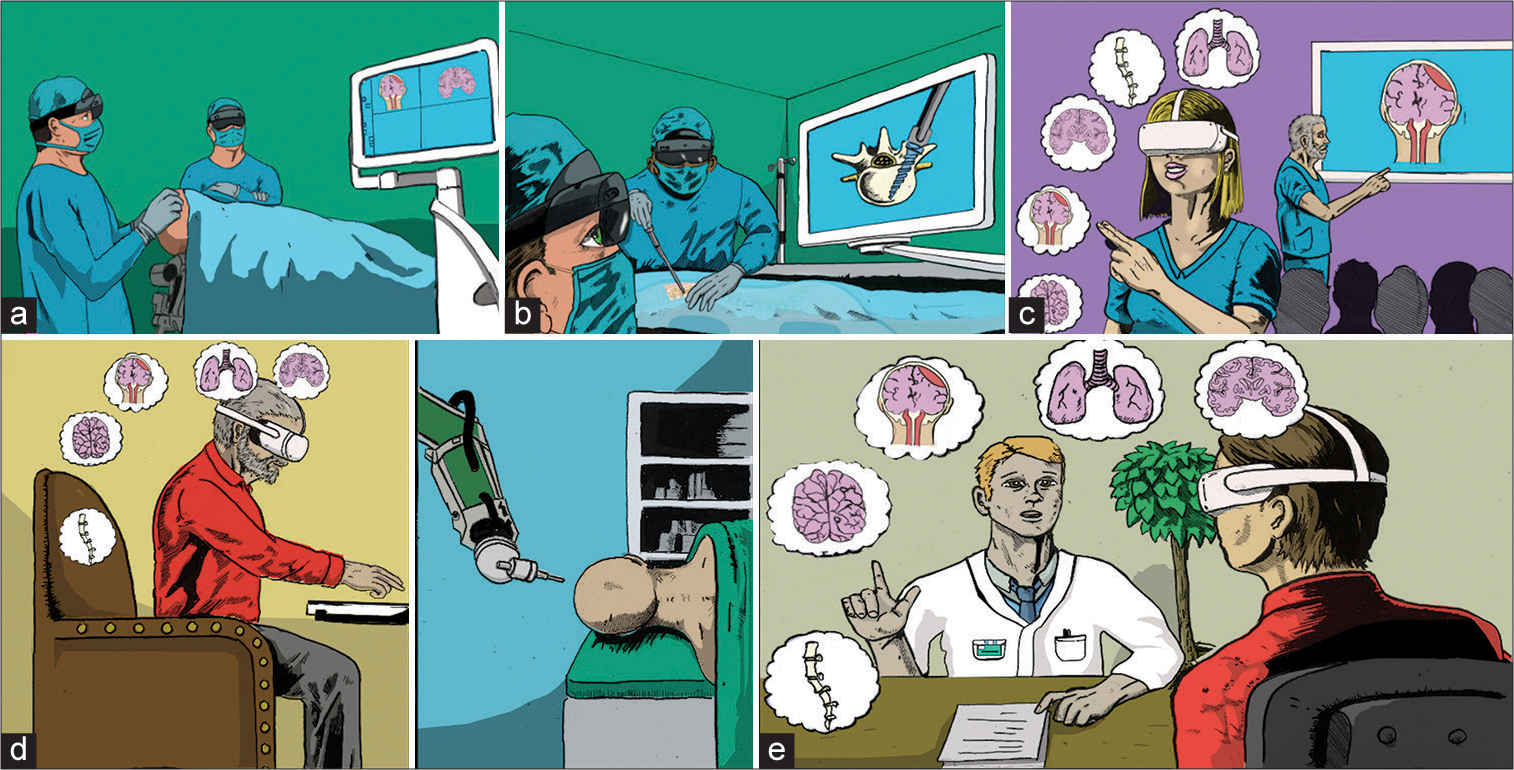
Evolution of the meta-neurosurgeon: A systematic review of the current technical capabilities, limitations, and applications of augmented reality in neurosurgery
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2024
Background: Augmented reality (AR) applications in neurosurgery have expanded over the past decade with the introduction of headset-based platforms. Many studies have focused on either preoperative planning to tailor the approach to the patient’s anatomy and pathology or intraoperative surgical navigation, primarily realized as AR navigation through microscope oculars. Additional efforts have been made to validate AR in trainee and patient education and to investigate novel surgical approaches. Our objective was to provide a systematic overview of AR in neurosurgery, provide current limitations of this technology, as well as highlight several applications of AR in neurosurgery.
