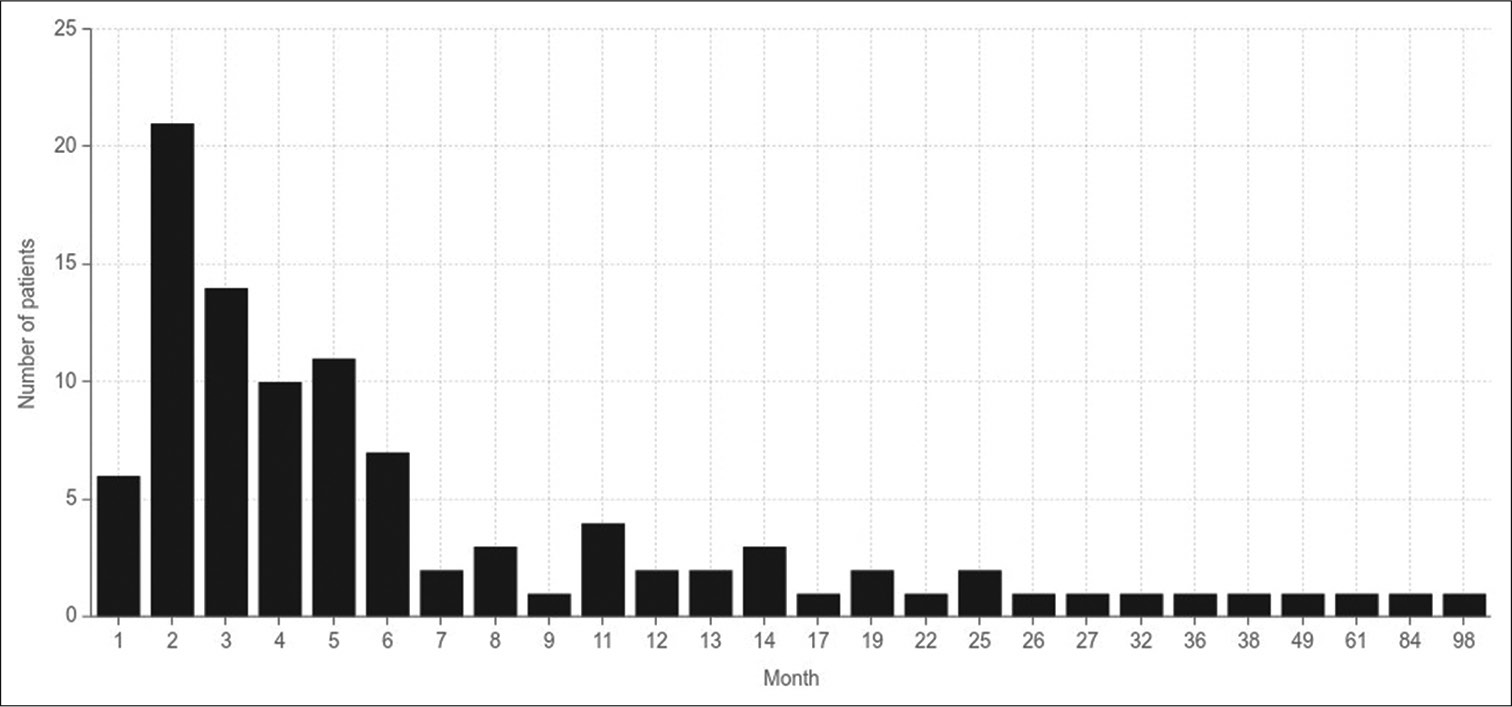
Effect of cranioplasty timing on the functional neurological outcome and postoperative complications
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: The optimal timing for performing cranioplasty and its effect on functional outcome remains debatable. Multiple confounding factors may come into role; including the material used, surgical technique, cognitive assessment tools, and the overall complications. The aim of this study is to assess the neurological outcome and postoperative complications in patients who underwent early versus late cranioplasty.
