The historic evolution of intracranial pressure and cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure concepts: Two centuries of challenges
Date of publication: 14-Jun-2021
Background: There is a consensus on the importance of monitoring intracranial pressure (ICP) during neurosurgery, and this monitoring reduces mortality during procedures. Current knowledge of ICP and cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure has been built thanks to more than two centuries of research on brain dynamics.
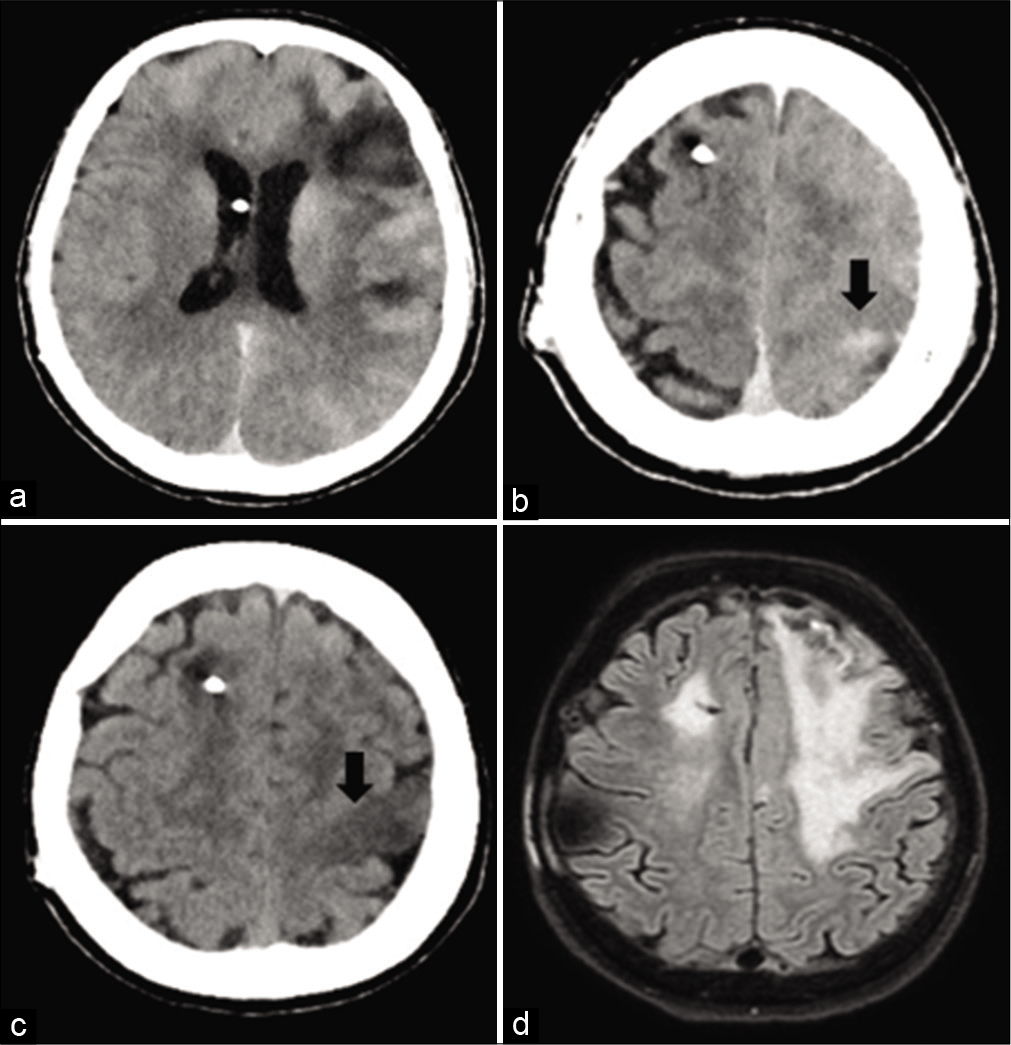
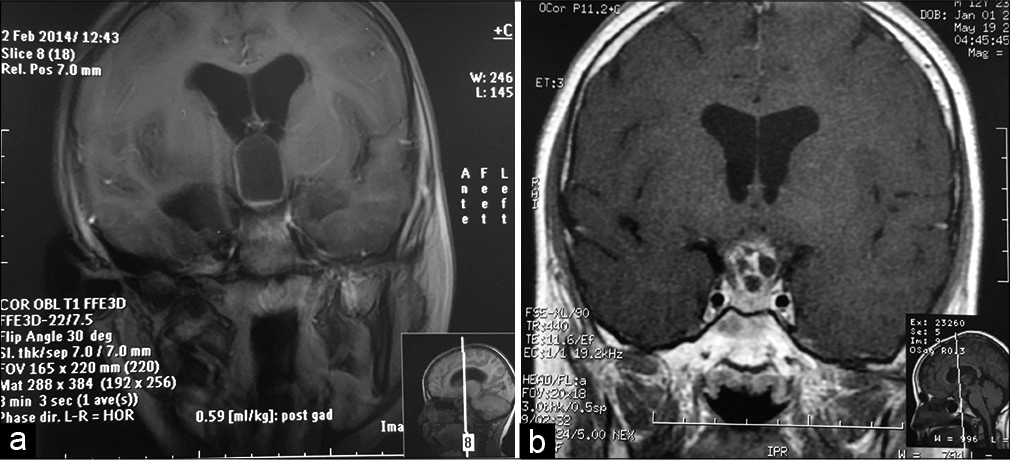
Contrast-induced encephalopathy and permanent neurological deficit: A case report and literature review
Date of publication: 14-Jun-2021
Background: Contrast-induced encephalopathy (CIE) is a rare condition that occurs after intravenous or intra-arterial contrast agent