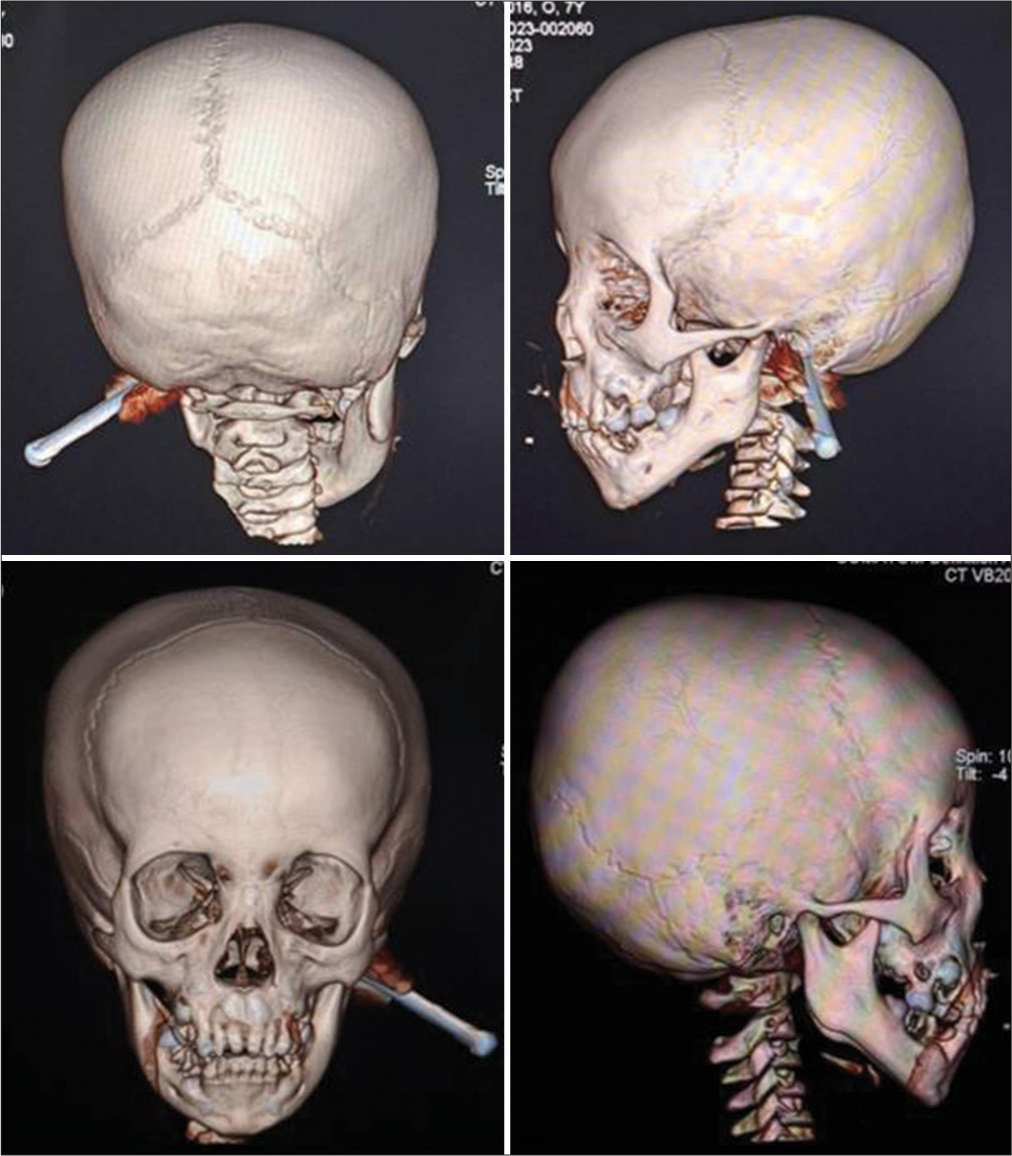
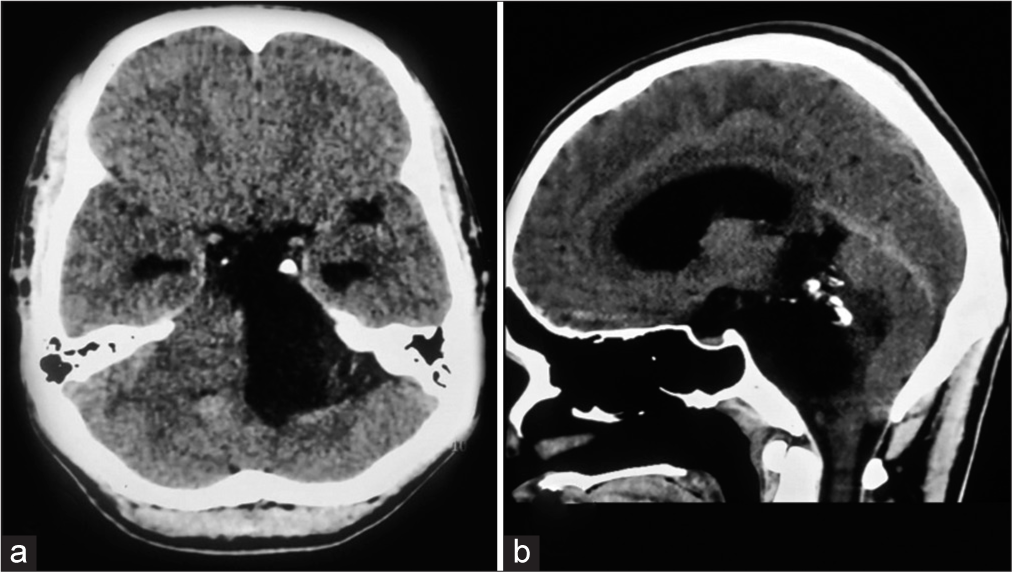
Transmastoid pediatric penetrating brain injury, interdisciplinary, and tailored patient’s treatment
Date of publication: 15-Mar-2024
Background: Pediatric penetrating brain injuries (PBIs) are rare but critical traumatic events, often involving foreign objects. This report will emphasize the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment strategies for pediatric PBI cases.
Comparison of propofol and desflurane for postoperative neurocognitive function in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A prospective randomized trial
Date of publication: 15-Mar-2024
Background: Following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage, 40–50% of survivors experience cognitive dysfunction, which affects their quality of life. Anesthetic agents play a pivotal role in aneurysm surgeries. However, substantial evidence regarding their effects on neurocognitive function is lacking. This study evaluated the effects of propofol and desflurane on postoperative neurocognitive function and serum S-100B levels.
Remote supratentorial intraparenchymal bleed after posterior fossa surgery: A rare occurrence
Date of publication: 15-Mar-2024
Background: Intraparenchymal hemorrhage at the operative site is one of the major complications of brain surgery. It is unusual to occur at a site remote from the operative site, but when it happens, it may cause significant morbidity and mortality.
Assessing the impact of mixed reality-assisted informed consent: A study protocol
Date of publication: 15-Mar-2024
Background: Informed consent is a crucial aspect of modern medicine, but it can be challenging due to the complexity of the information involved. Mixed reality (MR) has emerged as a promising technology to improve communication. However, there is a lack of comprehensive research on the impact of MR on medical informed consent. The proposed research protocol provides a solid foundation for conducting future investigations and developing MR-based protocols that can enhance patients’ understanding and engagement in the decision-making process.
