Intracranial malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor: A case report and comprehensive literature review
Date of publication: 22-Mar-2024
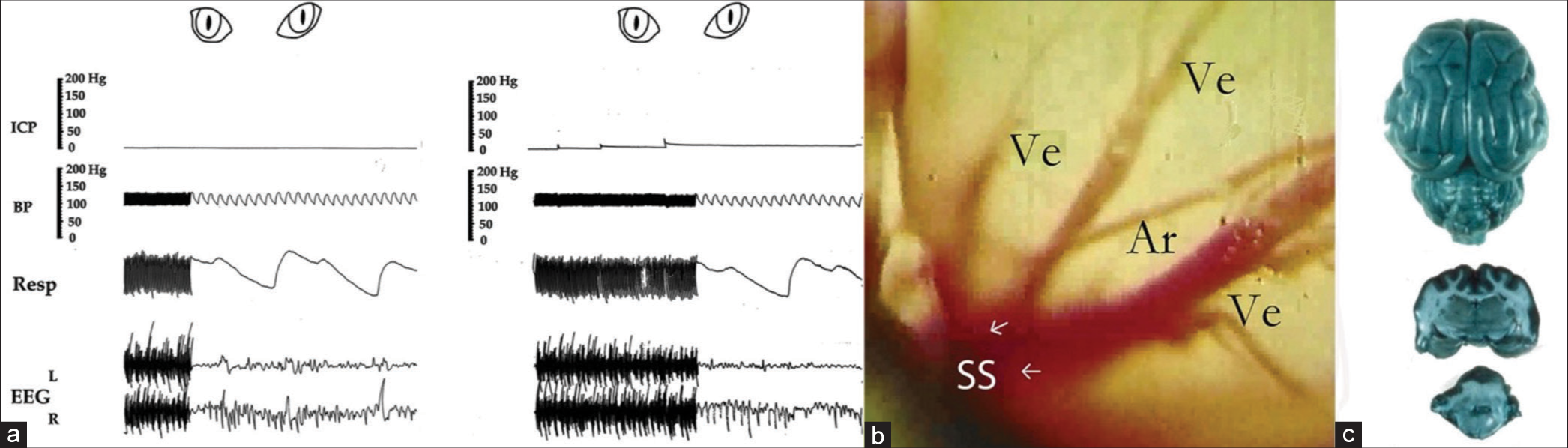
Background: Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs) are rare malignant soft-tissue sarcomas arising from peripheral nerves. Little data exist regarding MPNST originating intracranially. Here, we present a 7th/8th nerve complex MPNST, discuss the treatment strategy and patient outcome, and provide a comprehensive review of existing literature.