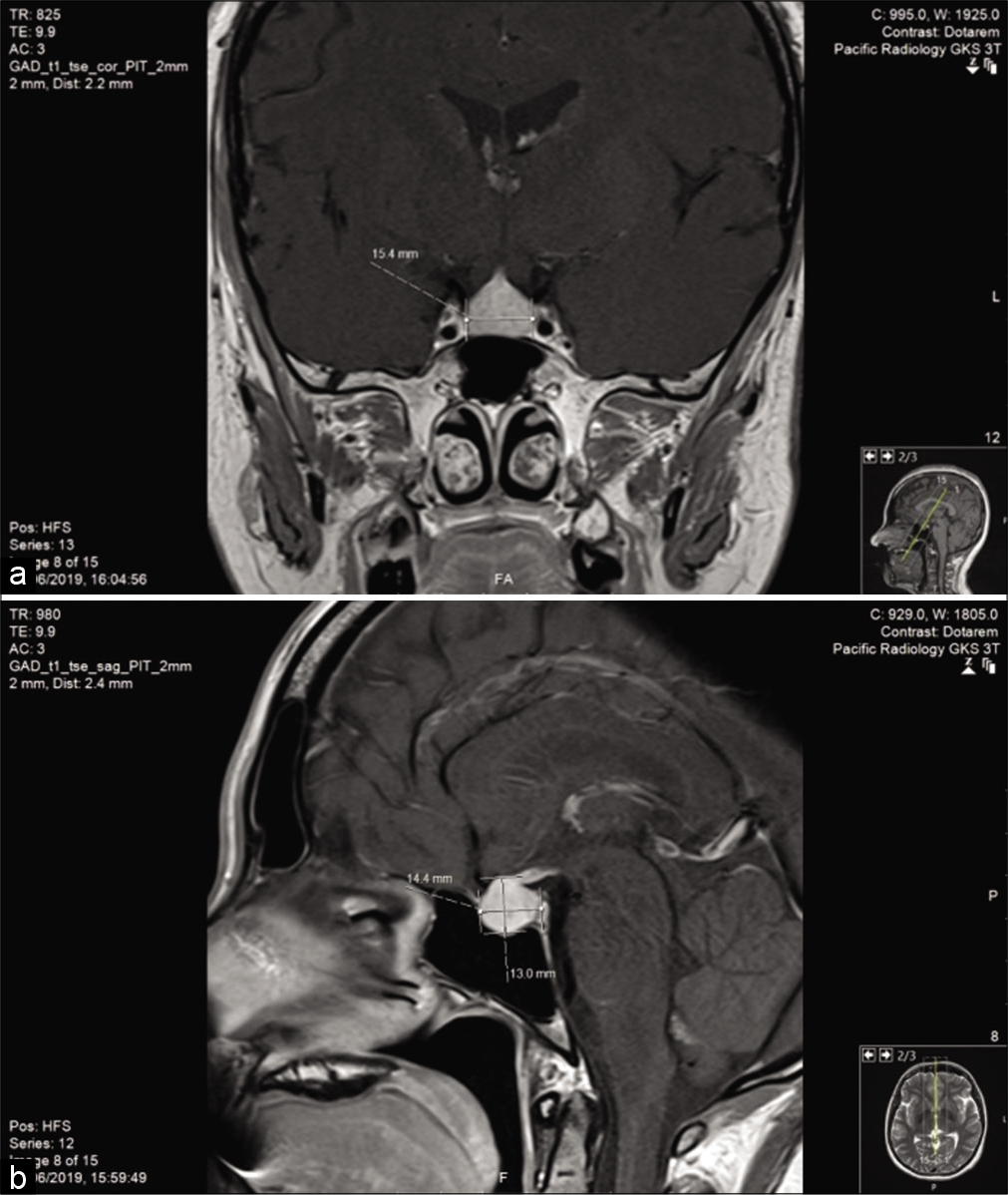
A case report of lymphocytic hypophysitis
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Lymphocytic hypophysitis (LH) is a rare condition that mostly affects women of the reproductive age. Because it is infrequently encountered, it is not often considered as a differential diagnosis of sellar masses. The diagnosis is made clinically with the aid of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and should be considered if the patient has endocrine derangements in addition to a sellar mass.
