Cerebral infarction following administration of andexanet alfa for anticoagulant reversal in a patient with traumatic acute subdural hematoma
Date of publication: 11-Aug-2023
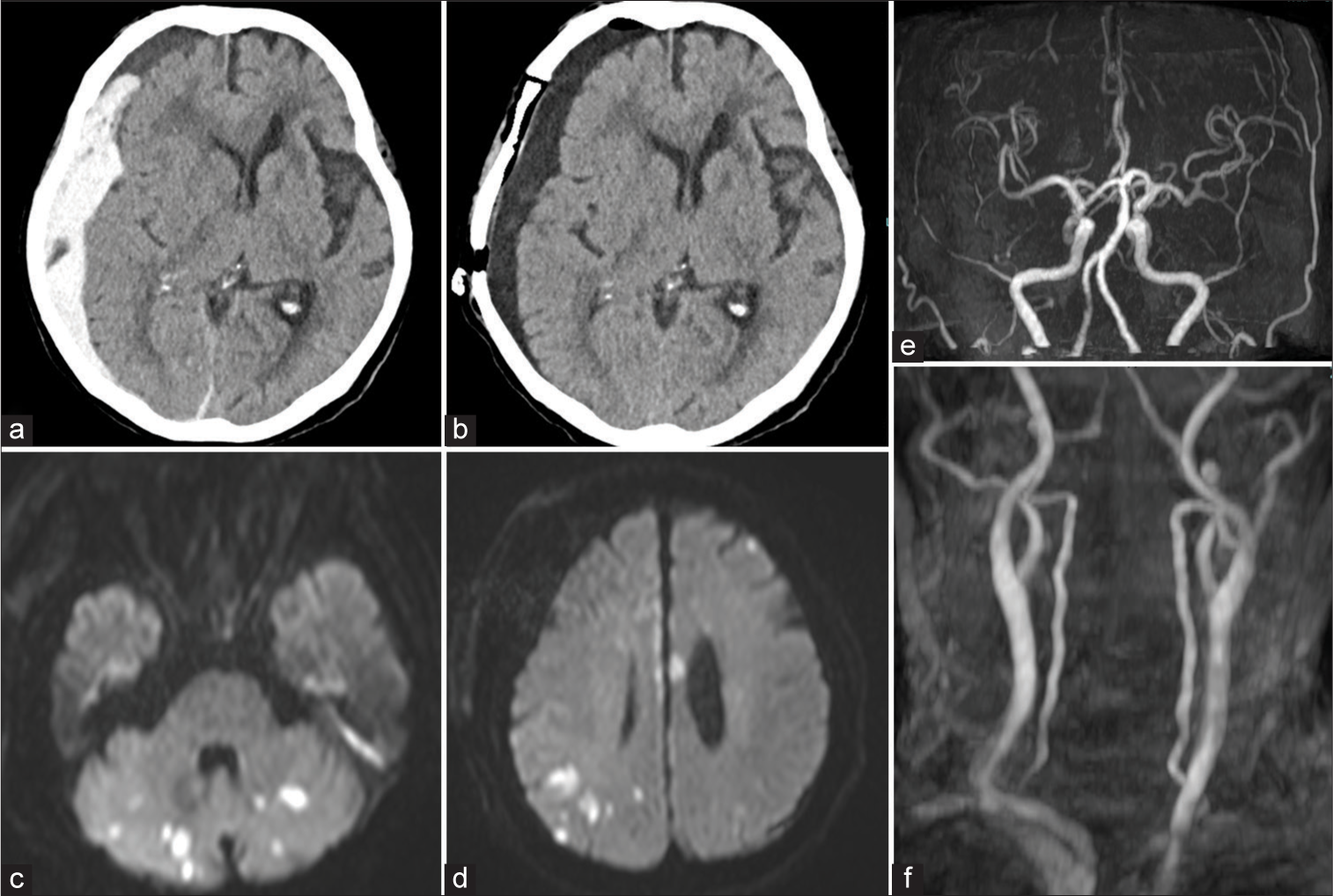
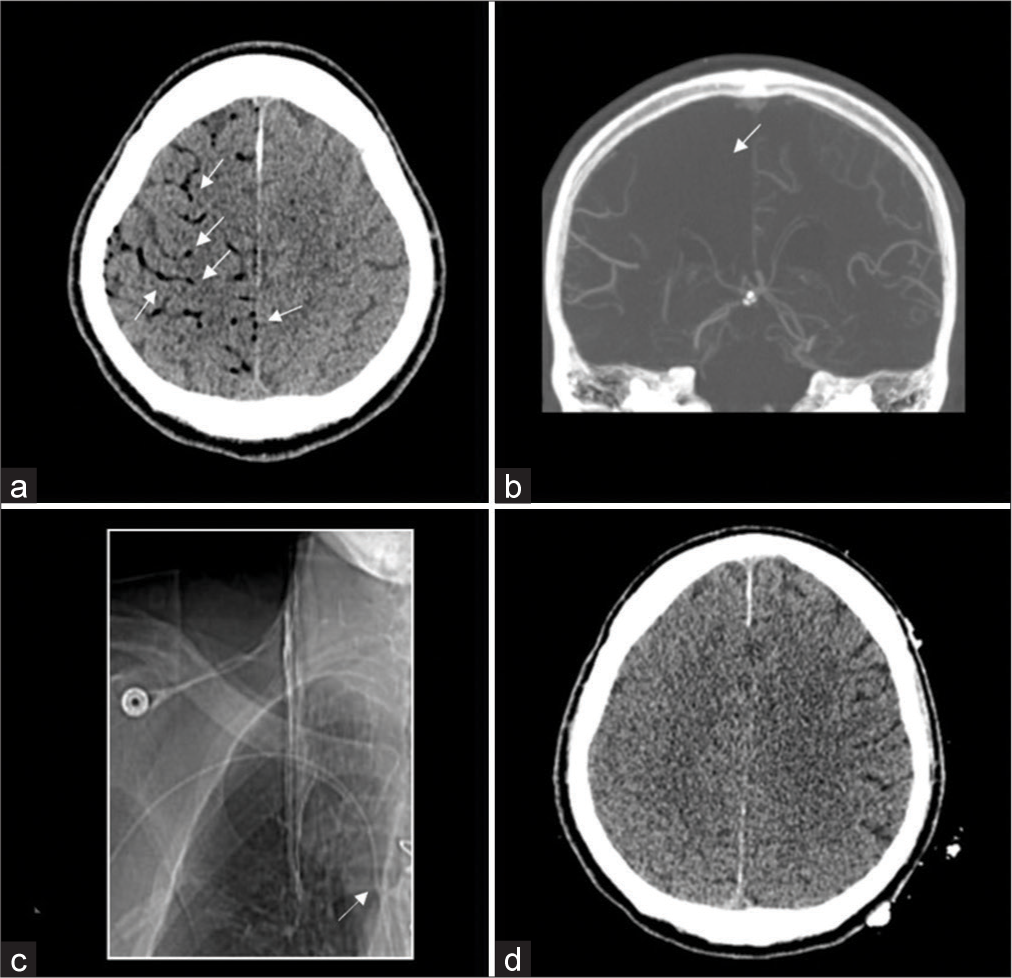
Background: Anticoagulants prevent thrombosis in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and venous thromboembolism but increase the risk of hemorrhagic complications. If severe bleeding occurs with anticoagulant use, discontinuation and rapid reversal are essential. However, the optimal timing for resuming anticoagulants after using reversal agents remains unclear. Here, we report early cerebral infarction following the use of andexanet alfa (AA), a specific reversal agent for factor Xa inhibitors, in a patient with traumatic acute subdural hematoma (ASDH). The possible causes of thromboembolic complication and the optimal timing for anticoagulant resumption are discussed.