Secondary normal pressure hydrocephalus following pituitary apoplexy: A case report
Date of publication: 22-Mar-2024
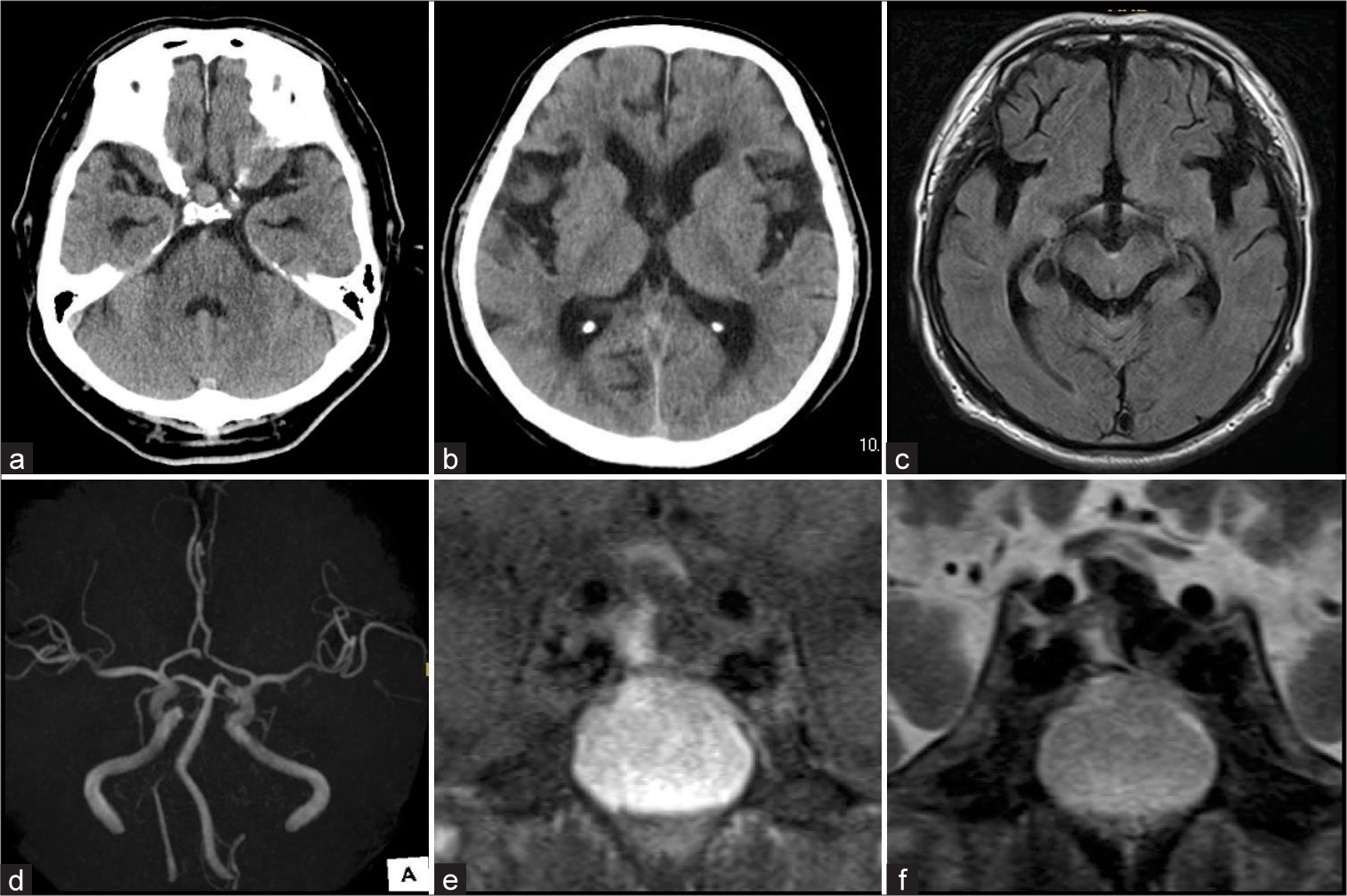
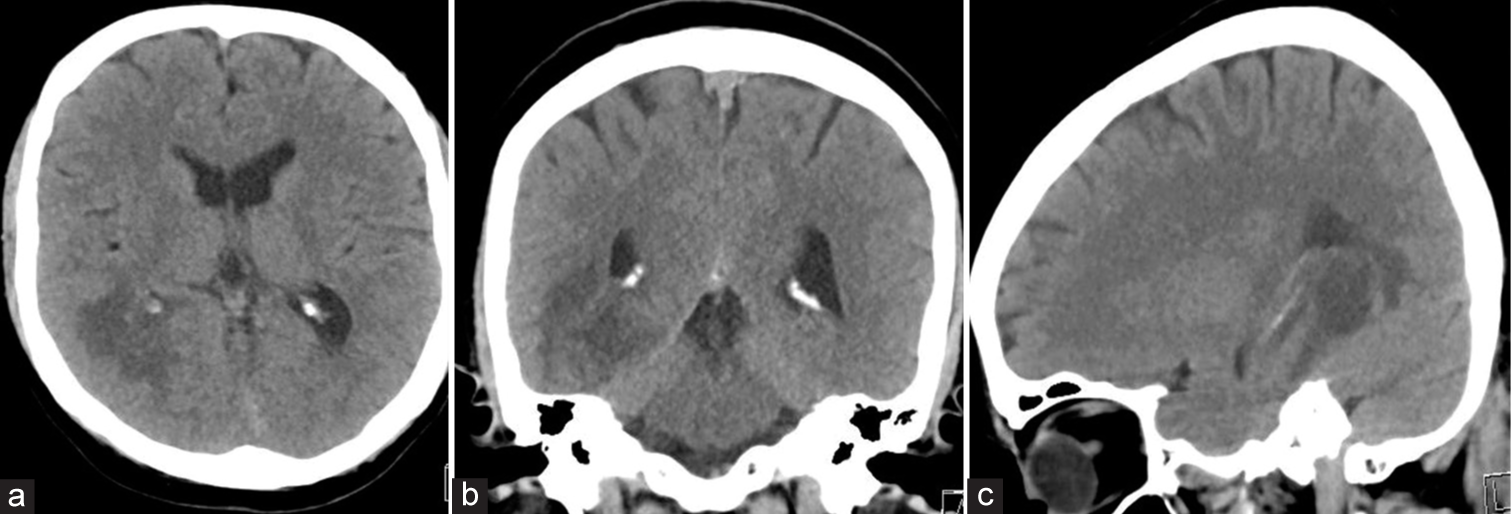
Background: Although secondary normal pressure hydrocephalus (sNPH) can occur in various central nervous system diseases, there are no reports of sNPH caused by pituitary lesions. Herein, we present a unique case of sNPH caused by pituitary apoplexy.