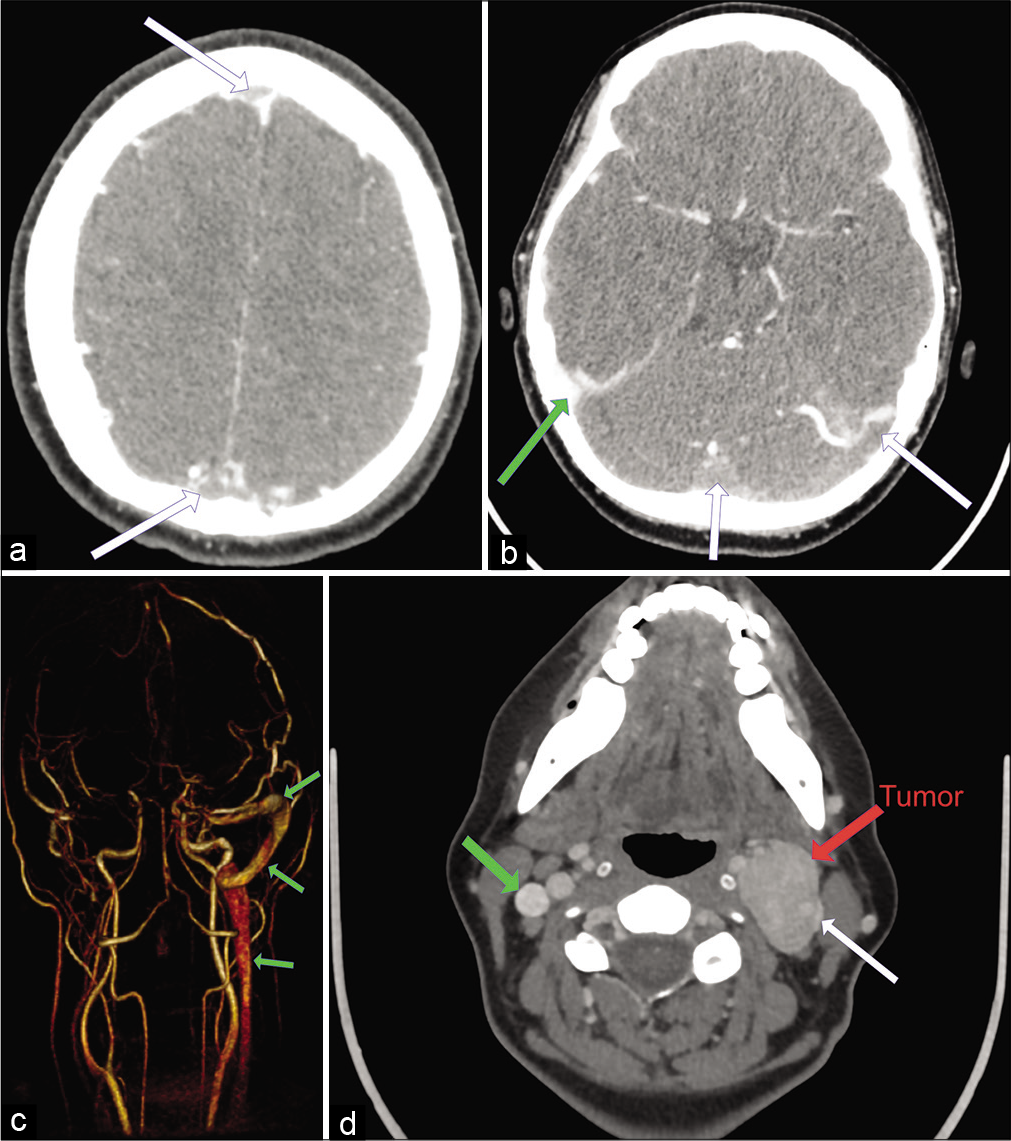
A rare case of carotid body tumor associated with near complete cerebral sinus thrombosis and idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Management strategy and review of the literature
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Carotid body tumors (CBTs) are rare hypervascular lesions with critical location which makes them very challenging to treat. In rare occasions, compression of the jugular vein from the tumor mass could predispose to progressive thrombosis of intracranial venous sinuses. The latter consequently leads to intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri) with the accompanying danger to the vision. Herewith, we present our management strategy for this rare presentation of CBTs.