Acute and subacute neurovascular impact of cryptogenic air emboli
Date of publication: 11-Aug-2023
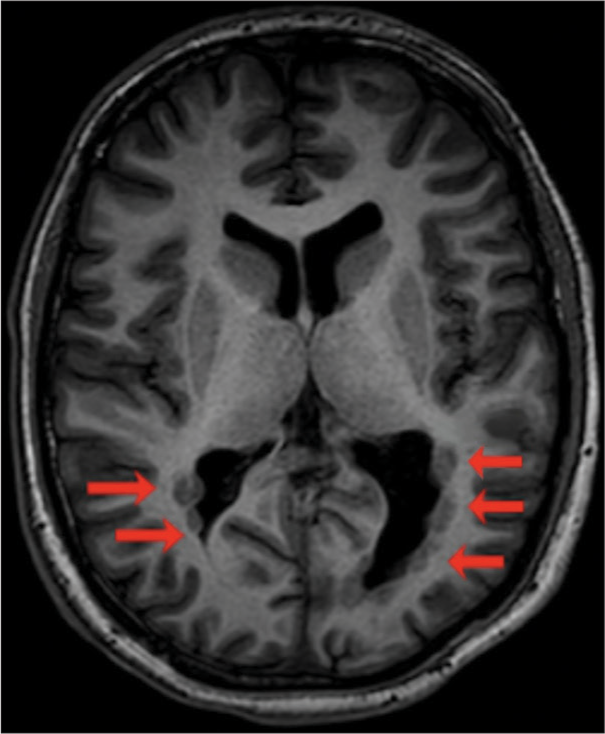
Background: Cerebral air embolism is a rare cause of acute ischemic stroke that is becoming increasingly well-described in the literature. However, the mechanism and severity of this type of injury can vary, with ischemia typically emerging early in the course of care. To the best of our knowledge, delayed ischemia in this setting has not yet been described.
Delayed blink R1 latency in a patient with trigeminal neuralgia due to a contralateral vestibular schwannoma: An illustrative case
Date of publication: 11-Aug-2023
Background: Although the blink reflex (BR) is effective in objectively evaluating trigeminal neuropathy, few studies have demonstrated its effect on trigeminal neuralgia (TN). The authors report a patient with TN due to contralateral vestibular schwannoma (VS) functionally diagnosed by delayed R1 latency of the BR.
Surgical treatment of epilepsy in a patient with bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia: A case report
Date of publication: 11-Aug-2023
Background: Periventricular nodular heterotopia (PNH) is a rare pathological condition characterized by the presence of nodules of gray matter located along the lateral ventricles of the brain. The condition typically presents with seizures and other neurological symptoms, and various methods of surgical treatment and postoperative outcomes have been described in the literature.
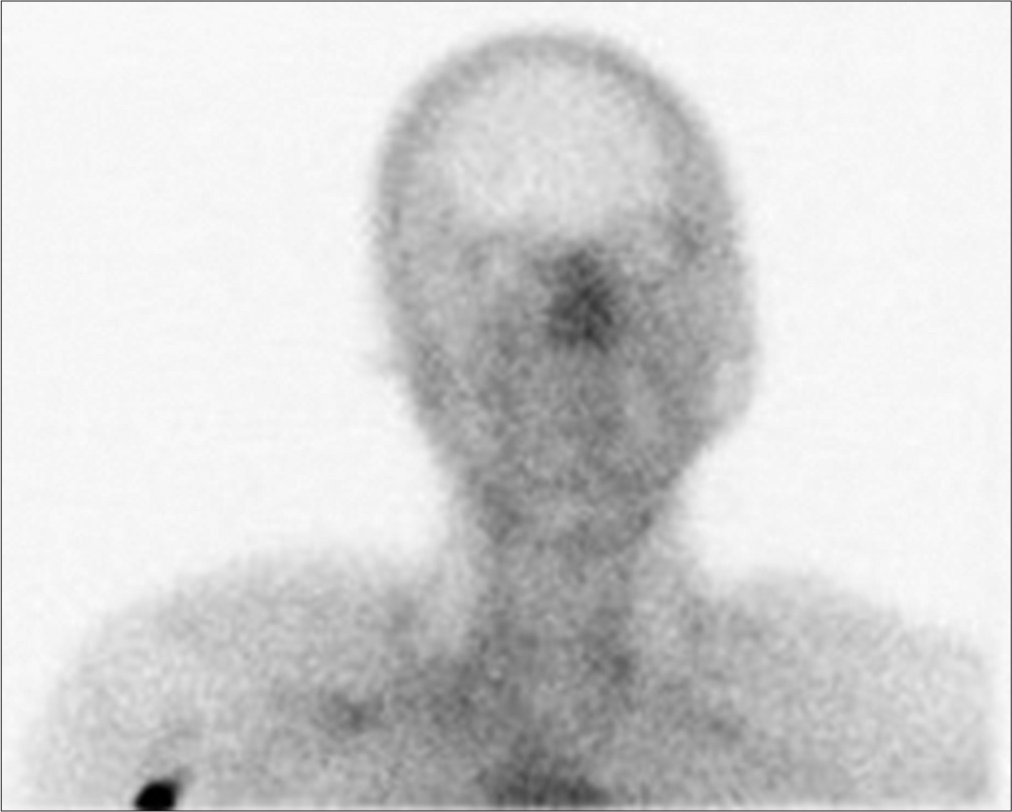
“Hot nose” sign in brain death
Date of publication: 11-Aug-2023
Background: Brain death testing is a rigorous process in which meticulous examination is crucial. In certain cases, ancillary testing is required.