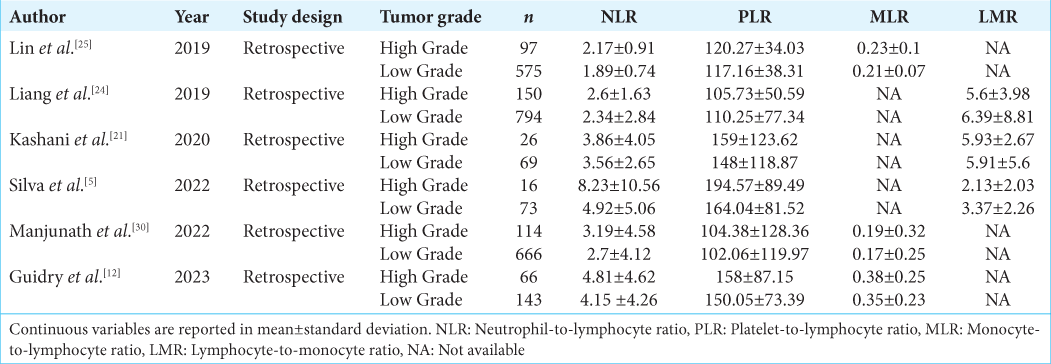
The role of preoperative hematological inflammatory markers as a predictor of meningioma grade: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Date of publication: 08-Mar-2024
Background: Inflammatory processes play an important role in the aggressiveness of a tumor. However, the relationship between inflammatory markers in meningioma grade is not well known. Knowledge of preoperative meningioma grade plays an important role in the prognosis and treatment of this tumor. This study aims to assess preoperative hematological inflammatory markers as a predictor of the pathological grade of meningioma.
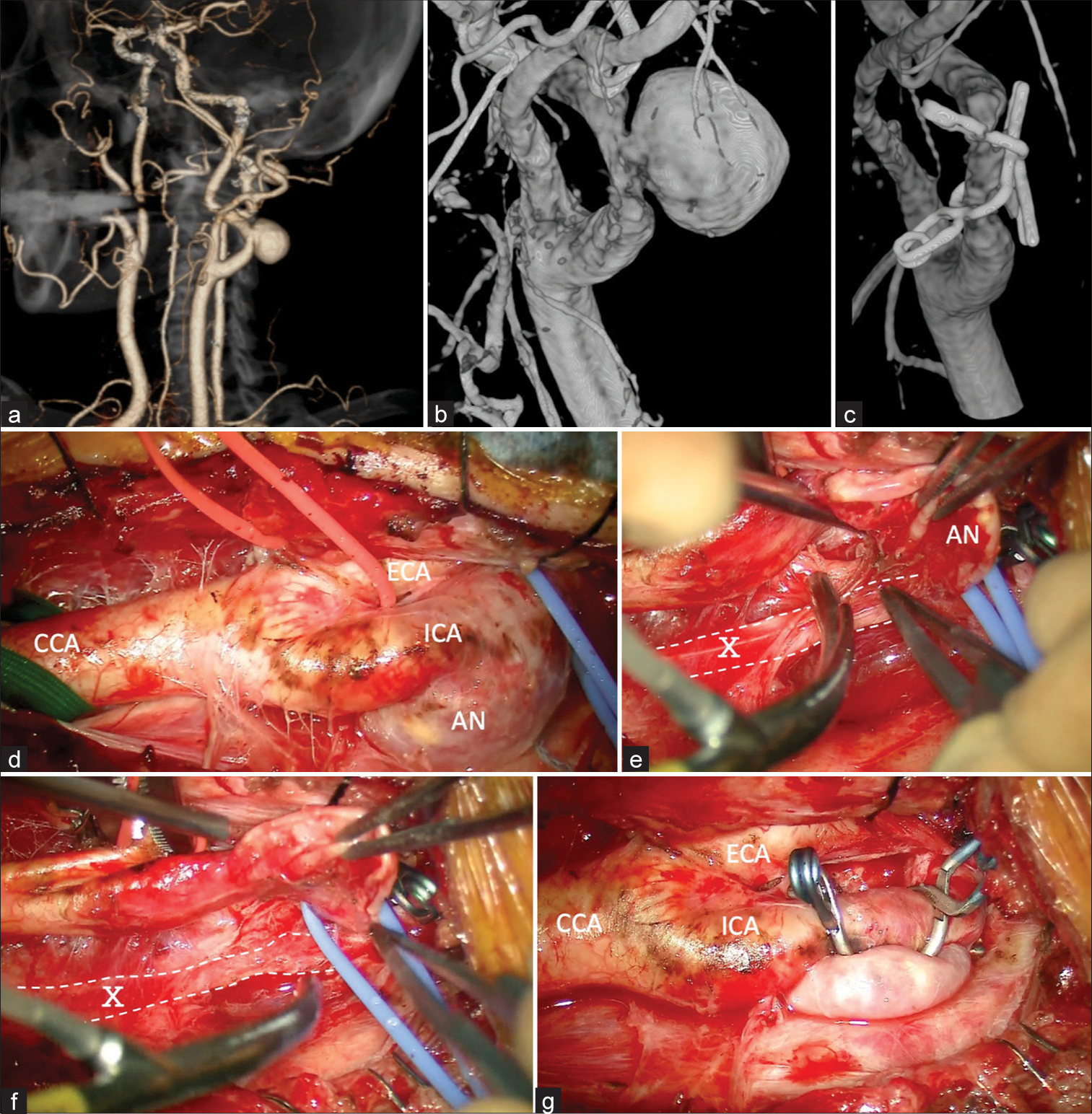
A technique for reconstruction of a giant extracranial internal carotid artery aneurysm: A technical note
Date of publication: 08-Mar-2024
Background: Surgery is effective for extracranial internal carotid artery (EICA) aneurysms. However, the risk of cranial nerve injury associated with surgical repair, such as graft-assisted resection and extracranial-intracranial bypass techniques, is relatively high. Here, we report two cases of surgical treatment for EICA aneurysms and describe the surgical techniques and strategies to avoid cranial nerve injury.