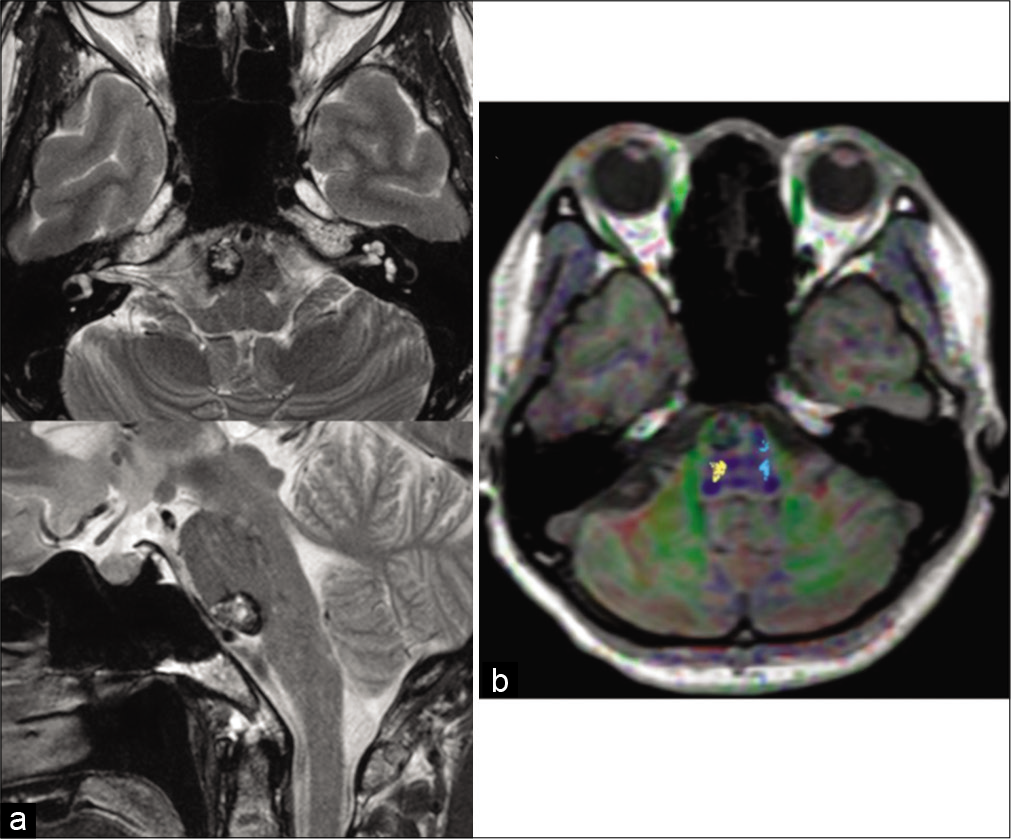
Anterior transpetrosal resection of the lower ventral pontine cavernous malformation: A technical case report with operative video
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Surgical treatment of pontine cavernous malformations (CMs) is challenging due to the anatomical difficulties and potential risks involved. We successfully applied an anterior transpetrosal approach (ATPA) to remove a lower ventral pontine CM, and herein we discuss the outline of our procedure accompanied by a surgical video.
Increase of the clivus-canal angle in patients with basilar invagination, without atlantoaxial displacement, treated with a simple maneuver of indirect decompression of the odontoid with the head clamp, during posterior occipitocervical arthrodesis
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Basilar invagination (BI) can be defined as the insinuation of the content of the craniovertebral junction through the foramen magnum toward the posterior fossa. BI is a prevalent condition in Northeast Brazil. The present study describes the changes in the clivus-canal angle (CCA) in the postoperative period in patients with symptomatic BI operated by a posterior approach, using a simple technique of indirect reduction of the odontoid associated with occipitocervical fixation.