administration. Patients generally show different ranges of neurological deficits, which generally resolve themselves spontaneously within 24–48 h or in rare cases within 2 weeks.
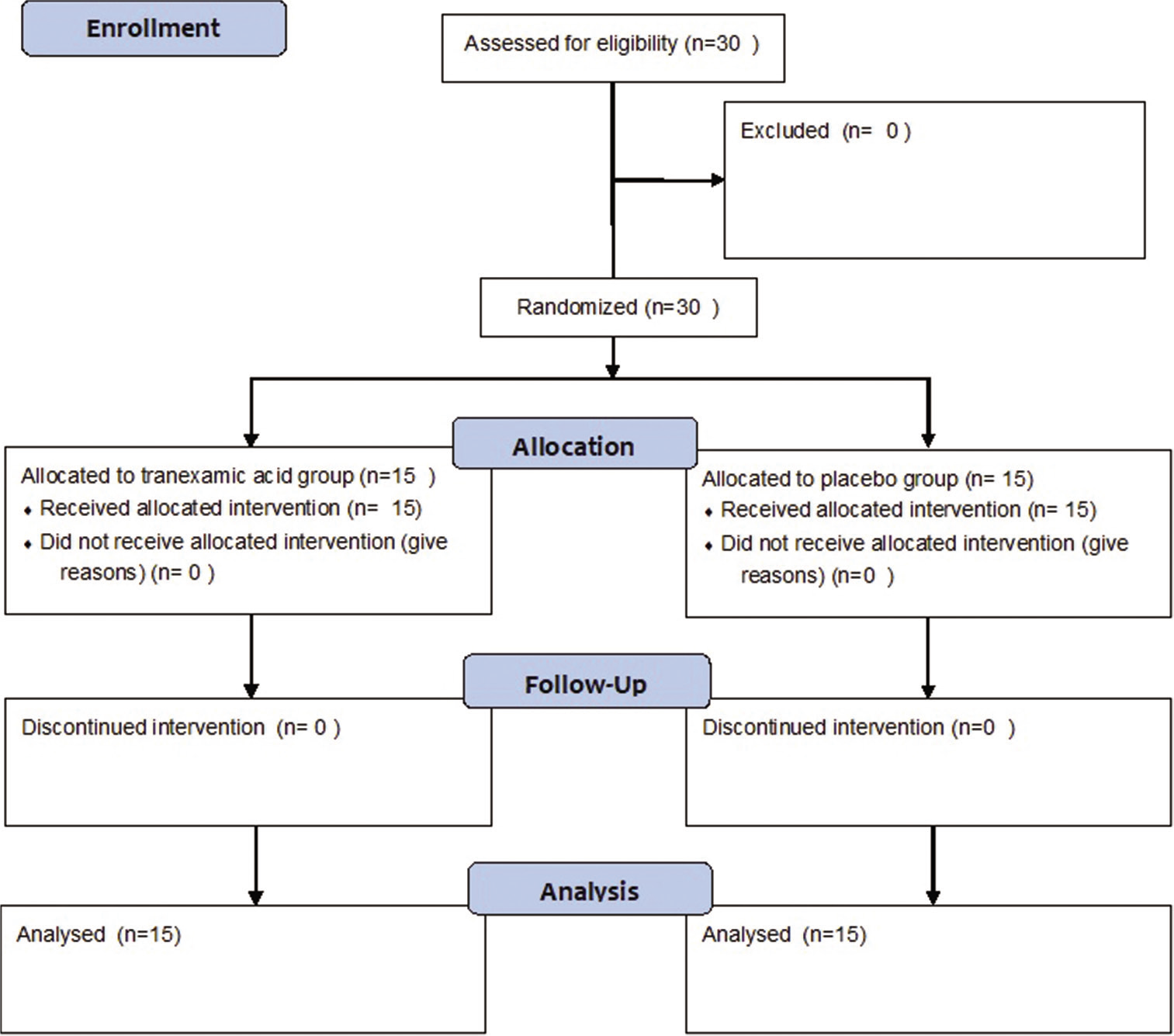
Effect of tranexamic acid on blood loss, coagulation profile, and quality of surgical field in intracranial meningioma resection: A prospective randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Resection of intracranial meningioma has been associated with significant blood loss. Providing a clear surgical field and maintaining hemodynamic stability are the major goals of anesthesia during meningioma surgery. Tranexamic acid has been used to reduce blood loss in various neurosurgical settings with limited evidence in literature. A randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial was conducted to evaluate the efficacy of tranexamic acid on blood loss, coagulation profile, and quality of surgical field during resection of intracranial meningioma.
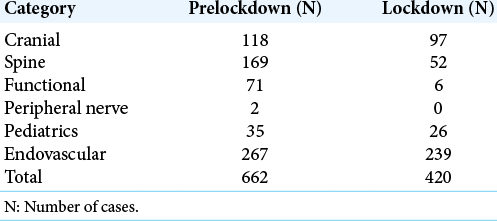
The effect of COVID-19 on trainee operative experience at a multihospital academic neurosurgical practice: A first look at case numbers
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: COVID-19 has had a significant impact on the economy, health care, and society as a whole. To prevent the spread of infection, local governments across the United States issued mandatory lockdowns and stay-at-home orders. In the surgical world, elective cases ceased to help “flatten the curve” and prevent the infection from spreading to hospital staff and patients. We explored the effect of the cancellation of these procedures on trainee operative experience at our high-volume, multihospital neurosurgical practice.