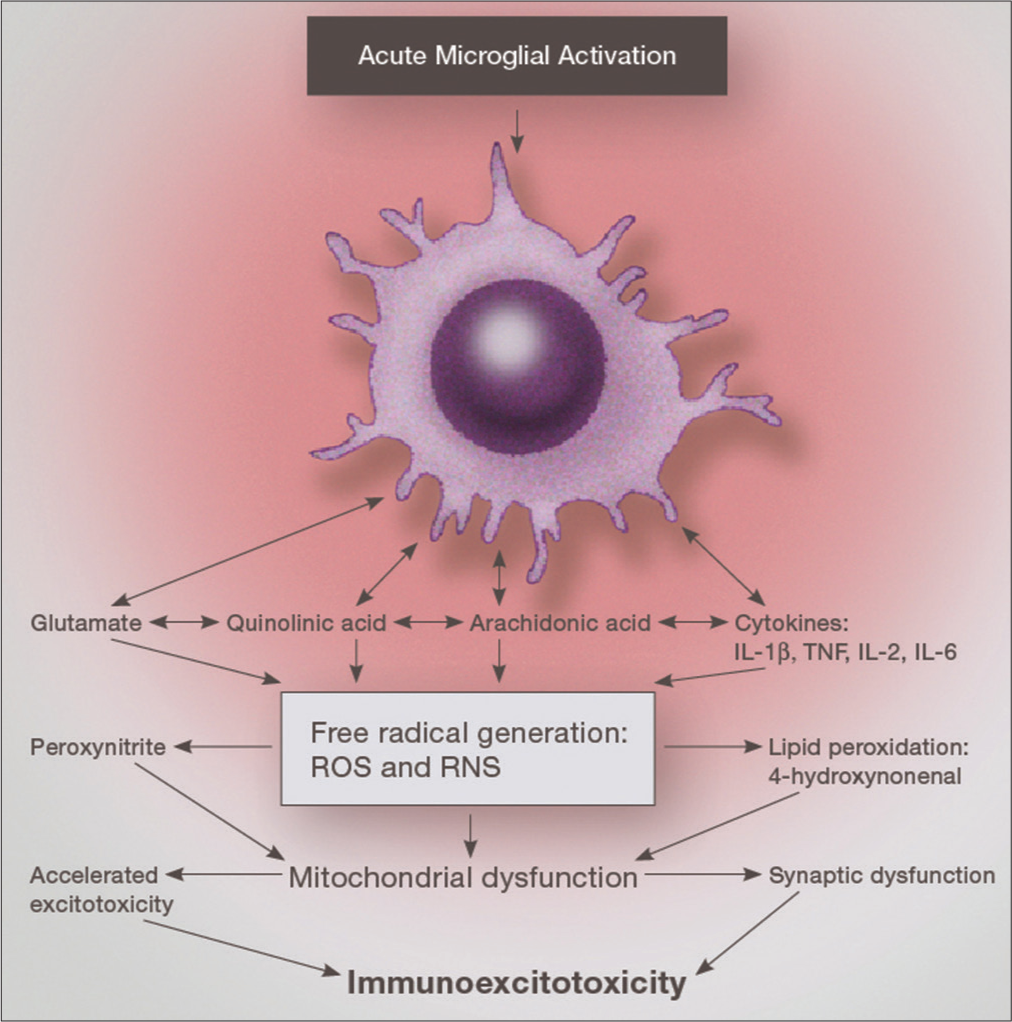
Why immunoexcitoxicity is the basis of most neurodegenerative diseases and systemic immune activation: An analysis
Date of publication: 04-Aug-2023
Minimizing blood loss with direct percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate embolization before corpectomy for vascular spinal tumors
Date of publication: 04-Aug-2023
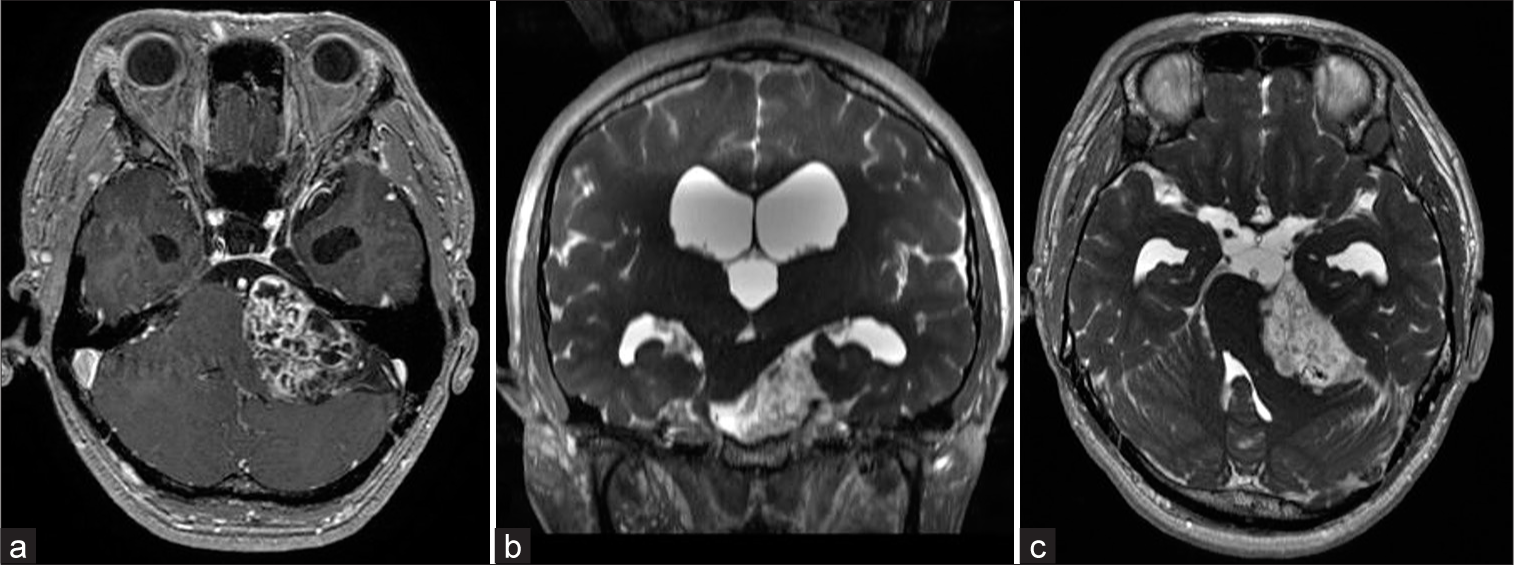
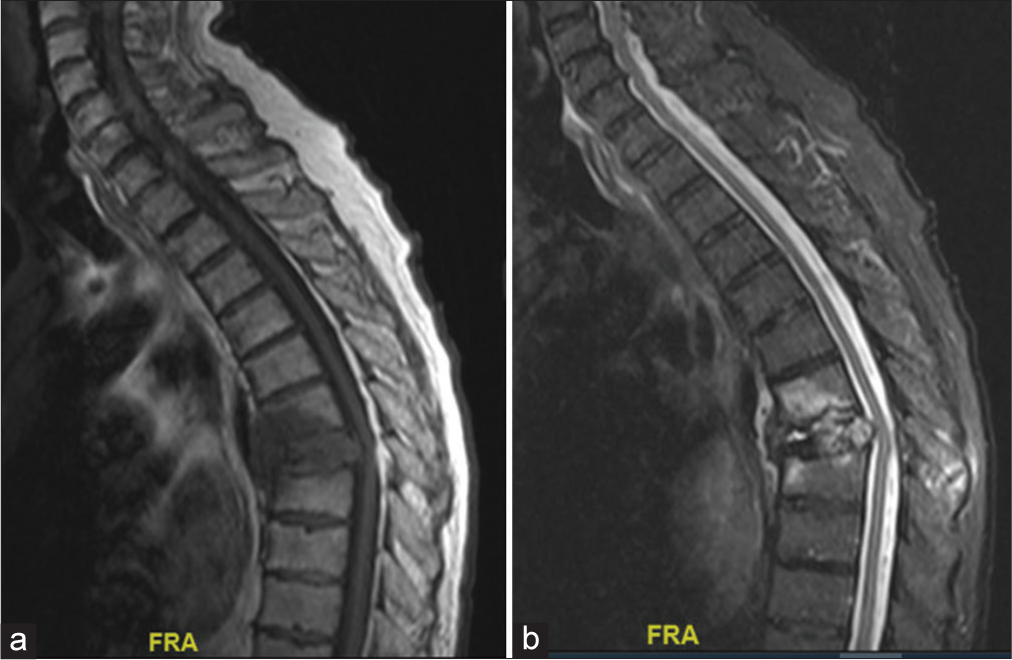