Experiences of a neurosurgical center in the United Kingdom during the COVID-19 pandemic
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
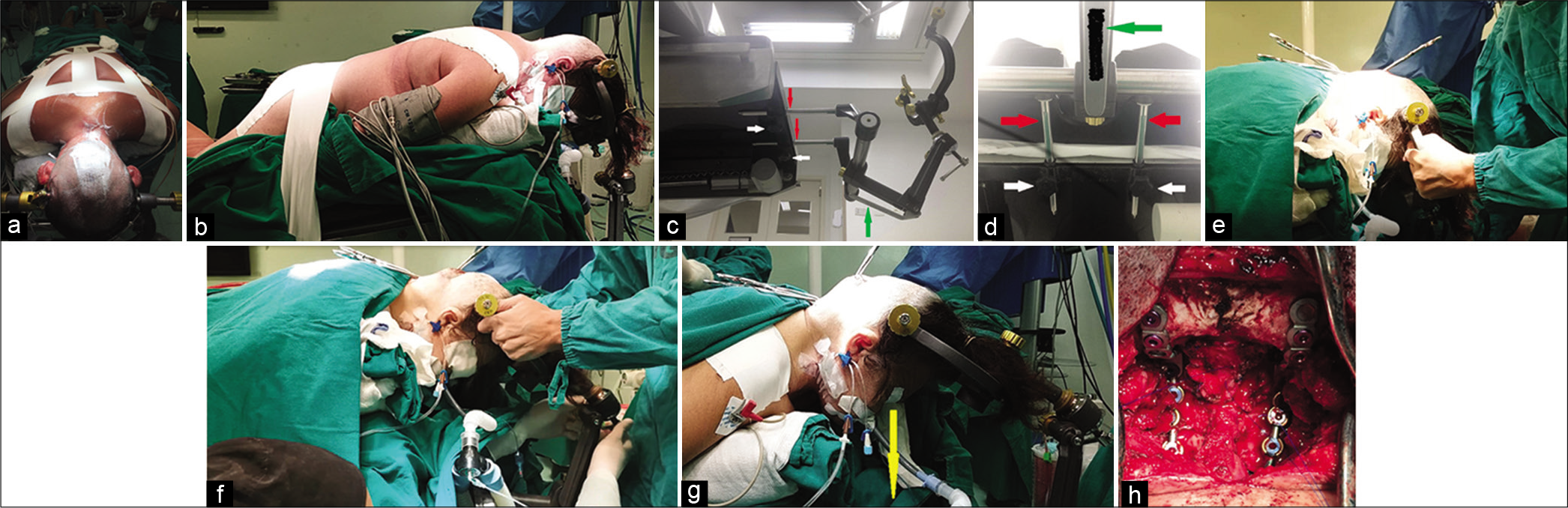
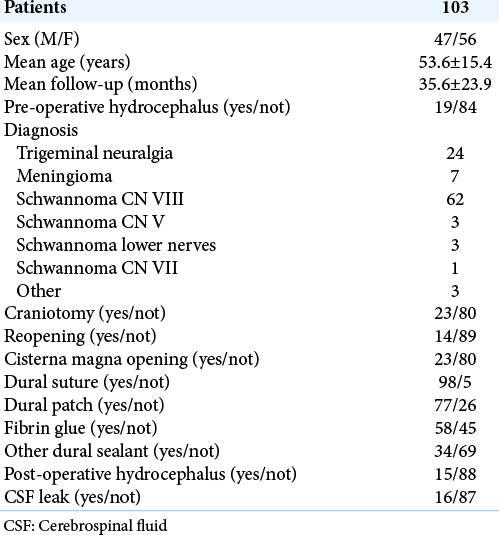
Factors associated with cerebrospinal fluid leak after a retrosigmoid approach for cerebellopontine angle surgery
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: The retrosigmoid approach represents a crucial surgical route to address different lesions in the cerebellopontine angle but cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak still remains the most frequent complication after this approach. Here, we analyzed the impact of different factors in CSF leak development after a retrosigmoid approach. Identifying risk factors related to a specific approach may help the surgeon to tailor the perioperative management and to appropriately counsel patients regarding their risk profile.