A case report of an unusual cerebral hydatid cyst
Date of publication: 22-Mar-2024
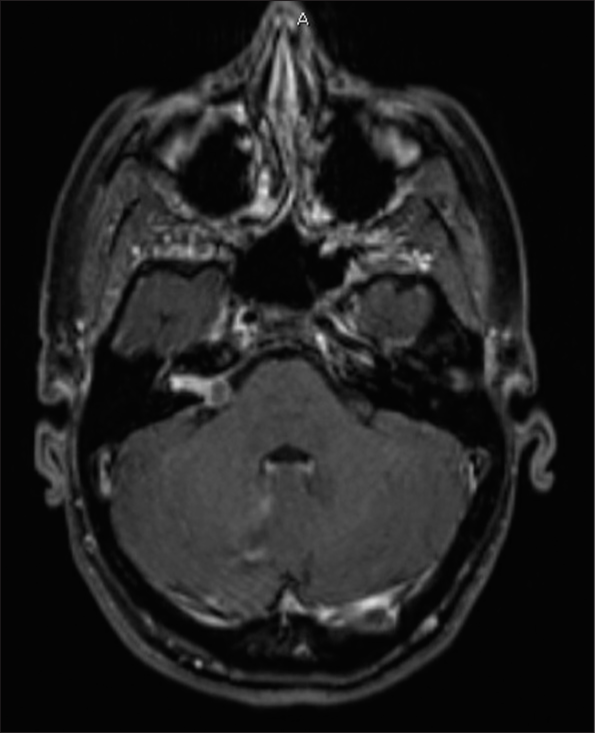
Background: Intracranial hydatid cyst is an exceedingly uncommon condition. Typically, it manifests as hydatid cysts in the liver, lungs, kidney, and spleen. In this report, we present a rare case of a hydatid cyst located in the brain, exhibiting atypical radiological characteristics, and successfully treated with complete microsurgical excision.
