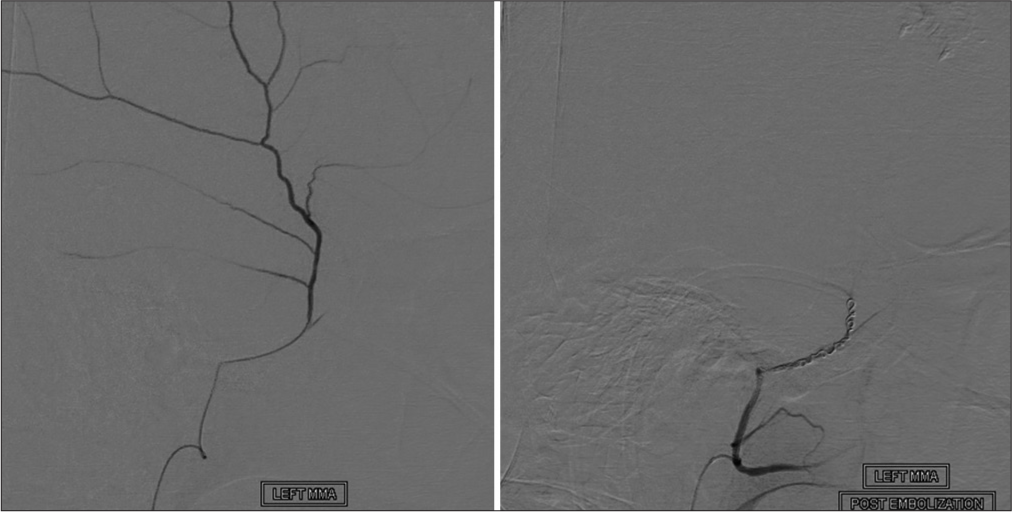
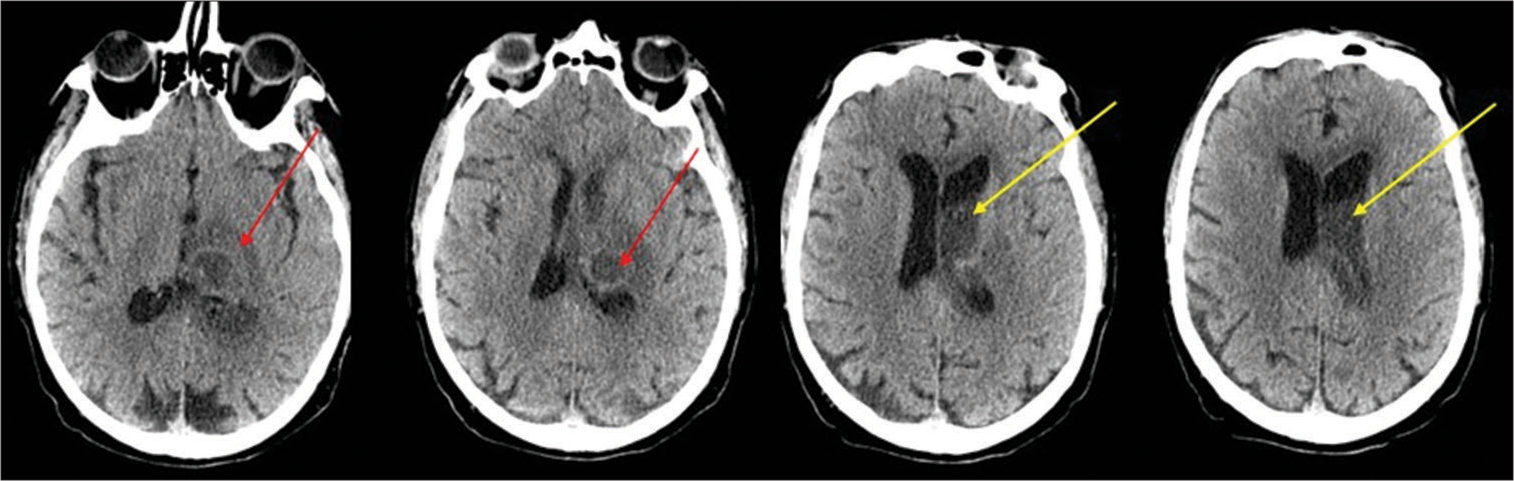
Analysis of middle meningeal artery embolization for the treatment of chronic, acute on chronic, and subacute subdural hematomas
Date of publication: 01-Mar-2024
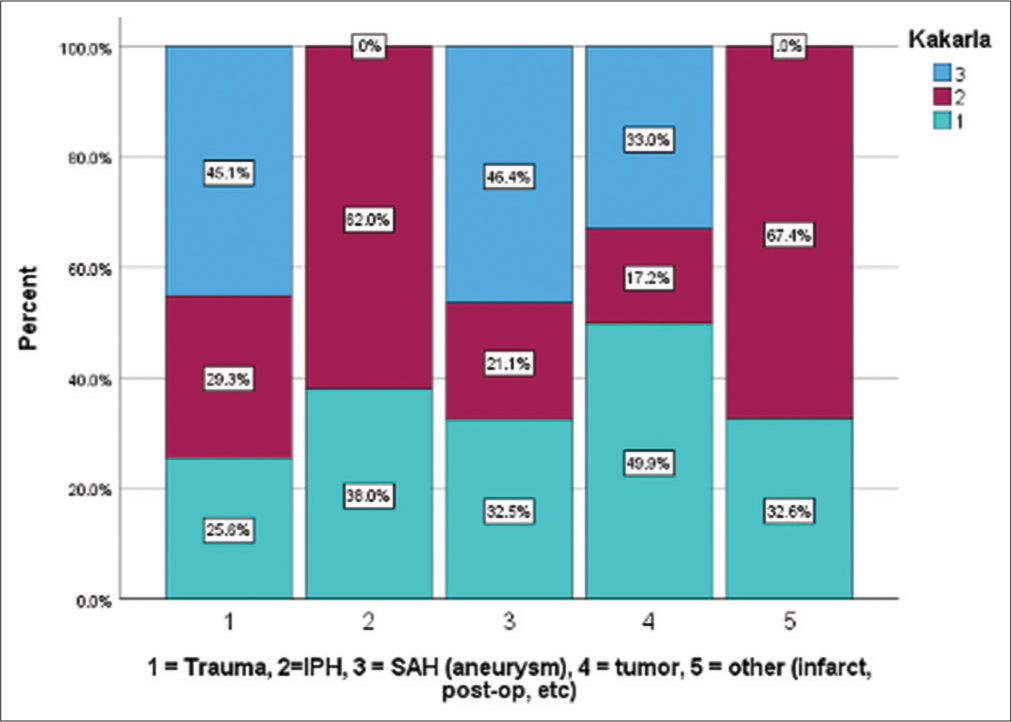
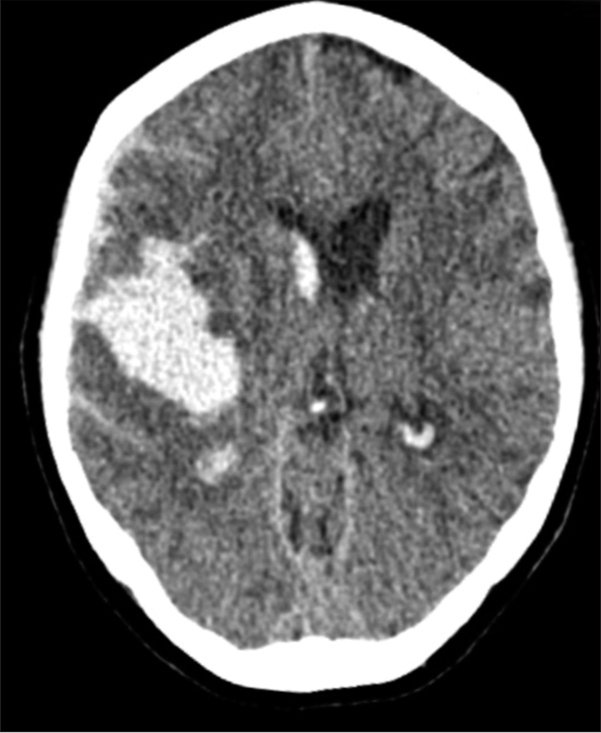
Background: Chronic subdural hematoma (cSDH) is a common sequela of traumatic brain injury. Middle meningeal artery embolization (MMAE) has shown promising results as an emerging minimally invasive alternative treatment. The purpose of this study is to examine the safety and efficacy of MMAE performed in patients with cSDH, acute-on-chronic, and subacute SDH with a traumatic etiology.