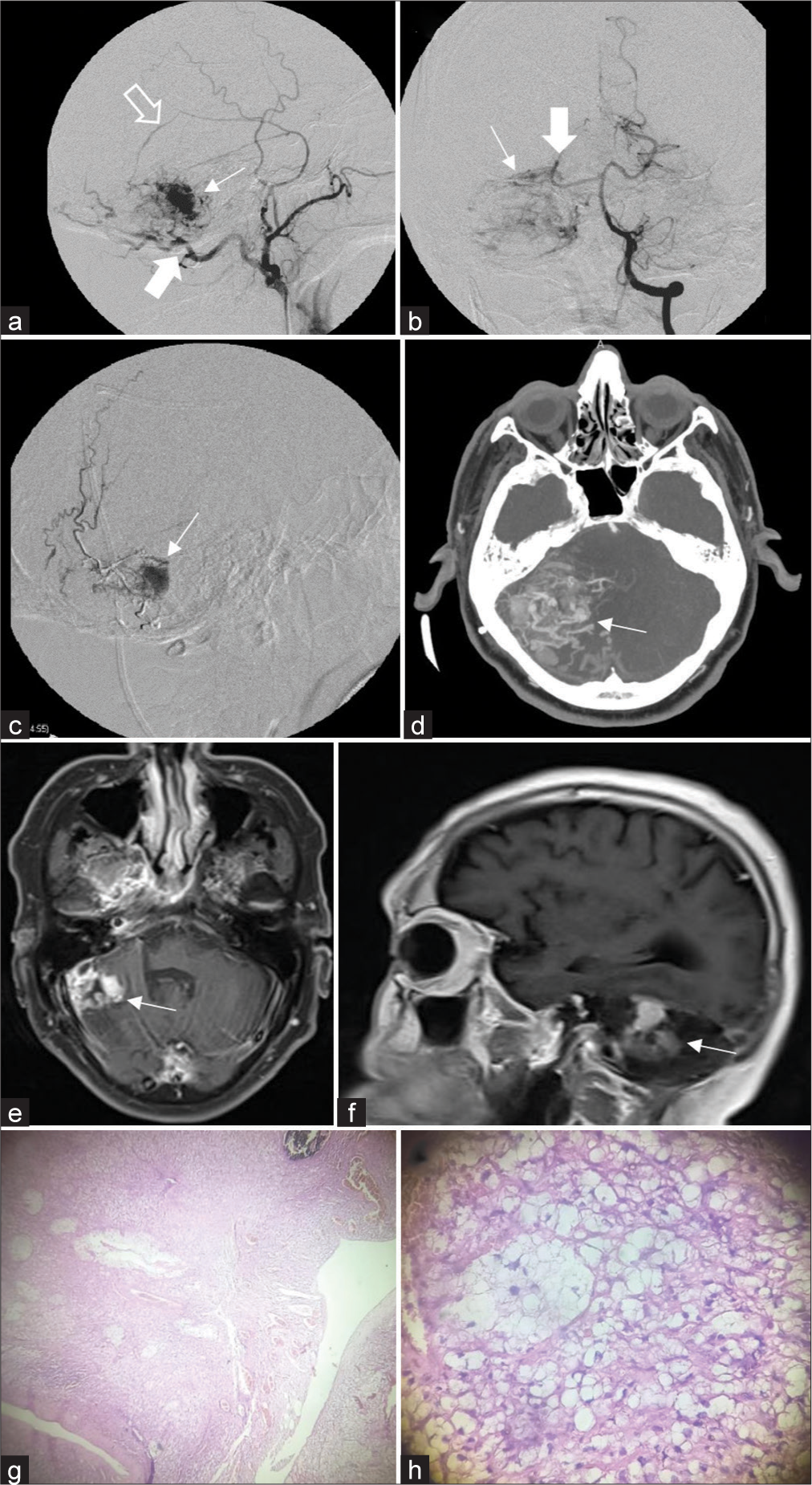
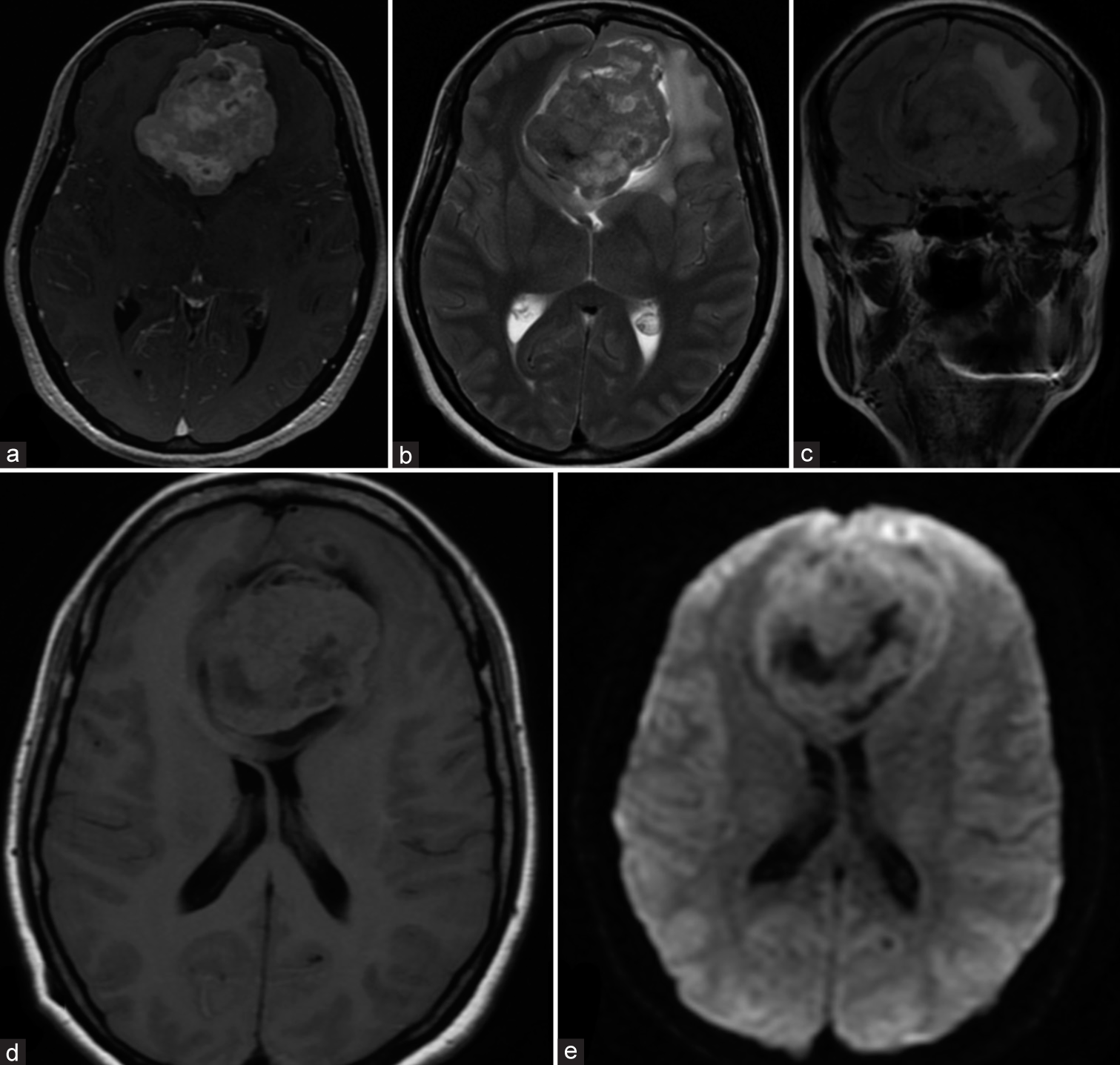
Multimodal management of giant solid hemangioblastomas in two patients with preoperative embolization
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2024
Background: Hemangioblastomas are benign vascular neoplasms, World Health Organization grade I, with the most frequent location in the cerebellum. Complete microsurgical resection can be a challenge due to excessive bleeding, which is why preoperative embolization takes importance.