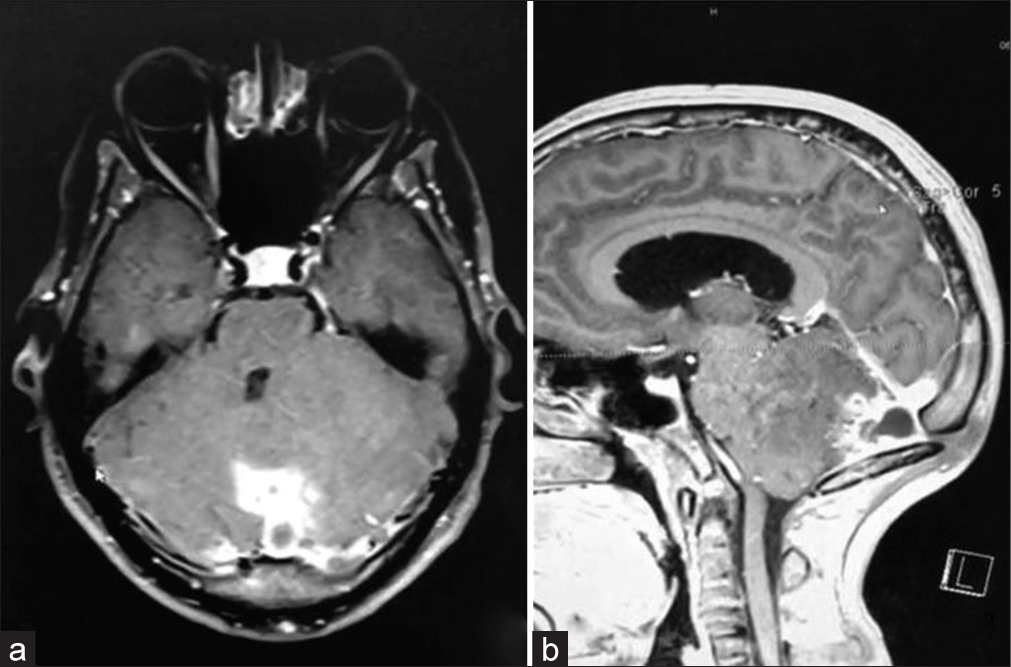
Spontaneous thrombosis and calcification of giant cavernous carotid artery aneurysm: A rare case and management insights
Date of publication: 22-Mar-2024
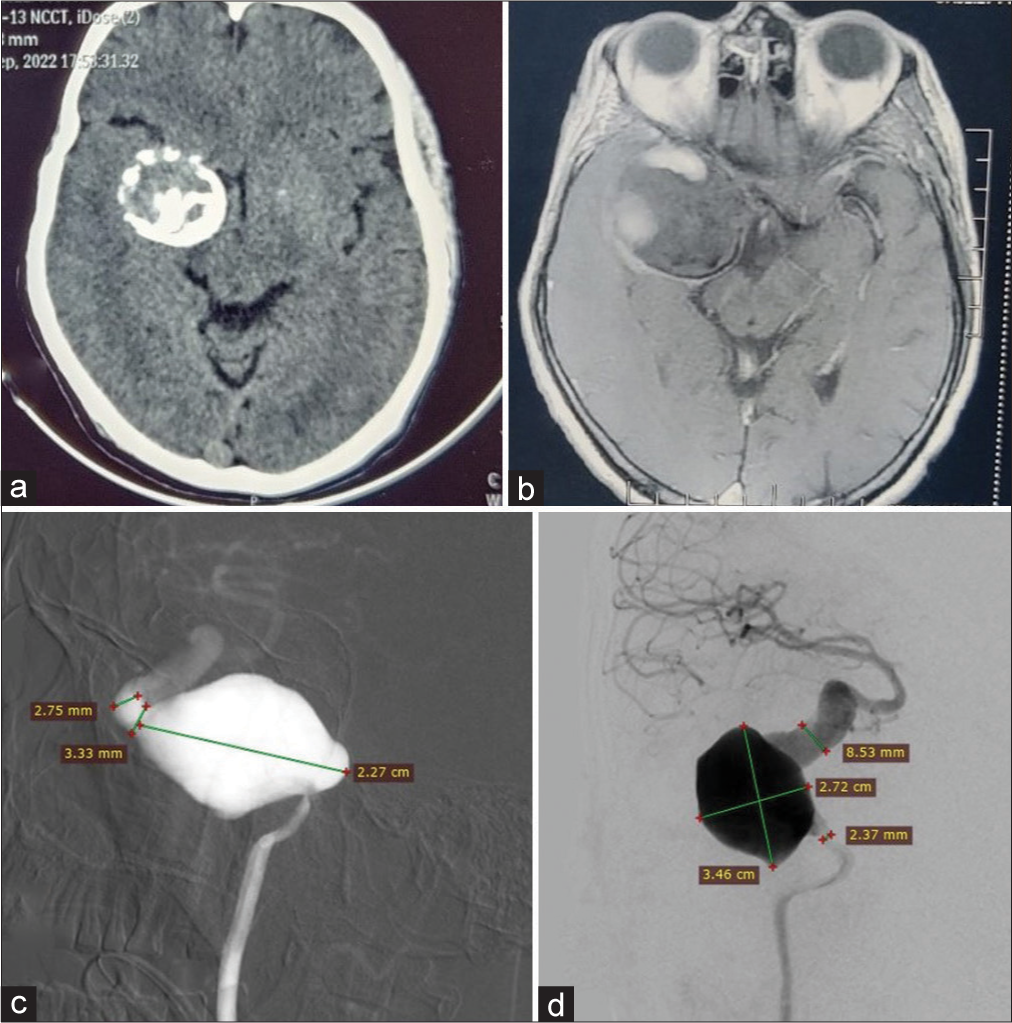
Background: Giant cavernous carotid artery aneurysms (>25 mm) are rare (3–5%), with some prone to spontaneous thrombosis (10–20% complete). We present a unique case of one of the largest aneurysms spontaneously thrombosing and calcifying.