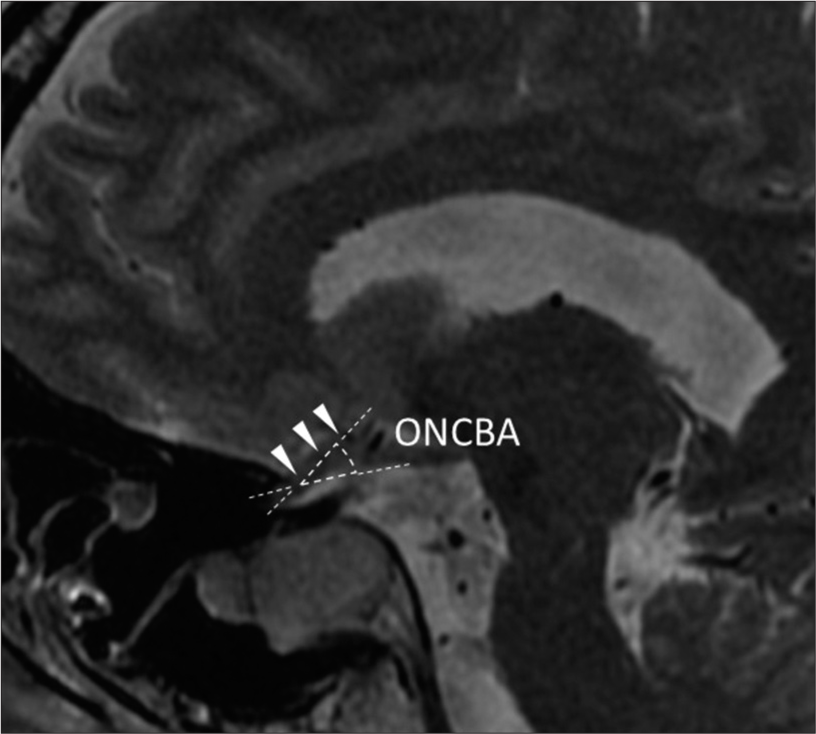
Inferior temporal quadrantanopia associated with pituitary adenomas and a potential mechanism of excessive optic nerve bending
Date of publication: 01-Mar-2024
Background: Pituitary adenomas show typical visual field defects that begin superiorly and progress inferiorly. The cause of atypical visual field defects that start inferiorly remains unclear. This study aimed to understand this phenomenon using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
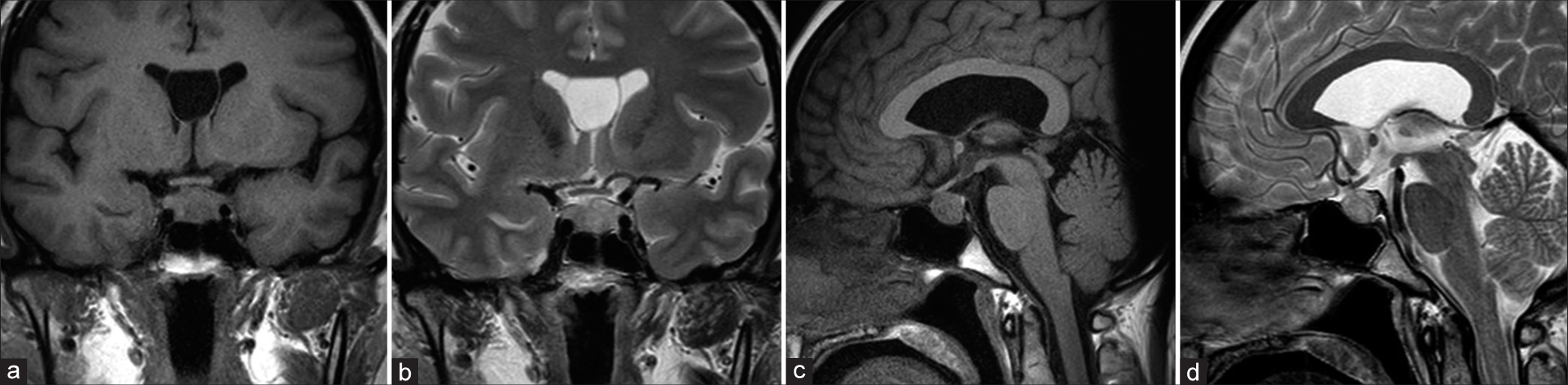
Secondary hypophysitis associated with Rathke’s cleft cyst resembling a pituitary abscess
Date of publication: 01-Mar-2024
Background: Although rare, cases of hypophysitis resembling a pituitary abscess (PA) have been reported. Differential diagnosis between hypophysitis and PA is crucial as the two diseases require different treatments.