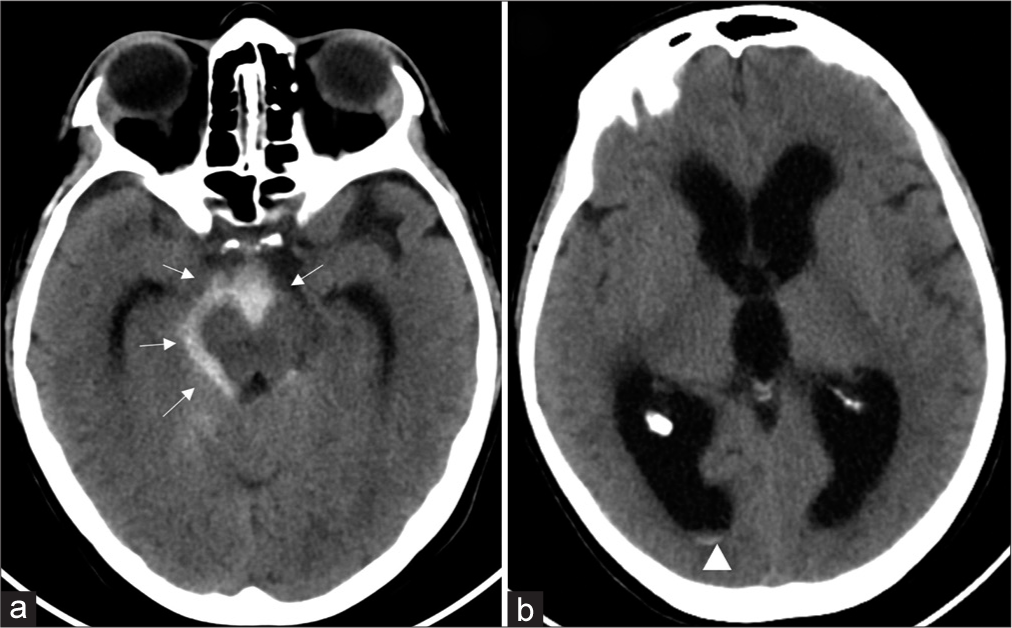
Multiple Abdominal abscesses following ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement in an immunosuppressed patient: An illustrative case
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2024
Background: Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt placement is one of the most performed procedures in neurosurgery to treat various types of hydrocephalus (HC). Immediate or late postoperative complications may quite commonly occur, especially in immunosuppressed patients, who are predisposed to develop rare and difficult-to-treat conditions.
Redefining cerebellar assessment: A comprehensive review of the cerebellum’s cognitive and affective roles and the efficacy of CCAS scales
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2024
Background: Emerging research expands our understanding of the cerebellum beyond motor control to include cognitive, emotional, and autonomic functions. This review examines the cerebellum’s complex role, spotlighting Schmahmann’s syndrome, or cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome (CCAS), which impairs executive functions, language, and spatial processing. It emphasizes advancements in diagnosing CCAS and the imperative of developing superior diagnostic tools for managing cerebellar pathologies effectively.