Perspective: How can risks to patients be limited during spine surgeons’ learning curves?
Date of publication: 22-Mar-2024
Background: Learning curves (LC) are typically defined by the number of different spinal procedures surgeons must perform before becoming “proficient,” as demonstrated by reductions in operative times, estimated blood loss (EBL), length of hospital stay (LOS), adverse events (AE), fewer conversions to open procedures, along with improved outcomes. Reviewing 12 studies revealed LC varied widely from 10-44 cases for open vs. minimally invasive (MI) lumbar diskectomy, laminectomy, transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF), anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF), and oblique/extreme lateral interbody fusions (OLIF/XLIF). We asked whether the risks of harm occurring during these LC could be limited if surgeons routinely utilized in-person/intraoperative mentoring (i.e., via industry, academia, or well-trained colleagues).
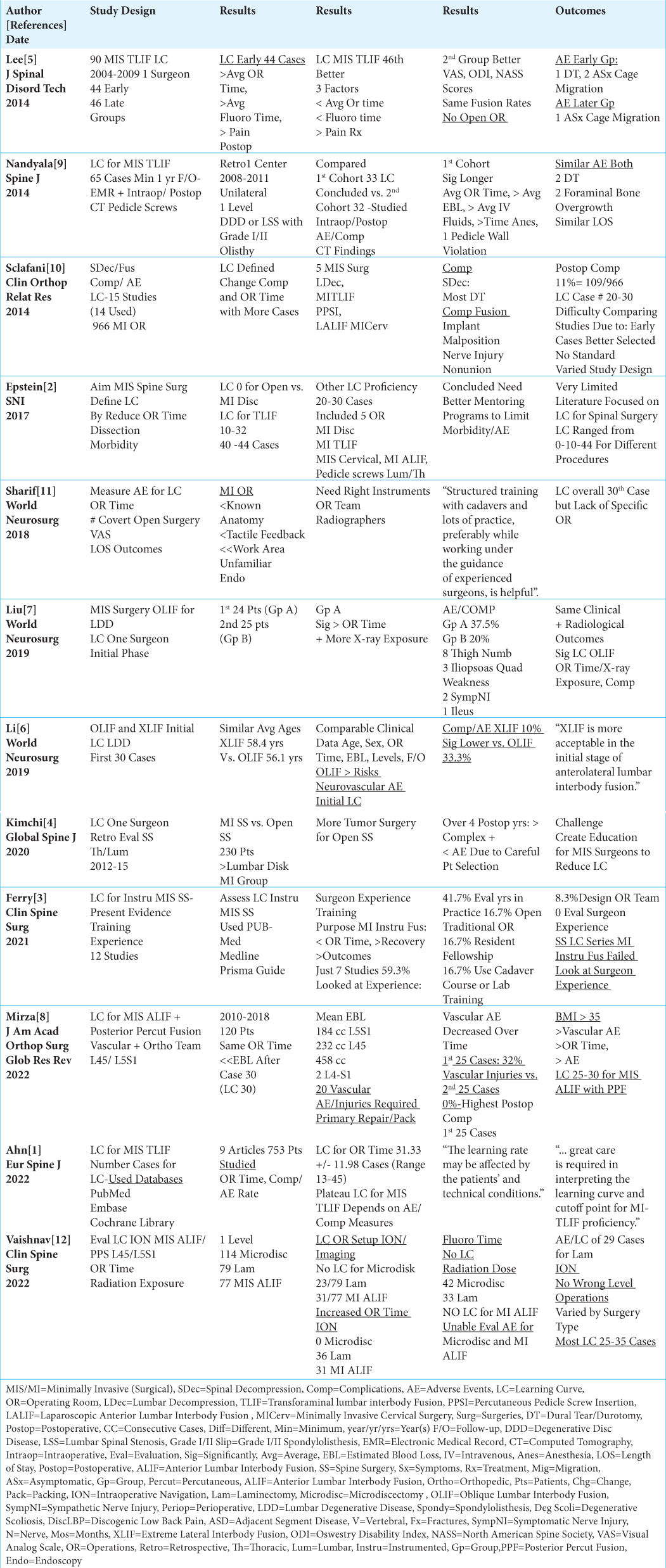
Correlation of cerebral microvascular circulation with vital signs in cerebral compression and the validity of three concepts: vasodilation, autoregulation, and terminal rise in arterial pressure
Date of publication: 22-Mar-2024
Background: Vasodilation, autoregulation, and rising arterial pressure are three common concepts in cerebral compression, believed to improve cerebral blood flow to maintain the brain’s nutrition. However, these concepts are unclear, unproven, and based on assumptions. This study aimed to correlate cerebral circulation with alterations of vital signs and to evaluate the above concepts based on physics and hemodynamics.