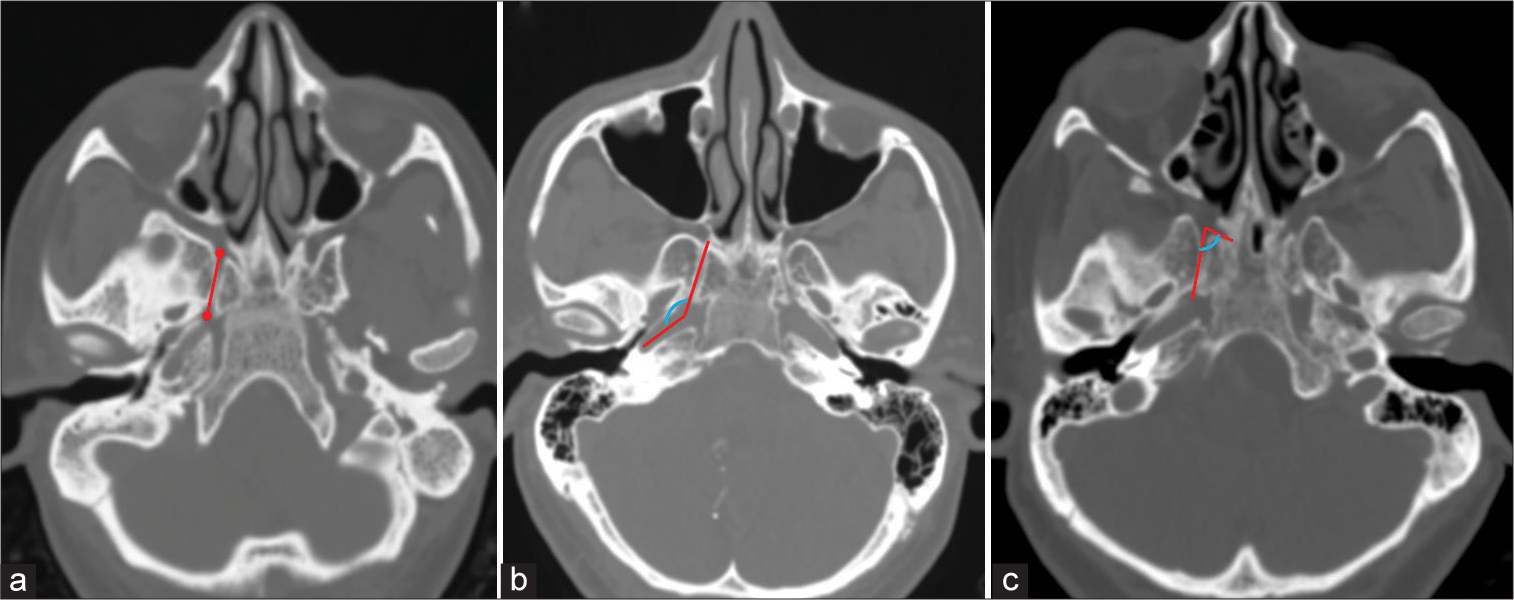
A computed tomography (CT)-based morphometric study of various skull base parameters and their anatomical relationships relevant to endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery
Date of publication: 01-Mar-2024
Background: Endoscopic skull base surgery requires a thorough understanding of skull base anatomy. Orientation to regional anatomy to avoid complications like internal carotid artery injury can be assisted by knowledge of certain bony landmarks. These landmarks are themselves highly variable structures. This study focuses on the radiological morphometric characterization of these landmarks, which can be of great assistance to surgeons for better planning of endoscopic skull base approaches.
Single institution series describing external ventricular drain (EVD) placement and short- and long-term complications related to placement accuracy
Date of publication: 01-Mar-2024
Background: The placement of an external ventricular drain (EVD) for the treatment of acute hydrocephalus is one of the most common life-saving procedures that neurosurgeons perform worldwide. There are many well-known complications associated with EVD placement, including tract hemorrhages, intra-parenchymal and subdural hemorrhages, infection, and catheter misplacement. Given the variety of complications associated with EVD placement and the inconsistent findings on the relationship of accuracy to complications, the present study reviewed short- and long-term complications related to EVD placement at our institution.