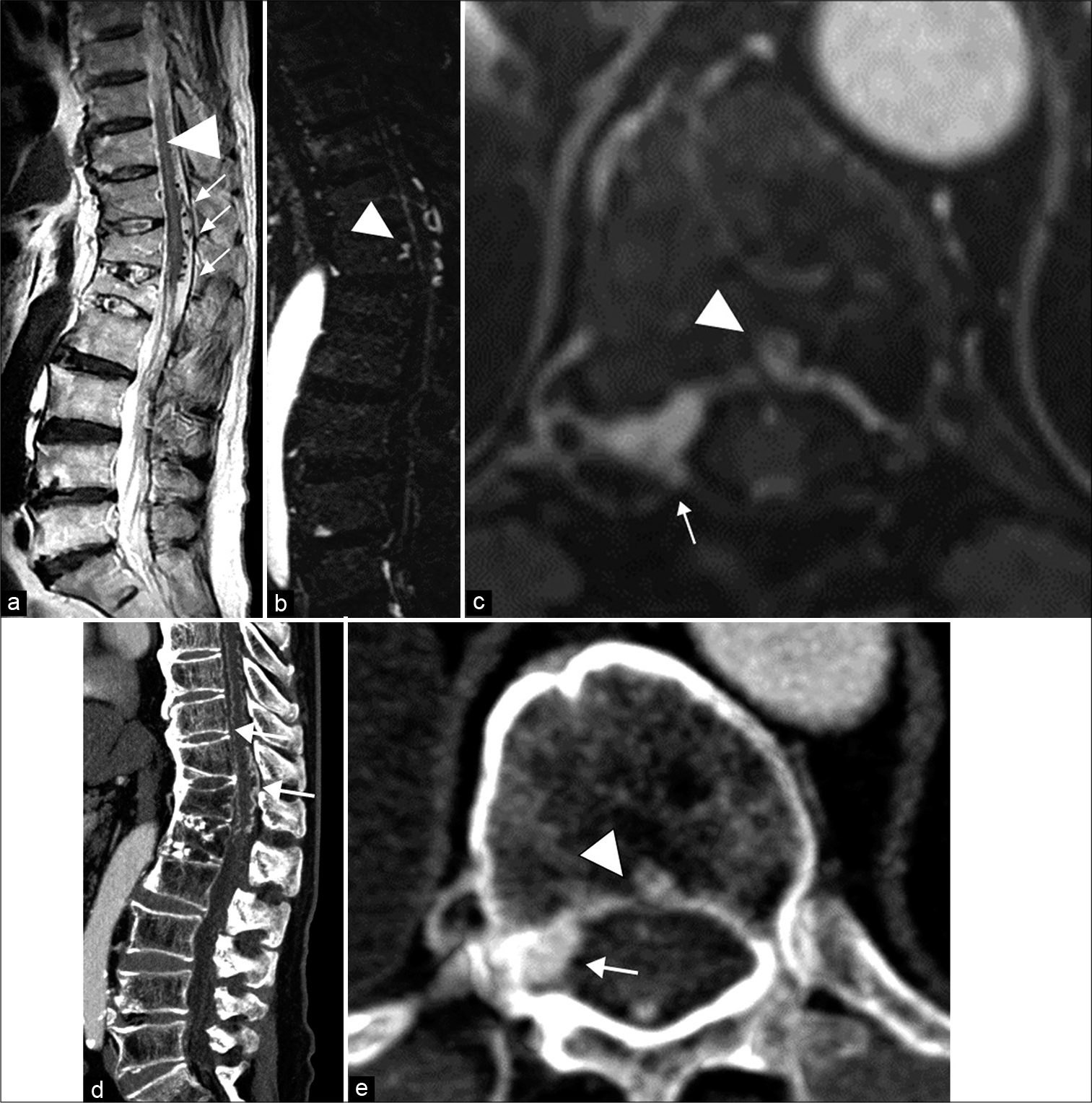
Thoracolumbar intraosseous spinal epidural arteriovenous fistulas after vertebral compression fracture: A case report and literature review
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: The pathophysiology of spinal epidural arteriovenous fistulas (SEAVFs) with perimedullary venous drainage remains to be elucidated. This report describes a case of intraosseous SEAVF in a patient with a history of a thoracolumbar vertebral fracture at the same level 10 years before presenting with progressive myelopathy secondary to retrograde venous reflux into the perimedullary vein.
Surgical techniques in the management of supratentorial pediatric brain tumors: 10 years’ experience at a tertiary care center in the Middle East
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: The goal of this retrospective study is to present the first epidemiological data on pediatric supratentorial central nervous system (CNS) tumors in Lebanon and to review the various surgical management strategies used.
Effect of comorbidities on ischemic stroke mortality: An analysis of the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) Database
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Stroke risk has been attributed to many pathological and behavioral conditions. Various modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors have been recognized and found consistent throughout epidemiological studies. Herein, we investigate the effect of comorbidities seen with patient’s suffering from ischemic stroke and its effect on in-hospital mortality.