Occipital dermal sinus associated with infectious teratoma in an adult patient affected by Klippel–Feil syndrome: Rare case report and literature review
Date of publication: 22-Mar-2024
Background: The Klippel–Feil syndrome (KFS) is a rare congenital anomaly characterized by the fusion of cervical vertebrae, which may be associated with other malformations, such as dermoid tumors and teratoma. Some theories explain the embryology of these associations. Another condition that may be present is the dermal sinus (DS), communication between intracranial tumors and the subcutaneous tissue, and predisposing infections. This case report aims to describe an association between these three pathologies as well as correlate them from the literature. This report was based on medical records retrospectively reviewed associated with the systematic bibliographical consultation using indexed databases based on inclusion and exclusion methods.
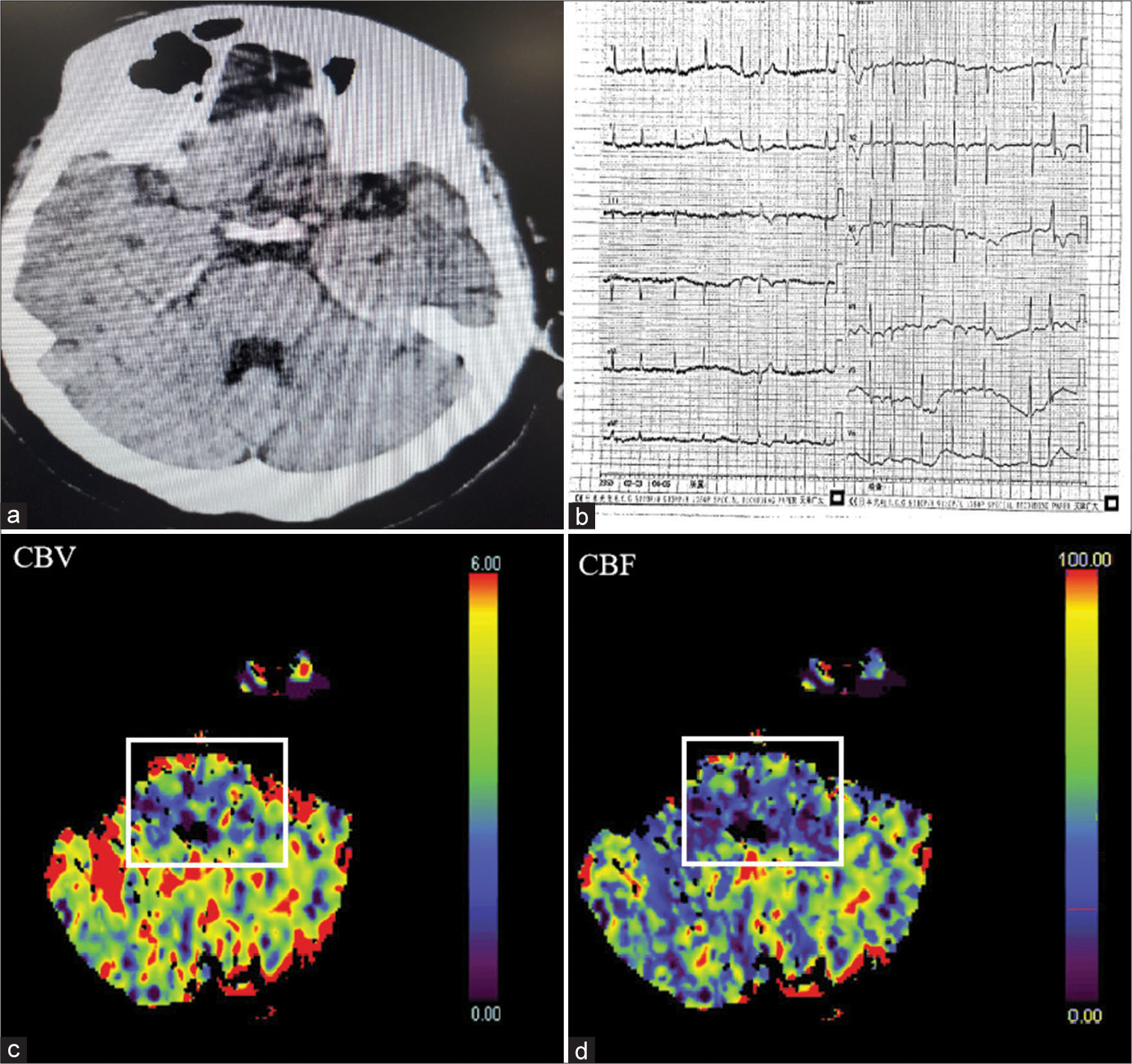
Comparison of propofol and desflurane for postoperative neurocognitive function in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A prospective randomized trial
Date of publication: 15-Mar-2024
Background: Following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage, 40–50% of survivors experience cognitive dysfunction, which affects their quality of life. Anesthetic agents play a pivotal role in aneurysm surgeries. However, substantial evidence regarding their effects on neurocognitive function is lacking. This study evaluated the effects of propofol and desflurane on postoperative neurocognitive function and serum S-100B levels.