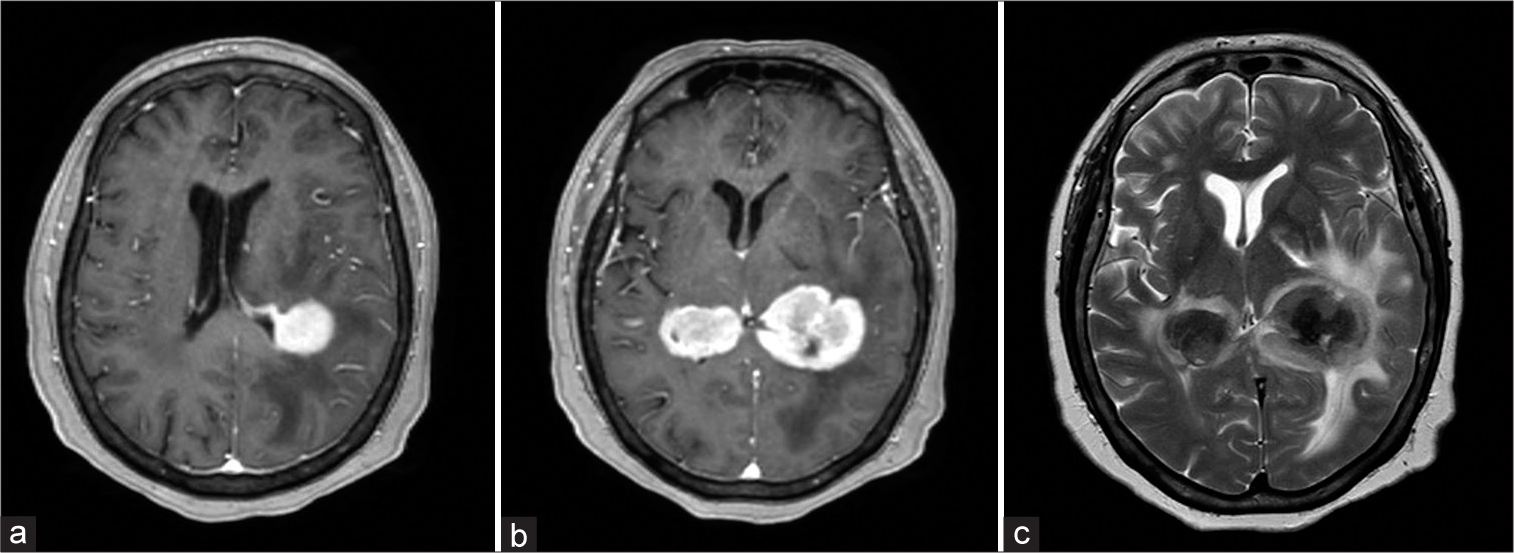
Primary central nervous system lymphoma: A mirror type presentation in an immunocompetent patient
Date of publication: 26-Apr-2024
Background: Primary central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma is a very rare extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The bilateral pattern, as we call it “mirror type”, has been identified in other CNS lesions such as gliomas, metastases, and demyelinating lesions, so the differential diagnosis includes imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging contrasted with spectroscopy, ruling out immunodeficiency or metastatic disease.
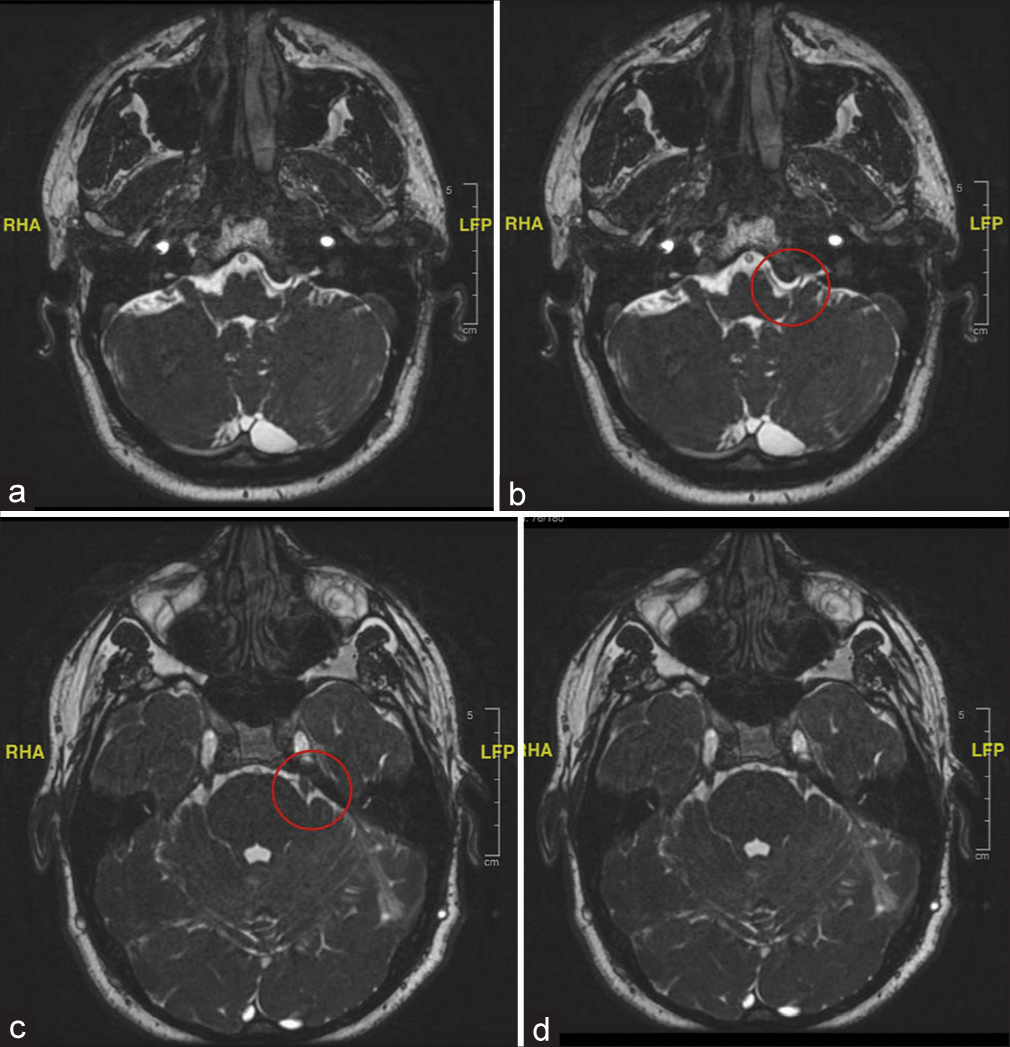
Endoscopic transsphenoidal resection of parasellar abducens nerve schwannoma: A video demonstration
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
Background: The abducens nerve schwannoma (ANS) in the sellar and parasellar region are extremely rare. Only around two dozen of ANS have been described in the world literature. These cases were, however, operated through the transcranial approach. We demonstrate, with the help of an edited video, that ANS located in the sellar and parasellar region can be safely and effectively operated through a transsphenoidal approach under endoscopic visualization.
Concurrent glossopharyngeal neuralgia and oromandibular dystonia resolved after microvascular decompression of the trigeminal and glossopharyngeal nerve: A rare presentation
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