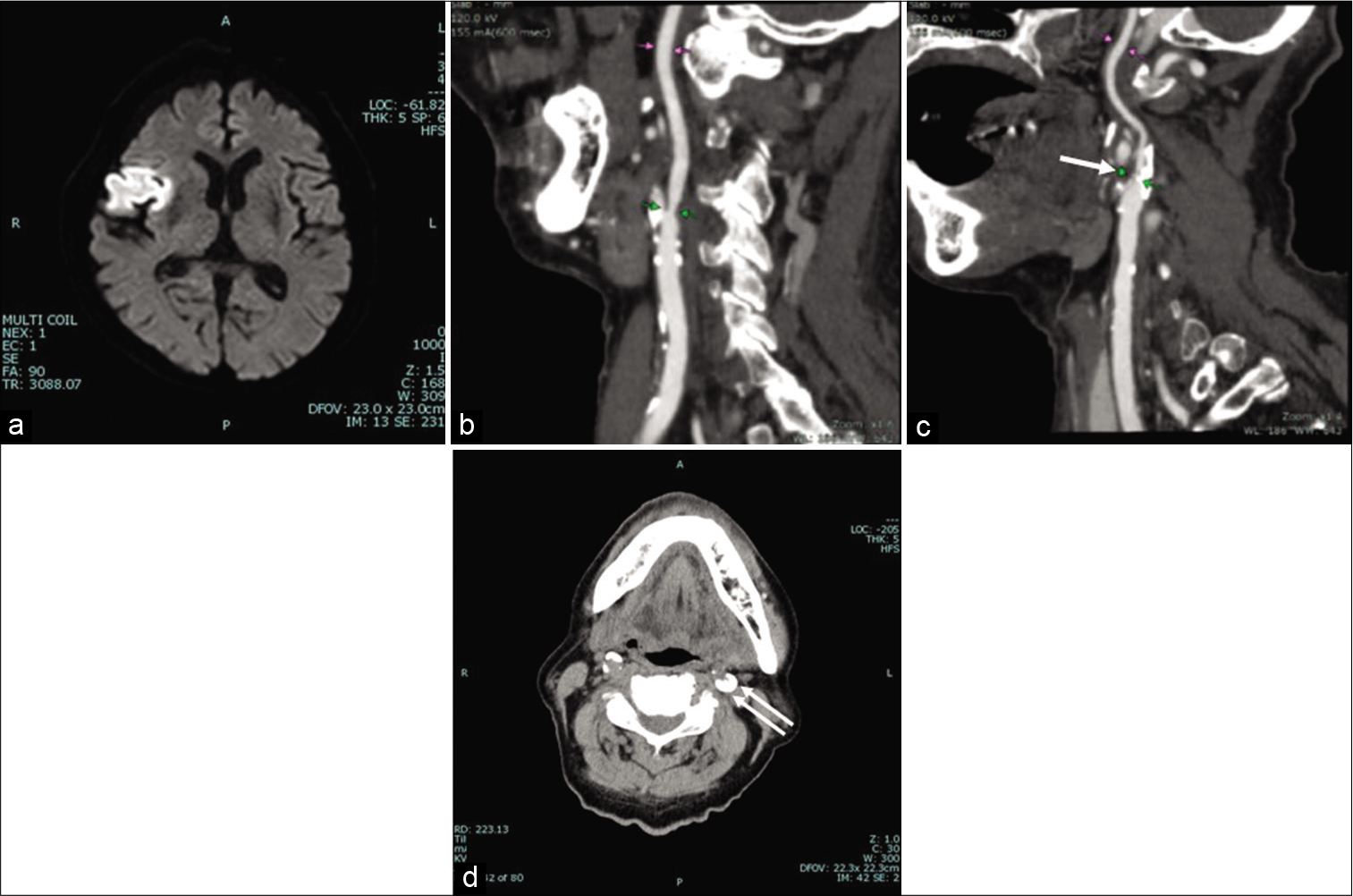
Eagle syndrome presenting as a neurological emergency: A case report
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Eagle syndrome, due to the elongation of the styloid process as well as the calcification of the stylohyoid ligament, rarely presents itself with a major neurological disorder such as a brain infarct.