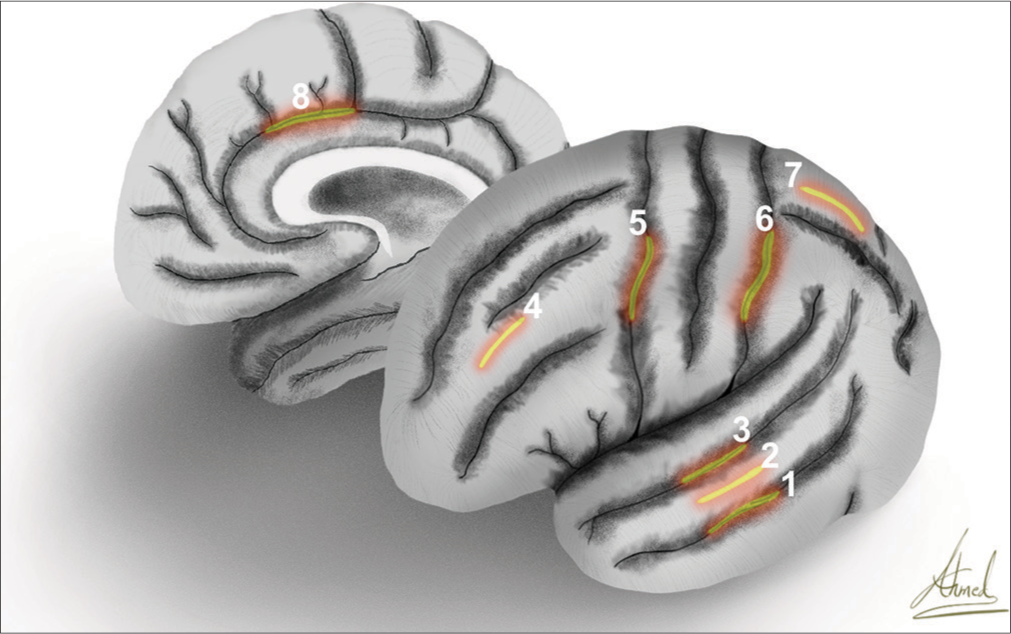
Cortical incisions and transcortical approaches for intra-axial and intraventricular lesions: A scoping review
Date of publication: 08-Mar-2024
Background: Transcortical approaches, encompassing various surgical corridors, have been employed to treat an array of intraparenchymal or intraventricular brain pathologies, including tumors, vascular malformations, infections, intracerebral hematomas, and epileptic surgery. Designing cortical incisions relies on the lesion location and characteristics, knowledge of eloquent functional anatomy, and advanced imaging such as tractography. Despite their widespread use in neurosurgery, there is a noticeable lack of systematic studies examining their common lobe access points, associated complications, and prevalent pathologies. This scoping review assesses current evidence to guide the selection of transcortical approaches for treating a variety of intracranial pathologies.