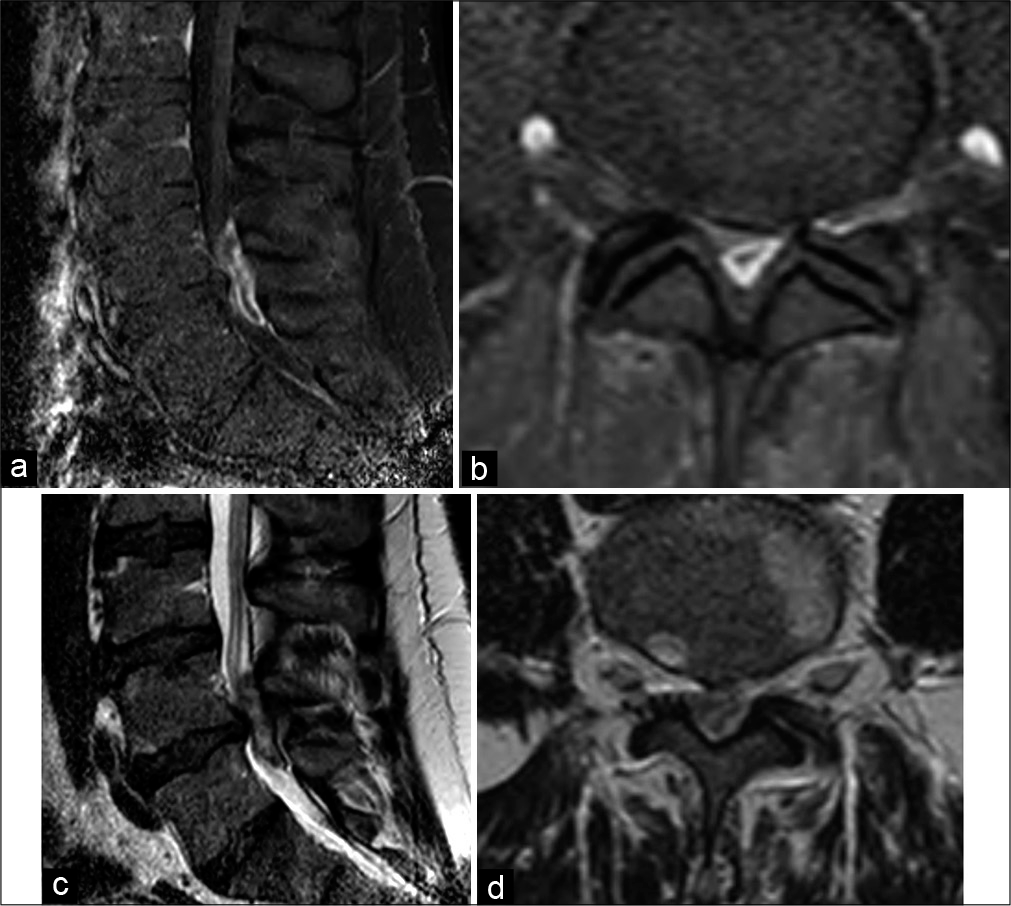
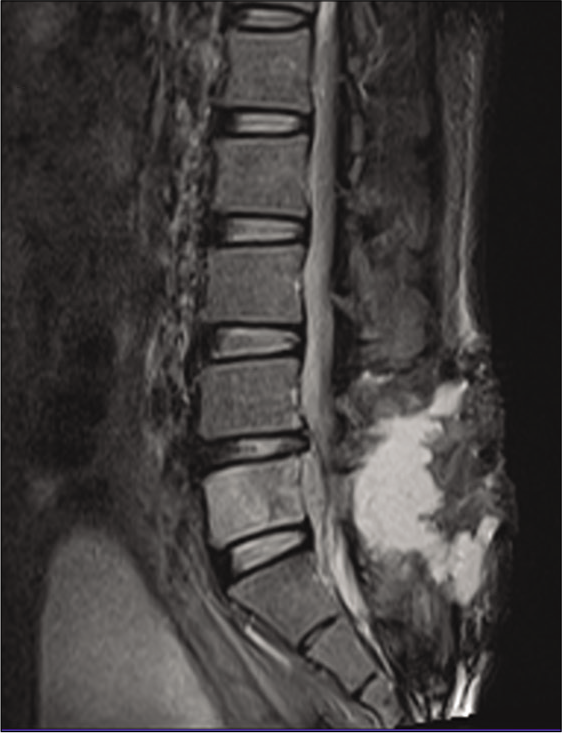
Difficulty differentiating between a posterior extradural lumbar tumor versus sequestered disc even with gadolinum-enhanced MRI
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Differentiating between posterior extradural tumors versus sequestered lumbar disc herniations may be difficult even utilizing contrast-enhanced MR scans.