Background: This type of pain syndrome occurs suddenly and briefly, beginning unilaterally from one side of the face. Modestly stimulating speech can provoke it, affecting the ear, tongue, throat, and jaw angle. Interestingly, it is the sensory distribution of the auricular and the pharyngeal branches of the cranial nerves IX and X. People have not had a confirmed case of glossopharyngeal neuralgia (GPN), along with oromandibular dystonia (OMD). Nevertheless, usually in the medical literature, this case report supplies information about a patient who has concurrent GPN and OMD.
Parasagittal meningeal hemangiopericytoma/solitary fibrous tumor: Two case reports and a literature review
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
Background: Solitary fibrous tumor/meningeal hemangiopericytoma (SFT/M-HPC) is a rare neoplasm which accounts for around 1% of the intracranial masses. This pathology has a high risk for recurrence and metastasis to distant locations such as the liver, lungs, and bones. Precise diagnosis necessitates detailed histopathological examination.
Do we need a neurosurgical frailty index?
Date of publication: 19-Apr-2024
Background: An increasing number of elderly patients now require neurosurgical intervention, and it is sometimes unclear if the benefits of surgery outweigh the risks, especially considering the confounding factor of numerous comorbidities and often poor functional states. Historically, many patients were denied surgery on the basis of age alone. This paper examines the current selection criteria being used to determine which patients get offered neurosurgical management and attempts to show if these patients have a good outcome. Particular focus is given to the increasing insight into the need to develop a neurosurgical frailty index.