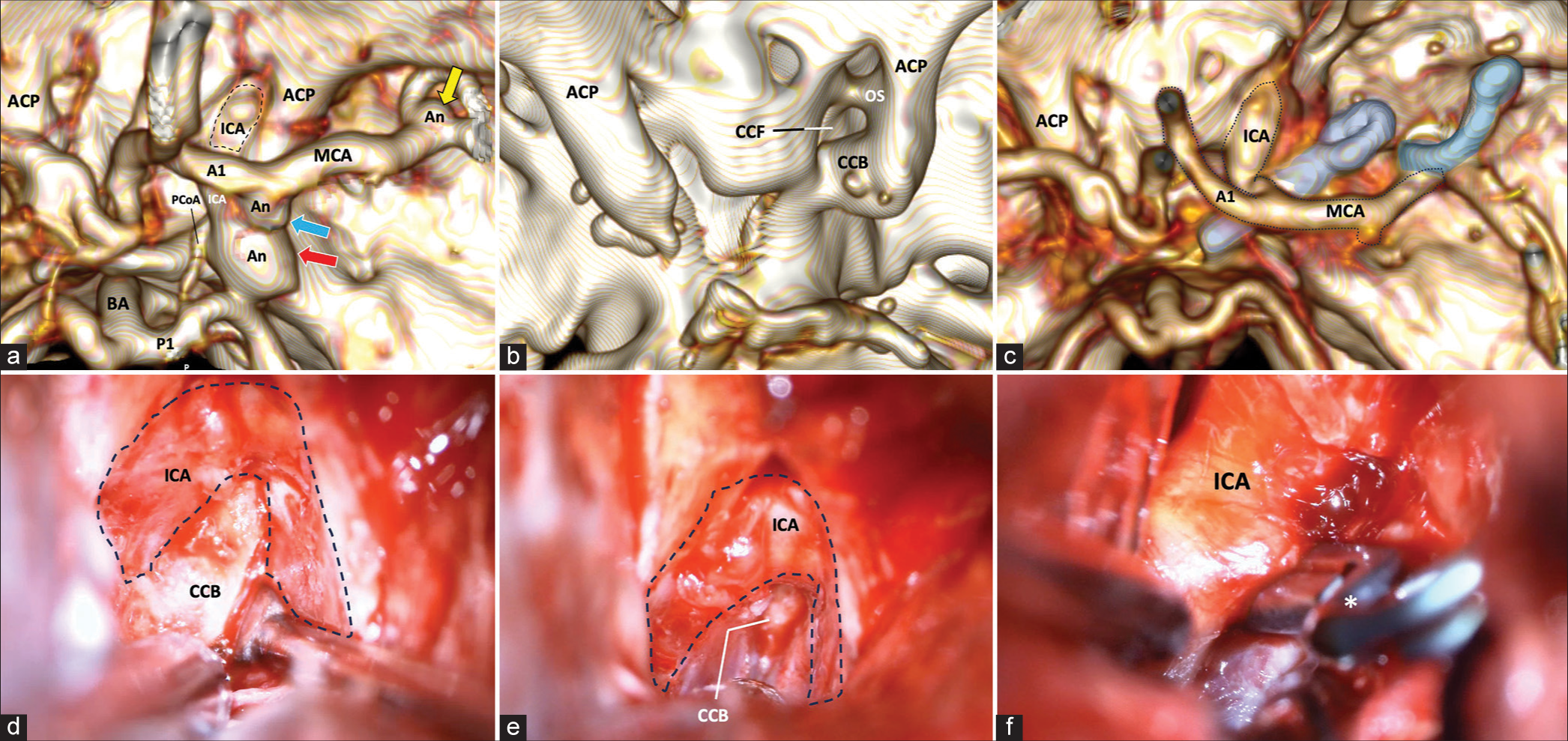
Bone anatomic variations of the parasellar region and its technical implications in para clinoid and posterior communicating segment aneurysms microsurgical clipping – Technical note
Date of publication: 08-Mar-2024
Background: Microsurgical treatment of paraclinoid aneurysms is a complex task that generally requires anterior clinoid process (ACP) removal to obtain adequate surgical exposure. This procedure poses a considerable technical difficulty due to the association of the ACP to critical neurovascular structures. Furthermore, anatomical variations in the parasellar region, such as the caroticoclinoid foramen (CCF) or an interclinoid bridge (ICB), may impose additional challenges and increase surgical complications. The present study aims to briefly review some anatomic variations in the parasellar region and describe a step-by-step surgical technique for a hybrid anterior clinoidectomy based on the senior author’s experience.