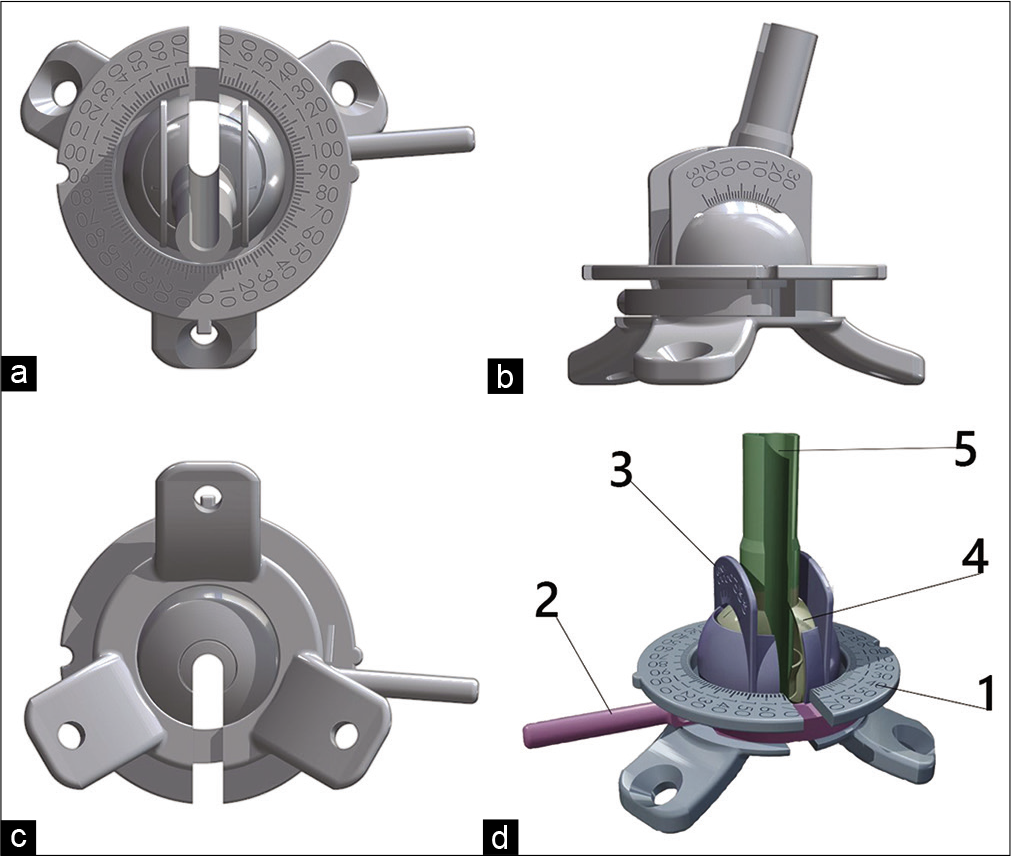
Neuronavigation device for stereotaxic external ventricular drainage insertion
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: The insertion of an external ventricular drainage (EVD) is one of the most frequently used neurosurgical procedures. It is performed to adjust intracranial hypertension in cases of severe craniocerebral injury, acute posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus, meningitis, and oncological diseases related to impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid circulation (CSF).
A case of postoperative tubercular spondylitis following microdiscectomy for lumbar disc herniation
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Postoperative infections are one of the most common complications of spine surgery. However, following a lumbar microdiscectomy, a postoperative infection involving Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) is extremely rare.