Background: Standard surgical treatment for vascular spinal tumors, including renal cell carcinomas and hemangiomas, may result in significant blood loss despite preoperative arterial tumor embolization.
Retained medullary cord and caudal lipoma with histopathological presence of terminal myelocystocele in the epidural stalk
Date of publication: 04-Aug-2023
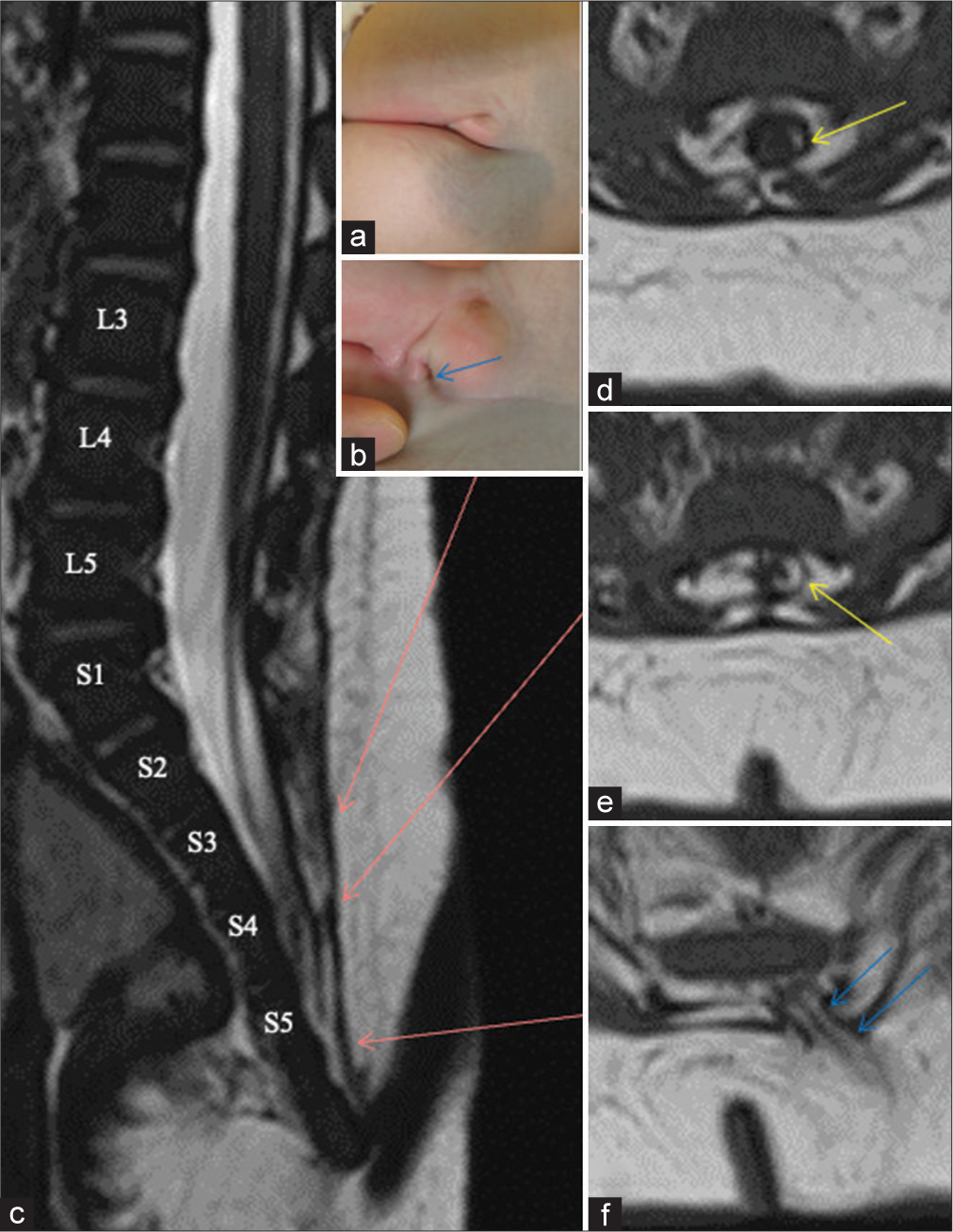