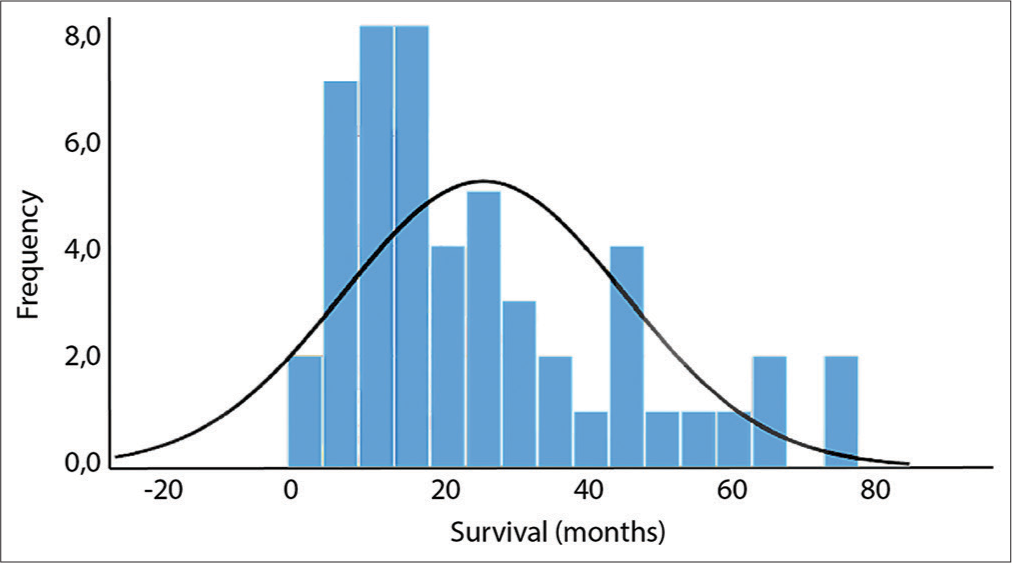
Analysis of prognostic factors and the role of epilepsy in neurosurgical patients with brain metastases
Date of publication: 08-Mar-2024
Background: Brain metastases (BMs) represent the most frequent brain tumors in adults. The identification of key prognostic factors is essential for choosing the therapeutic strategy tailored to each patient. Epilepsy can precede several months of other clinical presentations of BMs. This work aimed to study the impact of epilepsy and other prognostic factors on BMs patients’ survival.