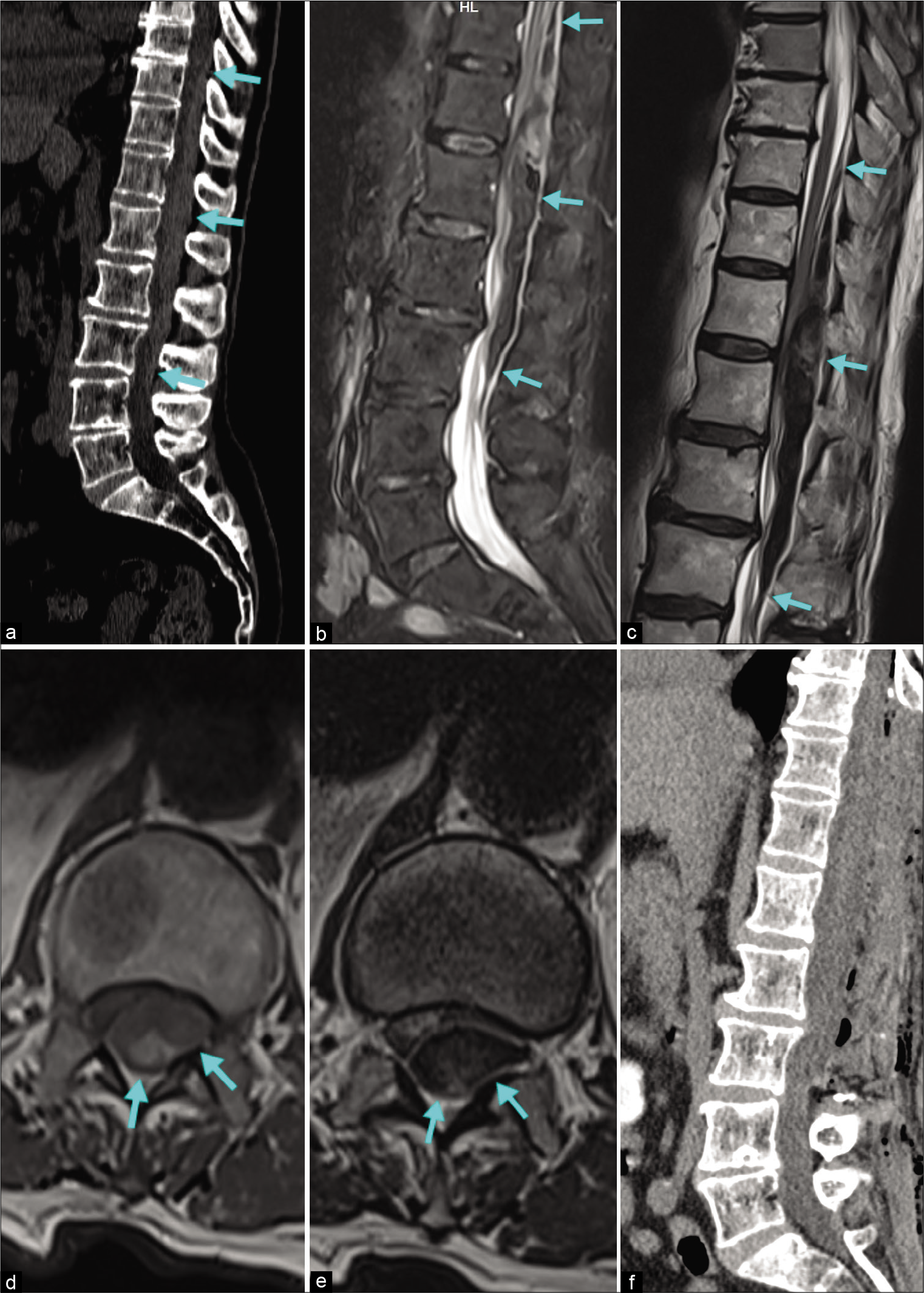
Spontaneous thoracolumbar epidural hematoma in an apixaban anticoagulated patient
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Spontaneous spinal epidural hematomas (SSEHs) are often attributed to anticoagulation. Although they are rare, they may contribute to significant morbidity and mortality.
Severe hemodynamic depression after carotid artery stenting: The problem overcome with a transvenous temporary cardiac pacemaker
Date of publication: 07-Jun-2021
Background: Carotid angioplasty stenting (CAS) may have adverse events including perioperative hemodynamic depression. A transvenous temporary cardiac pacemaker (TTCP) is an option for preventing devastating sequelae due to circulatory failure. An exploration of the predictors of hemodynamic depression following CAS is valuable for selecting candidates for preoperative TTCP implantation before CAS.