Successful endovascular thrombectomy using solitaire FR stent with intermediate catheter assisting technique for acute persistent primitive trigeminal artery and basilar artery occlusion: A case report and literature review
Date of publication: 15-Mar-2024
Background: The persistent primitive trigeminal artery (PPTA) is a persistent embryological carotid-basilar connection. Endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) for hypoplastic PPTA occlusion is a challenge. This case report aims to describe the successful recanalization of simultaneous occlusions in both the PPTA and basilar artery (BA) using the Solitaire FR (RECO SR)/Stent and Intermediate Catheter Assisting (SWIM) technique in a patient with acute cardiogenic cerebral embolism. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of such a case.
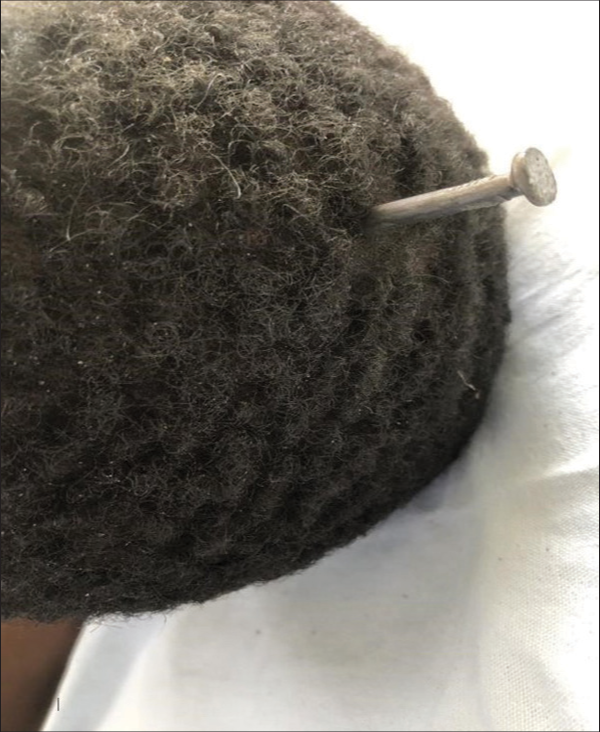
Penetrating head trauma resulting from vigilante street justice
Date of publication: 15-Mar-2024
Background: Penetrating brain injury (PBI) can be caused by a variety of objects ranging from simple to complicated items. Nonetheless, it is strange and unusual to attack someone in the head with a long nail. Due to its rarity, care for them is still being developed and may include many steps.