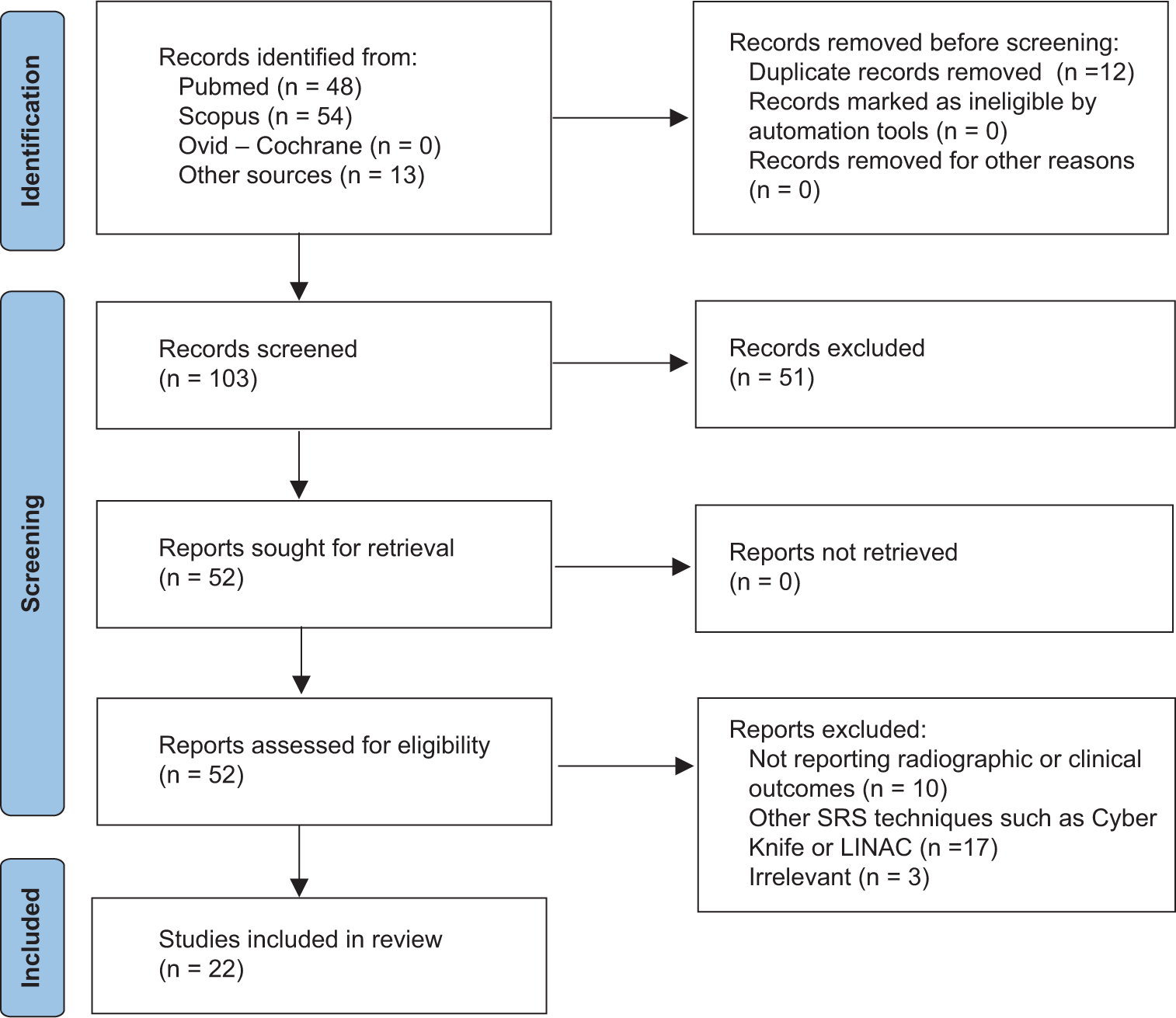
Gamma Knife radiosurgery for the management of glomus jugulare tumors: A systematic review and report of the experience of a radioneurosurgery unit in Latin America
Date of publication: 08-Mar-2024
Background: Glomus jugulare tumors (GJTs) are rare and mainly affect women between the 5th and 6th decades of life. Its localization and anatomic relationships make conventional surgical treatment difficult and with a considerable risk of complications. This manuscript aims to describe the results of Gamma Knife radiosurgery (GKR) in patients with GJT treated in a single center in Latin America, as well as to systematically review the literature to determine the clinical and radiological effectiveness of this technique.