Background: The retained medullary cord (RMC), caudal lipoma, and terminal myelocystocele (TMCC) are thought to originate from the failed regression spectrum during the secondary neurulation, and the central histopathological feature is the predominant presence of a central canal-like ependyma-lined lumen (CC-LELL) with surrounding neuroglial tissues (NGT), as a remnant of the medullary cord. However, reports on cases in which RMC, caudal lipoma, and TMCC coexist are very rare.
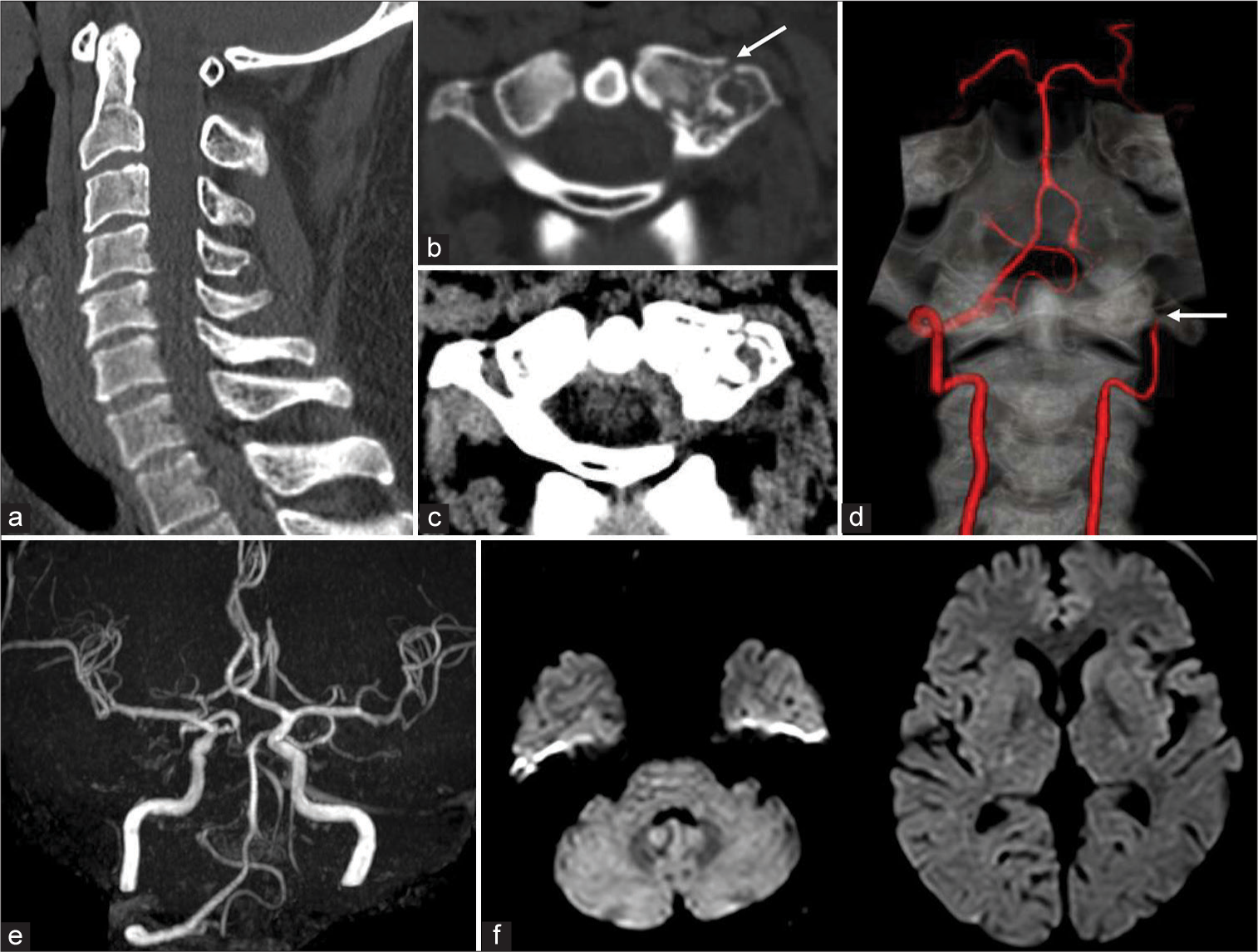
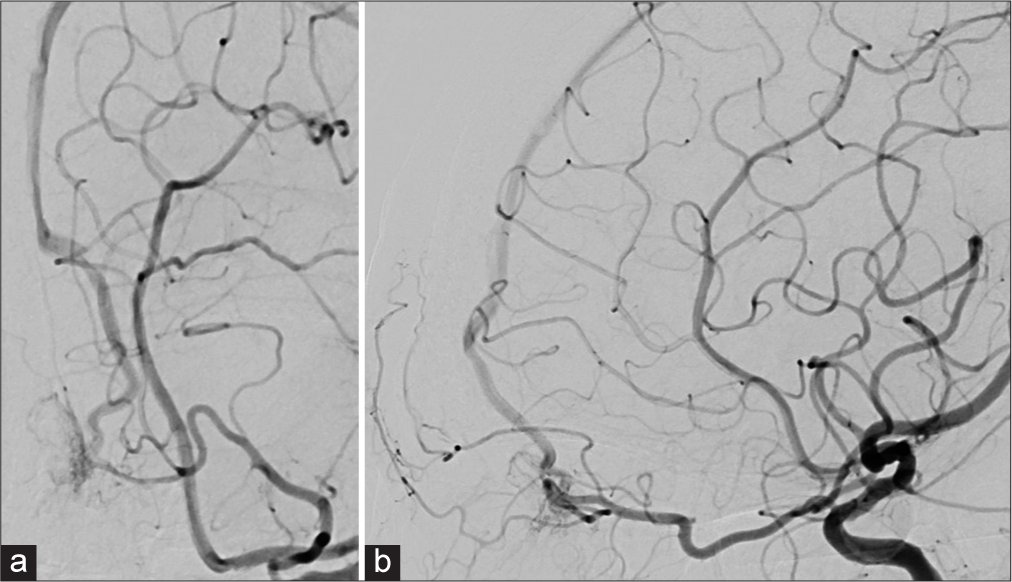
Parent artery occlusion for cerebral infarction after spontaneous recanalization in traumatic vertebral artery: A case report
Date of publication: 04-Aug-2023
Background: There is no established treatment strategy for traumatic vertebral artery occlusion that does not require cervical spine repair surgery.
Combined transarterial and transvenous embolization of anterior cranial fossa dural arteriovenous fistula
Date of publication: 04-Aug-2023
Background: Excessive glue injection into the drainage vein in patients with dural arteriovenous fistula (dAVF) can result in venous obstruction. We performed transarterial embolization (TAE) combined with transvenous embolization (TVE) with coils to prevent the glue from migrating into the normal cortical veins.