A challenging case of endoscopic third ventriculostomy
Date of publication: 01-Mar-2024
Background: Although controversial, endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) in the management of Myelomeningocele and Chiari type II malformation-related hydrocephalous is gaining wider popularity and use. With variable success rates, it can be proposed as a first or second option after shunt malfunction. ETV in post-infectious hydrocephalus may also be considered as an alternative to shunting. With reported success rates of 50–60%, failure is attributed to anatomical reasons and/or to pathological subarachnoid space scarring that may result from infectious processes. Similarly, ETV in repeated shunt malfunctions is an acceptable option that may offer shunt independency. In all situations, case-by-case selection and discussion are to be considered.
Successful relief of central poststroke pain with BurstDR spinal cord stimulation: A case series
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2024
Background: Central poststroke pain (CPSP) is a commonly undertreated condition that can negatively impact a patient’s quality of life. The efficacy of spinal cord stimulation (SCS) for the treatment of CPSP is not established due to limited studies.
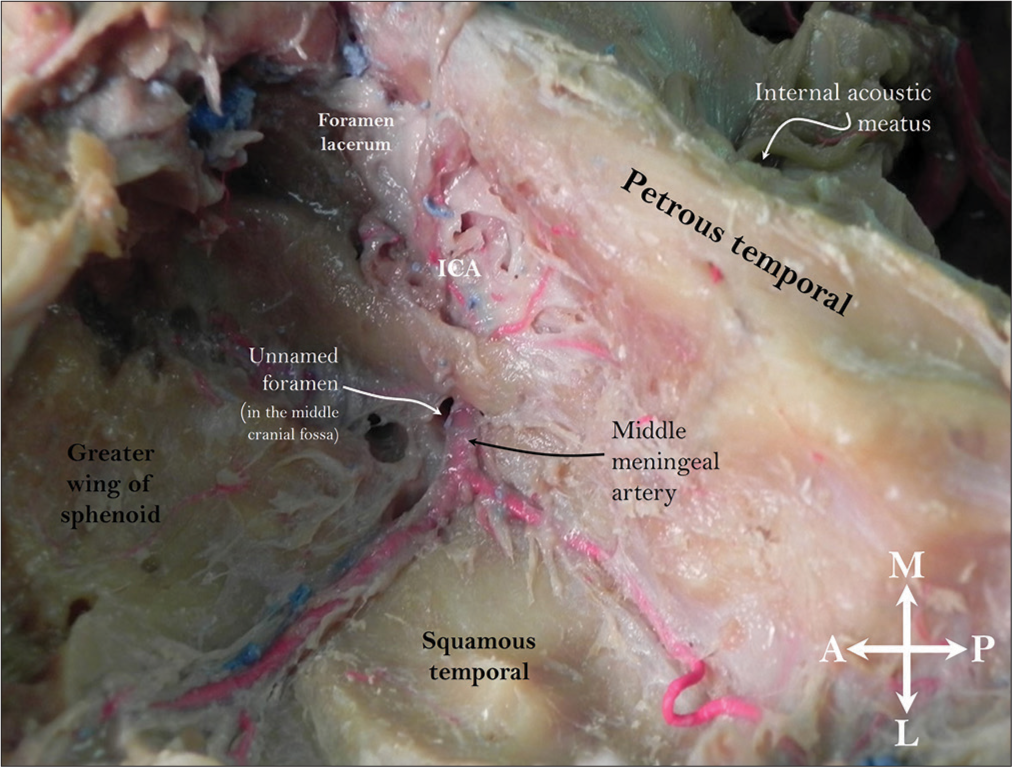
Middle meningeal artery arising from the petrous internal carotid artery: Outcome of unusual stapedial artery regression
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2024
Background: The internal and external carotid arterial systems are generally separate regarding branching patterns. However, these two systems do form collateral circulations with their terminal parts. On rare occasions, branches that belong to one arterial system may arise from the other.
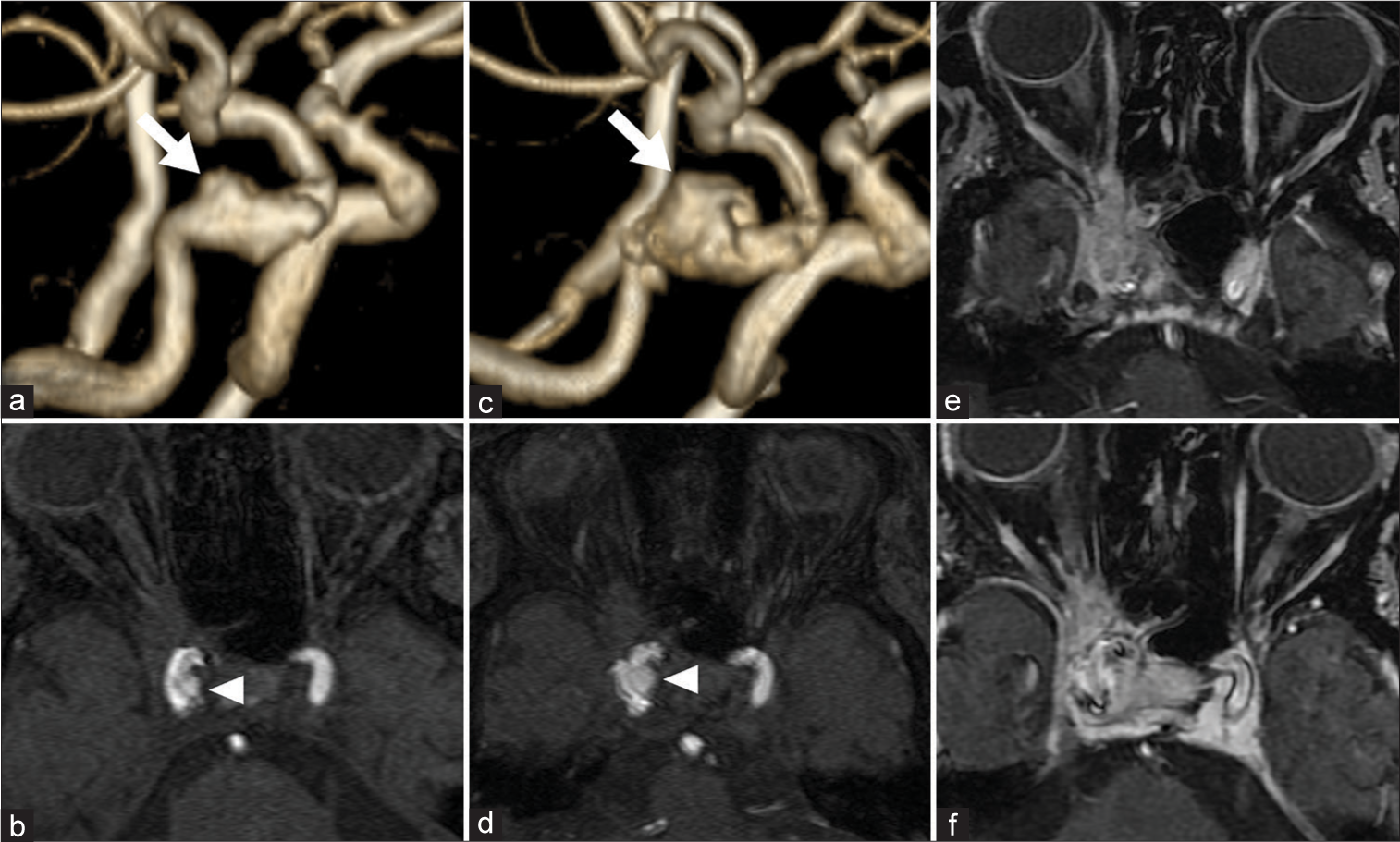
Fungal symptomatic intracranial aneurysm treated with a flow diverting stent: A case report
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2024
Background: Intracranial infectious aneurysms (IIAs) are very rare, and fungal aneurysms are infrequently reported. We report a case of an unruptured IIA caused by fungal rhinosinusitis and treated with a flow-diverting stent.
Stereotactic placement of dual lumen catheter system for continuous drainage, irrigation, and intraventricular antibiotic therapy for treatment of brain abscess with ventriculitis – A case report and literature review
Date of publication: 23-Feb-2024
Background: Cerebral abscesses complicated by ventriculitis present significant treatment challenges, often associated with high morbidity and mortality. Traditional management approaches, including systemic antibiotic therapy and external ventricular drainage (EVD), face limitations due to the blood-brain barrier and risks of catheter-related complications. This report discusses a case where the dual-lumen catheter system, an innovative neurosurgical tool integrating continuous irrigation with drainage, was employed.